- Page 1:
A REVIEW OF THECAVERNICOLE FAUNA OF
- Page 8:
. 1-----,, ,", ,\'"I/I~" )/Fig. I.-
- Page 12 and 13:
collected a troglobitic cirolanid i
- Page 14 and 15:
C. Bolivar and J. Carranza investig
- Page 16 and 17:
springs in the vicinity of Cautro C
- Page 18 and 19:
Cueva del Diablo near Orizaba, Vera
- Page 20 and 21:
Those species of troglobite which h
- Page 22 and 23:
Table 2.-(continued)1970. Eodrilus
- Page 25 and 26:
CAVE REGIONSOnly the cave regions o
- Page 27 and 28:
Table 3.-(continued)TroglobitesTrog
- Page 29 and 30:
y the waters of the Amistad Reservo
- Page 31 and 32:
Although a few caves in the Norther
- Page 33 and 34:
an elevation of about 900 meters. T
- Page 35 and 36:
the gryllid cricket Paracophus suba
- Page 37 and 38:
has been Jiscussed by Segerstrom (1
- Page 39 and 40:
only apparent troglophile is the ps
- Page 41 and 42:
The cave fauna of this region is ri
- Page 43 and 44:
igneous rock immediately east of th
- Page 45 and 46:
Rio Soto la Marina and terminates a
- Page 47 and 48:
caves studied are many large stream
- Page 49 and 50:
unusual species is Neogovea mexasca
- Page 52 and 53:
pallidus Rowland, the nesticid spid
- Page 54 and 55:
troglobites: the trichoniscid isopo
- Page 56 and 57:
Cambridge, and Pholcophora bispinos
- Page 58 and 59:
of the genus Lutzomyia has not been
- Page 60 and 61:
The principal cavernous fonnation i
- Page 62 and 63:
ocks of Paleocene to Pliocene age.
- Page 64 and 65:
Beach and Supra-tidal Zone, the I\o
- Page 66 and 67:
The aquatic fauna of Mexico and Cen
- Page 68 and 69:
oaxacae Hobbs from the Valle Nacion
- Page 70 and 71:
described, the genus occurs in cave
- Page 72 and 73:
large genus with numerous epigean s
- Page 74 and 75:
milliped, laniatorid harvestmen, an
- Page 76 and 77:
Table 4.-Summary of cave inhabiting
- Page 78 and 79:
Discussion.-This large, troglobitic
- Page 80 and 81:
any way a part of the true cave fau
- Page 82 and 83:
they have been washed in with soil
- Page 84 and 85:
part of the aquatic fauna. A very l
- Page 86 and 87:
The genus Helicodiscus is a signifi
- Page 88 and 89:
associated with true cave waters. P
- Page 90 and 91:
Family DaphnidaeWilson (1936) repor
- Page 92 and 93:
tul), Cueva de San Isidro, Cueva de
- Page 94 and 95:
30 m below entrance of Cueva de la
- Page 96 and 97:
underflow of rivers, alluvial grave
- Page 98 and 99:
the similarities between the distri
- Page 100 and 101:
Yucatan but did not identify the sp
- Page 102 and 103:
Protrichoniscus: Reddell, 1967a:24.
