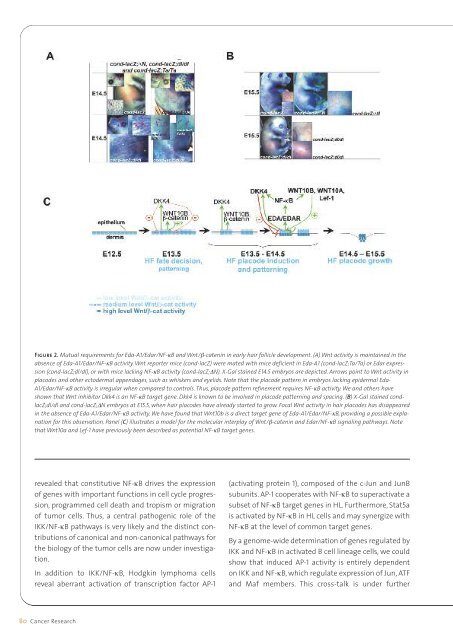
Figure 2. Mutual requirements for Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin in early hair follicle development. (A) Wnt activity is maintained in theabsence of Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB activity. Wnt reporter mice (cond-lacZ) were mated with mice deficient in Eda-A1 (cond-lacZ;Ta/Ta) or Edar expression(cond-lacZ;dl/dl), or with mice lacking NF-κB activity (cond-lacZ;∆N). X-Gal stained E14.5 embryos are depicted. Arrows point to Wnt activity inplacodes and other ectodermal appendages, such as whiskers and eyelids. Note that the placode pattern in embryos lacking epidermal Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB activity is irregular when compared to controls. Thus, placode pattern refinement requires NF-κB activity. We and others haveshown that Wnt inhibitor Dkk4 is an NF-κB target gene. Dkk4 is known to be involved in placode patterning and spacing. (B) X-Gal stained condlacZ;dl/dland cond-lacZ;∆N embryos at E15.5, when hair placodes have already started to grow. Focal Wnt activity in hair placodes has disappearedin the absence of Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB activity. We have found that Wnt10b is a direct target gene of Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB, providing a possible explanationfor this observation. Panel (C) illustrates a model for the molecular interplay of Wnt/β-catenin and Edar/NF-κB signaling pathways. Notethat Wnt10a and Lef-1 have previously been described as potential NF-κB target genes.revealed that constitutive NF-κB drives the expressionof genes with important functions in cell cycle progression,programmed cell death and tropism or migrationof tumor cells. Thus, a central pathogenic role of theIKK/NF-κB pathways is very likely and the distinct contributionsof canonical and non-canonical pathways forthe biology of the tumor cells are now under investigation.In addition to IKK/NF-κB, Hodgkin lymphoma cellsreveal aberrant activation of transcription factor AP-1(activating protein 1), composed of the c-Jun and JunBsubunits. AP-1 cooperates with NF-κB to superactivate asubset of NF-κB target genes in HL. Furthermore, Stat5ais activated by NF-κB in HL cells and may synergize withNF-κB at the level of common target genes.By a genome-wide determination of genes regulated byIKK and NF-κB in activated B cell lineage cells, we couldshow that induced AP-1 activity is entirely dependenton IKK and NF-κB, which regulate expression of Jun, ATFand Maf members. This cross-talk is under further80 Cancer <strong>Research</strong>
investigation, as is the cause of constitutive IKK/NF-κBand c-Jun activation in Hodgkin lymphoma.Functional control of IKK by transient interactionwith Hsp90 and Cdc37The IKK complex undergoes interactions with a numberof regulatory proteins, including the chaperones Cdc37and Hsp90. We had previously shown that pharmacologicalinhibition of Hsp90 abrogates constitutive IKKactivation in Hodgkin lymphoma cells, resulting instrongly enhanced apoptosis. Using an RNAi approach,we found that Cdc37 recruits Hsp90 to the IKK complexin a transitory manner, preferentially via IKKα. Bindingis conferred by N-terminal as well as C-terminalresidues of Cdc37 and results in the phosphorylation ofCdc37. Cdc37 is essential for the maturation of de novosynthesized IKKs into enzymatically competent kinases,but not for assembly of an IKK holocomplex. MatureIKKs, T-loop phosphorylated after stimulation either byreceptor-mediated signaling or upon DNA damage, furtherrequire Hsp90-Cdc37 to generate an enzymaticallyactivated state. Thus, the Hsp90-Cdc37 chaperone-cochaperonecomplex is an essential regulatory componentin IKK signaling cascades and a potential drug targetin tumor therapy.Mutual requirements of Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB andWnt/β-catenin signaling in early ectodermalorganogenesisTo allow a functional