Dictionary of Evidence-based Medicine.pdf
Dictionary of Evidence-based Medicine.pdf
Dictionary of Evidence-based Medicine.pdf
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Dictionary</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Evidence</strong>-<strong>based</strong> <strong>Medicine</strong> 85<br />
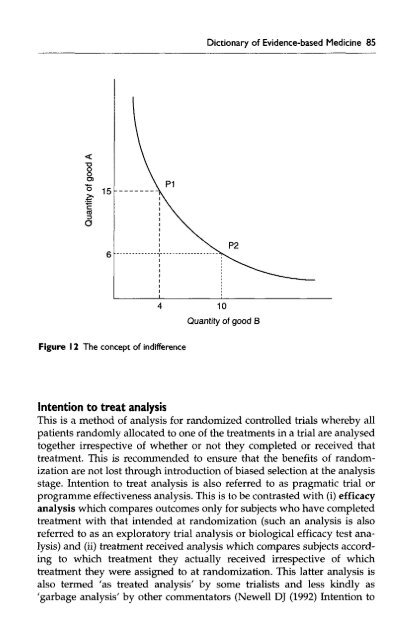
Figure 12 The concept <strong>of</strong> indifference<br />
Intention to treat analysis<br />
This is a method <strong>of</strong> analysis for randomized controlled trials whereby all<br />
patients randomly allocated to one <strong>of</strong> the treatments in a trial are analysed<br />
together irrespective <strong>of</strong> whether or not they completed or received that<br />
treatment. This is recommended to ensure that the benefits <strong>of</strong> randomization<br />
are not lost through introduction <strong>of</strong> biased selection at the analysis<br />
stage. Intention to treat analysis is also referred to as pragmatic trial or<br />
programme effectiveness analysis. This is to be contrasted with (i) efficacy<br />
analysis which compares outcomes only for subjects who have completed<br />
treatment with that intended at randomization (such an analysis is also<br />
referred to as an exploratory trial analysis or biological efficacy test analysis)<br />
and (ii) treatment received analysis which compares subjects according<br />
to which treatment they actually received irrespective <strong>of</strong> which<br />
treatment they were assigned to at randomization. This latter analysis is<br />
also termed 'as treated analysis' by some trialists and less kindly as<br />
'garbage analysis' by other commentators (Newell DJ (1992) Intention to