Invasive breast carcinoma - IARC
Invasive breast carcinoma - IARC
Invasive breast carcinoma - IARC
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
A<br />
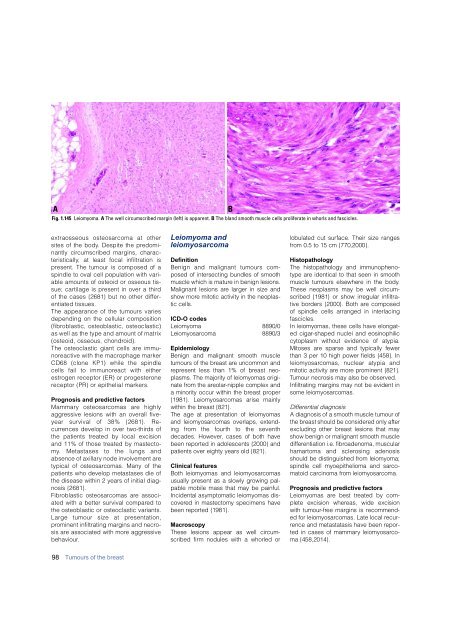
Fig. 1.145 Leiomyoma. A The well circumscribed margin (left) is apparent. B The bland smooth muscle cells proliferate in whorls and fascicles.<br />
B<br />
extraosseous osteosarcoma at other<br />
sites of the body. Despite the pre d o m i-<br />
nantly circumscribed margins, charact<br />
e r i s t i c a l l y, at least focal infiltration is<br />
p resent. The tumour is composed of a<br />
spindle to oval cell population with variable<br />
amounts of osteoid or osseous tissue;<br />
cartilage is present in over a third<br />
of the cases {2681} but no other diff e r-<br />
entiated tissues.<br />
The appearance of the tumours varies<br />
depending on the cellular composition<br />
( f i b roblastic, osteoblastic, osteoclastic)<br />
as well as the type and amount of matrix<br />
(osteoid, osseous, chondroid).<br />
The osteoclastic giant cells are immun<br />
o reactive with the macrophage marker<br />
CD68 (clone KP1) while the spindle<br />
cells fail to immunoreact with either<br />
e s t rogen receptor (ER) or pro g e s t e ro n e<br />
receptor (PR) or epithelial markers.<br />
Prognosis and predictive factors<br />
M a m m a ry osteosarcomas are highly<br />
a g g ressive lesions with an overall fiveyear<br />
survival of 38% {2681}. Rec<br />
u r rences develop in over two-thirds of<br />
the patients treated by local excision<br />
and 11% of those treated by mastectom<br />
y. Metastases to the lungs and<br />
absence of axillary node involvement are<br />
typical of osteosarcomas. Many of the<br />
patients who develop metastases die of<br />
the disease within 2 years of initial diagnosis<br />
{2681}.<br />
F i b roblastic osteosarcomas are associated<br />
with a better survival compared to<br />
the osteoblastic or osteoclastic variants.<br />
Large tumour size at pre s e n t a t i o n ,<br />
p rominent infiltrating margins and necrosis<br />
are associated with more aggre s s i v e<br />
b e h a v i o u r.<br />
Leiomyoma and<br />
leiomyosarcoma<br />
D e f i n i t i o n<br />
Benign and malignant tumours composed<br />
of intersecting bundles of smooth<br />
muscle which is mature in benign lesions.<br />
Malignant lesions are larger in size and<br />
show more mitotic activity in the neoplastic<br />
cells.<br />
ICD-O codes<br />
L e i o m y o m a 8890 / 0<br />
L e i o m y o s a rc o m a 8890 / 3<br />
E p i d e m i o l o g y<br />
Benign and malignant smooth muscle<br />
tumours of the <strong>breast</strong> are uncommon and<br />
re p resent less than 1% of <strong>breast</strong> neoplasms.<br />
The majority of leiomyomas originate<br />
from the are o l a r-nipple complex and<br />
a minority occur within the <strong>breast</strong> pro p e r<br />
{1981}. Leiomyosarcomas arise mainly<br />
within the <strong>breast</strong> {821}.<br />
The age at presentation of leiomyomas<br />
and leiomyosarcomas overlaps, extending<br />
from the fourth to the seventh<br />
decades. However, cases of both have<br />
been re p o rted in adolescents {2000} and<br />
patients over eighty years old {821}.<br />
Clinical features<br />
Both leiomyomas and leiomyosarc o m a s<br />
usually present as a slowly growing palpable<br />
mobile mass that may be painful.<br />
Incidental asymptomatic leiomyomas disc<br />
o v e red in mastectomy specimens have<br />
been re p o rted {1981}.<br />
M a c r o s c o p y<br />
These lesions appear as well circ u m-<br />
scribed firm nodules with a whorled or<br />
lobulated cut surface. Their size ranges<br />
f rom 0.5 to 15 cm {770,2000}.<br />
H i s t o p a t h o l o g y<br />
The histopathology and immunophenotype<br />
are identical to that seen in smooth<br />
muscle tumours elsewhere in the body.<br />
These neoplasms may be well circ u m-<br />
scribed {1981} or show irregular infiltrative<br />
borders {2000}. Both are composed<br />
of spindle cells arranged in interlacing<br />
fascicles.<br />
In leiomyomas, these cells have elongated<br />
cigar-shaped nuclei and eosinophilic<br />
cytoplasm without evidence of atypia.<br />
Mitoses are sparse and typically fewer<br />
than 3 per 10 high power fields {458}. In<br />
l e i o m y o s a rcomas, nuclear atypia and<br />
mitotic activity are more prominent {821}.<br />
Tumour necrosis may also be observed.<br />
Infiltrating margins may not be evident in<br />
some leiomyosarc o m a s .<br />
D i ff e rential diagnosis<br />
A diagnosis of a smooth muscle tumour of<br />
the <strong>breast</strong> should be considered only after<br />
excluding other <strong>breast</strong> lesions that may<br />
show benign or malignant smooth muscle<br />
d i ff e rentiation i.e. fibroadenoma, muscular<br />
h a m a rtoma and sclerosing adenosis<br />
should be distinguished from leiomyoma;<br />
spindle cell myoepithelioma and sarc o-<br />
matoid <strong>carcinoma</strong> from leiomyosarc o m a .<br />
Prognosis and predictive factors<br />
Leiomyomas are best treated by complete<br />
excision whereas, wide excision<br />
with tumour- f ree margins is re c o m m e n d-<br />
ed for leiomyosarcomas. Late local re c u r-<br />
rence and metastatasis have been re p o r-<br />
ted in cases of mammary leiomyosarc o-<br />
ma {458,2014}.<br />
98 Tumours of the <strong>breast</strong>