- Page 104 and 105:
It indudes five spccies, of which t
- Page 106 and 107:
Type-locality.-Pozzo, Etla, Oaxaca,
- Page 108 and 109:
Records.-Campeche: Volc
- Page 110 and 111:
164; Pearse, 1945:167, 168, fig. 13
- Page 112 and 113:
Family AtyidaeThe family Atyidae is
- Page 115 and 116:
Creaseria morleyi (Creaser)Blind sh
- Page 117 and 118:
the pond which is fed by the cave s
- Page 119 and 120:
philes. Pseudothelphusa (Pseudothel
- Page 121 and 122:
Typhlochactas elliotti MitchellTyph
- Page 123 and 124:
Distribution.-Known only from the t
- Page 125 and 126:
(Dumitresco and Orghidan, 1977); th
- Page 127 and 128:
Leucohya magnifica MuchmoreUndescri
- Page 129 and 130:
Discussion.-This is the largest spe
- Page 131 and 132:
Type-Iocality.-S6tano de Huitzmolot
- Page 133 and 134:
Bartolo is a name applied to two ne
- Page 135 and 136:
Rowland, 1975b:19, 20; Dumitresco,
- Page 137 and 138:
Type-Iocality.-Actlin Kaua, Yucatan
- Page 139 and 140:
Distribution.-Known only from caves
- Page 141 and 142:
een collected. It is frequently fou
- Page 143 and 144:
Distribution.-Known from two caves
- Page 146 and 147:
actually a natural cave artificiall
- Page 148 and 149:
Discussion.-This large species has
- Page 150 and 151:
and T. patellaris Bryant from caves
- Page 152 and 153:
estricted to the Mexican Plateau (s
- Page 154 and 155:
maya Chamberlin and Ivie from Campe
- Page 156 and 157:
Metagonia chiquita GertschMetagonia
- Page 158 and 159:
Metagonia capilla: Mitchell and Kaw
- Page 160 and 161:
the cave and in general association
- Page 162 and 163:
DiscWlSion.-This is a delicate, eye
- Page 164 and 165: Type-Iocality.-Cueva de Los Sabinos
- Page 166 and 167: family. Clarence and Marie Goodnigh
- Page 168 and 169: n. 2, San Luis Potosi; and K. rugos
- Page 170 and 171: Type-locality.-Cueva de Apoala, San
- Page 172 and 173: Records.-Chiapas: Sumidero de Canad
- Page 174 and 175: Family HeterozerconidaeSpecimens of
- Page 176 and 177: only one species. All known epigean
- Page 178 and 179: nation must await study, but it is
- Page 180 and 181: Mexico and Guatemala, and several u
- Page 182 and 183: Type-locality.-Gruta de Atoyac, Ver
- Page 184 and 185: Records.-San Luis PotOSI: Sotano de
- Page 186 and 187: Records.-Veracruz: Grutas de Atoyac
- Page 188 and 189: the genus Synoptura and removed the
- Page 190 and 191: known from caves all contain troglo
- Page 192 and 193: las Perlas, Cueva Chica de la Perra
- Page 194 and 195: Discussion.-This species is distinc
- Page 196 and 197: Speodesmus pecki ShearPolydesmidae,
- Page 198 and 199: appears to be most closely related
- Page 200 and 201: this is almost certainly M. russell
- Page 202 and 203: Table 21.-Summary of cave inhabitin
- Page 204 and 205: Type-Iocality.-Cueva Bonita del Pre
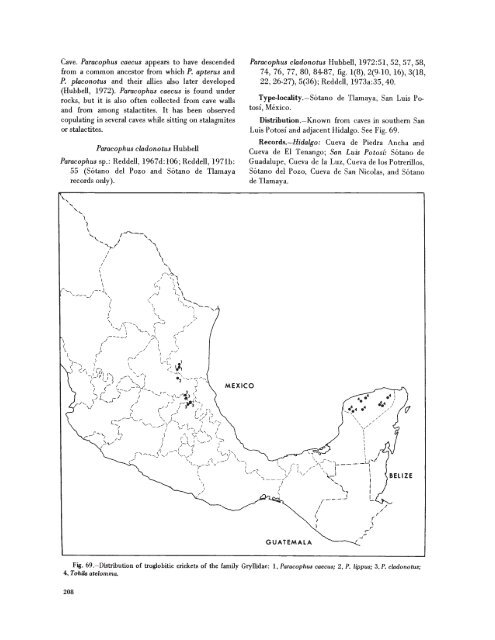
- Page 206 and 207: Type-Iocality.-Cueva de El Jobo, El
- Page 208 and 209: Order DipluraFamily CampodeidaeAlth
- Page 210 and 211: of small soil inhabiting japygoids
- Page 212 and 213: (Linnaeus) has been collected from
- Page 216 and 217: the most poorly known species in th
- Page 218 and 219: Family EpipsocidaeThe family Epipso
