Invasive breast carcinoma - IARC
Invasive breast carcinoma - IARC
Invasive breast carcinoma - IARC
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
origin, the mitochondrial DNA is of<br />
m a t e rnal origin {146}.<br />
Partial hydatidiform mole<br />
Definition<br />
A hydatidiform mole having two populations<br />
of chorionic villi, one of normal size<br />
and the other hydropic, with focal trophoblastic<br />
proliferation. The lesion typically<br />
has a triploid karyotype.<br />
Fig. 4.52 “Early” complete mole. Some villi have<br />
toe-like bulbous protrusions. Trophoblastic proliferation<br />
and cavitation are minimal. The stroma is<br />
hypercellular and myxoid.<br />
Fig. 4.54 Markedly atypical implantation site trophoblast<br />
in a case of early hydatidiform mole.<br />
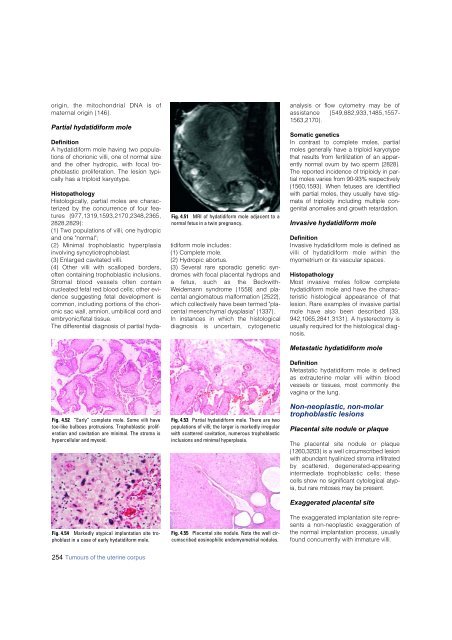
Fig. 4.51 MRI of hydatidiform mole adjacent to a<br />
normal fetus in a twin pregnancy.<br />
Histopathology<br />
Histologically, partial moles are characterized<br />
by the concurrence of four feat<br />
u res {977,1319,1593,2170,2348,2365,<br />
2828,2829}:<br />
(1) Two populations of villi, one hydropic<br />
and one "normal";<br />
(2) Minimal trophoblastic hyperplasia<br />
involving syncytiotrophoblast.<br />
(3) Enlarged cavitated villi.<br />
(4) Other villi with scalloped borders,<br />
often containing trophoblastic inclusions.<br />
S t romal blood vessels often contain<br />
nucleated fetal red blood cells; other evidence<br />
suggesting fetal development is<br />
common, including portions of the chorionic<br />
sac wall, amnion, umbilical cord and<br />
embryonic/fetal tissue.<br />
The diff e rential diagnosis of partial hydat<br />
i d i f o rm mole includes:<br />
(1) Complete mole.<br />
(2) Hydropic abort u s .<br />
(3) Several rare sporadic genetic synd<br />
romes with focal placental hydrops and<br />
a fetus, such as the Beckwith-<br />
Weidemann syndrome {1558} and placental<br />
angiomatous malformation {2522},<br />
which collectively have been termed "placental<br />
mesenchymal dysplasia" {1337}.<br />
In instances in which the histological<br />
diagnosis is uncertain, cytogenetic<br />
Fig. 4.53 Partial hydatidiform mole. There are two<br />
populations of villi; the larger is markedly irregular<br />
with scattered cavitation, numerous trophoblastic<br />
inclusions and minimal hyperplasia.<br />
Fig. 4.55 Placental site nodule. Note the well circumscribed<br />
eosinophilic endomyometrial nodules.<br />
analysis or flow cytometry may be of<br />
assistance {549,882,933,1485,1557-<br />
1563,2170}.<br />
Somatic genetics<br />
In contrast to complete moles, part i a l<br />
moles generally have a triploid kary o t y p e<br />
that results from fertilization of an apparently<br />
normal ovum by two sperm {2828}.<br />
The re p o rted incidence of triploidy in partial<br />
moles varies from 90-93% re s p e c t i v e l y<br />
{1560,1593}. When fetuses are identified<br />
with partial moles, they usually have stigmata<br />
of triploidy including multiple congenital<br />
anomalies and growth re t a rd a t i o n .<br />
<strong>Invasive</strong> hydatidiform mole<br />
Definition<br />
<strong>Invasive</strong> hydatidiform mole is defined as<br />
villi of hydatidiform mole within the<br />
myometrium or its vascular spaces.<br />
Histopathology<br />
Most invasive moles follow complete<br />
hydatidiform mole and have the characteristic<br />
histological appearance of that<br />
lesion. Rare examples of invasive partial<br />
mole have also been described {33,<br />
942,1065,2841,3131}. A hysterectomy is<br />
usually required for the histological diagnosis.<br />
Metastatic hydatidiform mole<br />
Definition<br />
Metastatic hydatidiform mole is defined<br />
as extrauterine molar villi within blood<br />
vessels or tissues, most commonly the<br />
vagina or the lung.<br />
Non-neoplastic, non-molar<br />
trophoblastic lesions<br />
Placental site nodule or plaque<br />
The placental site nodule or plaque<br />
{1260,3203} is a well circumscribed lesion<br />
with abundant hyalinized stroma infiltrated<br />
by scattered, degenerated-appearing<br />
i n t e rmediate trophoblastic cells; these<br />
cells show no significant cytological atypia,<br />
but rare mitoses may be present.<br />
Exaggerated placental site<br />
The exaggerated implantation site represents<br />
a non-neoplastic exaggeration of<br />
the normal implantation process, usually<br />
found concurrently with immature villi.<br />
254 Tumours of the uterine corpus