Invasive breast carcinoma - IARC
Invasive breast carcinoma - IARC
Invasive breast carcinoma - IARC
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Mixed germ cell-sex cord-stromal<br />
tumours<br />
A. Talerman<br />
P. Schwartz<br />
This group of neoplasms is composed of<br />
a mixture of germ cell and sex cord-stromal<br />
elements. They have mainly benign<br />
clinical behaviour except in cases with a<br />
malignant germ cell component.<br />
Gonadoblastoma<br />
Definition<br />
A neoplasm composed of tumour cells<br />
closely resembling dysgerminoma or<br />
seminoma, intimately admixed with sex<br />
c o rd derivatives resembling immature<br />
Sertoli or granulosa cells and in some<br />
cases containing stromal derivatives<br />
mimicking luteinized stromal or Leydig<br />
cells devoid of Reinke crystals.<br />
ICD-O code<br />
Gonadoblastoma 9073/1<br />
Epidemiology<br />
Gonadoblastomas typically are identified<br />
in children or young adults with one-third<br />
of the tumours being detected before the<br />
age of 15 {2598}.<br />
Aetiology<br />
Gonadoblastomas are frequently associated<br />
with abnormalities in the secondary<br />
sex organs {2598,2847}. In over 90% of<br />
the cases of gonadoblastoma a Y chromosome<br />
was detected {2598,2605,2849,<br />
2850}.<br />
Localization<br />
Gonadoblastoma is found more often in<br />
the right gonad than in the left and is<br />
bilateral in 38% of cases {2598}. Recent<br />
reports suggest an even higher frequency<br />
of bilateral involvement {2850}.<br />
Clinical features<br />
Signs and symptoms<br />
The usual patient with a gonadoblastoma<br />
is a phenotypic female who is frequently<br />
virilized {2605}. A minority may present<br />
as phenotypic males with vary i n g<br />
degrees of feminization.<br />
The clinical presentation of a patient with<br />
a gonadoblastoma can vary considerably<br />
depending upon whether or not a<br />
tumour mass is present, on the nature of<br />
the underlying abnormal gonads, on the<br />
development of secondary sex organs<br />
and the occasional secretion of steroid<br />
hormones {2598}. A patient with pure<br />
gonadal dysgenesis may present with a<br />
failure to develop secondary sex organs<br />
and characteristics at puberty but has a<br />
n o rmal height, and other congenital<br />
anomalies are absent. Those with Turner<br />
s y n d rome have sexual immaturity, a<br />
height of less than 150 cm and one or<br />
m o re congenital anomalies including<br />
neonatal lymphedema, web neck, prognathism,<br />
shield-shaped chest, widely<br />
spaced nipples, cubitus valgus, congenital<br />
nevi, coarctation of the aorta, renal<br />
anomalies, short fifth metacarpal bones<br />
and others {2598}. If a germ cell malignancy<br />
develops in the dysgenetic<br />
gonad, the patient may present with<br />
lower abdominal or pelvic pain.<br />
Macroscopy<br />
Pure gonadoblastoma varies from a histological<br />
lesion to 8 cm, and most<br />
tumours are small, measuring only a few<br />
cm {2598,2849,2850}. When a<br />
gonadoblastoma is overgrown by dysgerminoma<br />
or other neoplastic germ cell<br />
elements, much larger tumours are<br />
encountered. The macroscopic appearance<br />
of gonadoblastoma varies depending<br />
on the presence of hyalinization and<br />
calcification and on the overgrowth by<br />
other malignant germ cell elements.<br />
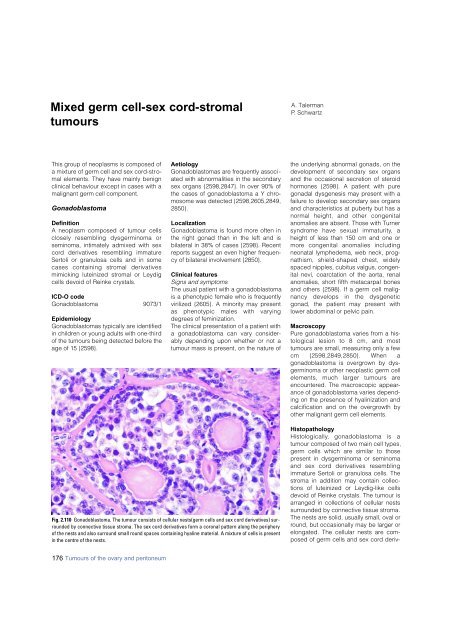
Fig. 2.110 Gonadoblastoma. The tumour consists of cellular nests(germ cells and sex cord derivatives) surrounded<br />
by connective tissue stroma. The sex cord derivatives form a coronal pattern along the periphery<br />
of the nests and also surround small round spaces containing hyaline material. A mixture of cells is present<br />
in the centre of the nests.<br />
Histopathology<br />
H i s t o l o g i c a l l y, gonadoblastoma is a<br />
tumour composed of two main cell types,<br />
germ cells which are similar to those<br />
present in dysgerminoma or seminoma<br />
and sex cord derivatives re s e m b l i n g<br />
immature Sertoli or granulosa cells. The<br />
stroma in addition may contain collections<br />
of luteinized or Leydig-like cells<br />
devoid of Reinke crystals. The tumour is<br />
arranged in collections of cellular nests<br />
surrounded by connective tissue stroma.<br />
The nests are solid, usually small, oval or<br />
round, but occasionally may be larger or<br />
elongated. The cellular nests are composed<br />
of germ cells and sex cord deriv-<br />
176 Tumours of the ovary and peritoneum