- Page 220 and 221: citata Van Tyne in Cenote de Piste,
- Page 222 and 223: een found in caves and mines in Yuc
- Page 224 and 225: ground dwelling habit, many beetles
- Page 226 and 227: Type-Iocality.-Sotano de Tejamanil,
- Page 228 and 229: Vigna Taglianti, 1972:118, 121-127,
- Page 230 and 231: Veracruz) belongs in another subgen
- Page 232 and 233: Troglobacanius sbordonii VomeroTrog
- Page 234 and 235: Ptomaphagus (Adelops) is a group of
- Page 236 and 237: (A.) speLaeus, from Grutas de Cacah
- Page 238 and 239: epresented by many species. Tenebri
- Page 240 and 241: Myodopsylla gentilis Jordan and Rot
- Page 242 and 243: genus Pholeomyia have been collecte
- Page 244 and 245: Wheeler (1938) has reported the pre
- Page 246 and 247: 263.264, 265, 267, 270, 273, fig. 5
- Page 248 and 249: Anophthyctys jordani: Stefanelli, 1
- Page 250 and 251: Prietella phreatophila Carranza, 19
- Page 252 and 253: TyphlilJs: Pearse, 1938a:13, 15; Hu
- Page 254 and 255: Family BufonidaeFour species of toa
- Page 256 and 257: Oaxaca; and E. yucatanensis Lynch f
- Page 258 and 259: sity of bats in the tropics. In add
- Page 260 and 261: Three species of short-tailed bats
- Page 262 and 263: abundant in the entrance area of Cu
- Page 264 and 265:
Andrews, E. W., IV. 1970. Balankanc
- Page 266 and 267:
Bolivar y Pieltain, C. 1940. Explor
- Page 268 and 269:
Brignoli, P. M. 1979a. The morpholo
- Page 270 and 271:
Conde, B. 1975. Description du prem
- Page 272 and 273:
Ediger, G. 1970. The Birthday Passa
- Page 274 and 275:
Gonzalez Ochoa, A. 1963b. Relacione
- Page 276 and 277:
Hobbs, H. H.,Jr., and T. C. Barr, J
- Page 278 and 279:
Jordan, c. B. 1937. Bringing in the
- Page 280 and 281:
McKenzie, D. 1965a. Caves of the Si
- Page 282 and 283:
Monod, T. 1975. Sur la distribution
- Page 284 and 285:
Peck, S. B., and J. J. Lewis. 1977.
- Page 286 and 287:
Reddell, J. R., and W. R. Elliott.
- Page 288 and 289:
Sanborn, C. C. 1936. Records and me
- Page 290 and 291:
Stone, B. 1979. The 1979 San Agusti
- Page 292 and 293:
Villa R., B. 1956. Una extrana y se
- Page 294 and 295:
Wimsatt, W. A. 1969. Transient beha
- Page 296 and 297:
+*Cueva de los Chivos, 5 km E Altam
- Page 298 and 299:
Sumidero Yochib, Yochib, 8 km NE Te
- Page 300 and 301:
Serrania del Burro RegionCave, Haci
- Page 302 and 303:
+Cueva de Tezoapa, 1.5 km E Acahuiz
- Page 304 and 305:
*Gruta Sur de San Bartolo, 9 km S S
- Page 306 and 307:
*Cueva del Puente de Fierro, 1.5 km
- Page 308:
Cueva de los Riscos, 2 km S Rancho
- Page 311 and 312:
Cueva de El Coy-see Cueva del Nacun
- Page 313 and 314:
+*Cueva del Aire, 1.8 km at S85°W
- Page 315 and 316:
*Sistema Purificacion, Conrado Cast
- Page 317 and 318:
*Cueva del Nacimiento del Rio Frio,
- Page 319 and 320:
Sotano de Humo, 5 km NW San Andres,
- Page 321 and 322:
and Bohor, 1975:25-27, 26m; Reddell
- Page 323 and 324:
*Actun Xpukil, 3 km S Calcehtok, Mp
- Page 325 and 326:
Appendix 2LIST OF TROGLOBITES BY ST
- Page 327 and 328:
Paravachonium superbum-I'seudoscorp
- Page 329 and 330:
SUPPLEMENTWhile this manuscript was
- Page 331 and 332:
Cambala speobia (Chamberlin) (p. 19
- Page 333:
mida (Arachnida) in the New World.