part 1: overview of cogeneration and its status in asia - Fire
part 1: overview of cogeneration and its status in asia - Fire
part 1: overview of cogeneration and its status in asia - Fire
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
14 Part I: Overview <strong>of</strong> <strong>cogeneration</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>its</strong> <strong>status</strong> <strong>in</strong> Asia<br />
Diesel eng<strong>in</strong>es can run on a variety <strong>of</strong> fuels such as diesel, heavy fuel oil, light fuel oil, LPG,<br />
natural gas, producer gas, digester gas, etc. The diesel eng<strong>in</strong>es that are converted to gas<br />
eng<strong>in</strong>es are also known as dual-fuel eng<strong>in</strong>es. In their operation, the ma<strong>in</strong> fuel is gas, which is<br />
ignited by a small quantity <strong>of</strong> pilot oil, usually diesel oil. The pilot oil is used to make sure that<br />
the gas <strong>in</strong> the cyl<strong>in</strong>der will ignite. The gas/oil ratio is normally controlled so that the proportion<br />
<strong>of</strong> pilot oil at full eng<strong>in</strong>e power will be around 5 per cent <strong>of</strong> the fuel quantity supplied. Diesel<br />
eng<strong>in</strong>es runn<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> gas eng<strong>in</strong>e mode can be classified <strong>in</strong> another way <strong>in</strong>to two groups: lowpressure<br />
dual-fuel eng<strong>in</strong>es <strong>and</strong> high-pressure dual-fuel eng<strong>in</strong>es.<br />
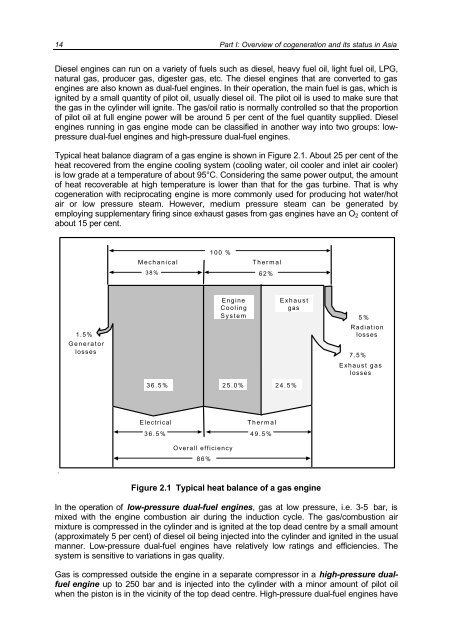
Typical heat balance diagram <strong>of</strong> a gas eng<strong>in</strong>e is shown <strong>in</strong> Figure 2.1. About 25 per cent <strong>of</strong> the<br />
heat recovered from the eng<strong>in</strong>e cool<strong>in</strong>g system (cool<strong>in</strong>g water, oil cooler <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>let air cooler)<br />
is low grade at a temperature <strong>of</strong> about 95°C. Consider<strong>in</strong>g the same power output, the amount<br />
<strong>of</strong> heat recoverable at high temperature is lower than that for the gas turb<strong>in</strong>e. That is why<br />
<strong>cogeneration</strong> with reciprocat<strong>in</strong>g eng<strong>in</strong>e is more commonly used for produc<strong>in</strong>g hot water/hot<br />
air or low pressure steam. However, medium pressure steam can be generated by<br />
employ<strong>in</strong>g supplementary fir<strong>in</strong>g s<strong>in</strong>ce exhaust gases from gas eng<strong>in</strong>es have an O2 content <strong>of</strong><br />
about 15 per cent.<br />
1.5%<br />
Generator<br />
losses<br />
100 %<br />
Mechanical Thermal<br />
38%<br />
62%<br />
36.5% 25.0% 24.5%<br />
Electrical Thermal<br />
36.5% 49.5%<br />
Overall efficiency<br />
86%<br />
Eng<strong>in</strong>e<br />
Cool<strong>in</strong>g<br />
System<br />
Exhaust<br />
gas<br />
Figure 2.1 Typical heat balance <strong>of</strong> a gas eng<strong>in</strong>e<br />
5%<br />
Radiation<br />
losses<br />
7.5%<br />
Exhaust gas<br />
losses<br />
In the operation <strong>of</strong> low-pressure dual-fuel eng<strong>in</strong>es, gas at low pressure, i.e. 3-5 bar, is<br />
mixed with the eng<strong>in</strong>e combustion air dur<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>in</strong>duction cycle. The gas/combustion air<br />
mixture is compressed <strong>in</strong> the cyl<strong>in</strong>der <strong>and</strong> is ignited at the top dead centre by a small amount<br />
(approximately 5 per cent) <strong>of</strong> diesel oil be<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>jected <strong>in</strong>to the cyl<strong>in</strong>der <strong>and</strong> ignited <strong>in</strong> the usual<br />
manner. Low-pressure dual-fuel eng<strong>in</strong>es have relatively low rat<strong>in</strong>gs <strong>and</strong> efficiencies. The<br />
system is sensitive to variations <strong>in</strong> gas quality.<br />
Gas is compressed outside the eng<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong> a separate compressor <strong>in</strong> a high-pressure dualfuel<br />
eng<strong>in</strong>e up to 250 bar <strong>and</strong> is <strong>in</strong>jected <strong>in</strong>to the cyl<strong>in</strong>der with a m<strong>in</strong>or amount <strong>of</strong> pilot oil<br />
when the piston is <strong>in</strong> the vic<strong>in</strong>ity <strong>of</strong> the top dead centre. High-pressure dual-fuel eng<strong>in</strong>es have