analysis of NF-κB in early embryonicdevelopment and in disease models, we have generatedNF-κB repressor and reporter mice. The repressormice carry a dominant negative IκBα mutant (IκBα∆N)as a conditional knock-in allele, while the reporter miceexpress an NF-κB-driven β-gal transgene. Using thesemice, we could previously demonstrate novel morphogenicfunctions for NF-κB, including an early role inthe development of epidermal organs, such as hair follicles(HF). In early HF placodes, NF-κB is specifically activatedby TNF family members Eda-A1 and its receptorEdar. Furthermore we have identified an intense molecularcross-talk of Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB with other signalingpathways required for HF development, such as Wntand Sonic Hedgehog (SHH).According to our current knowledge, Wnt/β-cateninsignaling specifies the initial hair fate decision of epidermalkeratinocytes, while NF-κB is required for hairplacode growth by activating SHH signaling andrepressing Bone Morphogenic Protein (BMP) activity. Incollaboration with the laboratory of Dr. Sarah E. Millar(U. Pennsylvania, Philadeplhia, USA) we have nowdemonstrated that Wnt/β-catenin is initially activatedindependently of Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB, but depends onNF-κB activity for focal hair placode patterning. In contrast,initial Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB signaling is not activatedin skin of mice expressing the secreted Wnt inhibitorDKK1, or lacking epithelial β-catenin (Figure 2). In thiscontext we have shown that Wnt/β-catenin isabsolutely essential for NF-κB activation and have providedevidence that Edar is a direct Wnt/β-catenin targetgene. However, at later time points of hair follicledevelopment, localized Wnt activity disappears fromEda-A1/Edar/NF-κB mutant skin, implying that Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB is required for the maintenance of Wntsignaling (Figure 2).We found that NF-κB is essential forplacodal up-regulation of Wnt10a and Lef-1, and wecould identify Wnt10b as a direct target gene of NF-κB.Our data reveal a complex interplay and interdependenceof Wnt/β-catenin and Eda-A1/Edar/NF-κB signalingpathways, which may not only have importantimplications in organ development and morphogenesis,but also in cancer and inflammatory diseases.Our current and future studies will continue to focus onthe Wnt/NF-κB cross-talk in development/morpho -genesis and disease. Furthermore, in collaboration withDr. Nathaniel Heintz (Rockefeller I., New York, NY, USA)and Ines Ibañez-Tallon (<strong>MDC</strong>) we have developed amouse model (bacTRAP: translating ribosome affinitypurification (TRAP)) that allows the specific isolation ofHF keratinocytes. This mouse model will be used toidentify novel NF-κB target genes in early HF developmentand to perform detailed gene profiling studies onthe molecular controls of HF induction.Selected publicationsSchmidt-Ullrich, R, Tobin, DJ, Lenhard, D, Schneider, P, Paus, R, Scheidereit,C. (2006). NF-κB transmits Eda A1/EdaR signaling to activate Shh andcyclin D1 expression, and controls post-initiation hair placode downgrowth.Development 133, 1045-1057.Oeckinghaus, A, Wegener, E, Welteke, V, Ferch, U, Çöl Arslan, S, Ruland, J,Scheidereit, C, Krappmann, D. (2007). TRAF6 mediated Malt1 ubiquitinationtriggers IKK/NF-κB signaling upon T cell activation. EMBO J. 26,4634-4645.Hinz, M, Broemer, M, Çöl Arslan, S, Dettmer, R, Scheidereit, C. (2007).Signal-responsiveness of IκB kinases is determined by Cdc37-assistedtransient interaction with Hsp90. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 32311-32319.Zhang, Y, Tomann, P, Andl, T, Gallant, N, Huelsken, J, Jerchow, B, Birchmeier,W, Paus, R, Piccolo, S, Mikkola, ML, Morrisey, EE, Overbeek, PA, Scheidereit,C, Millar, SE, Schmidt-Ullrich, R. (2009). Reciprocal requirements forEda/Edar/NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in hair follicleinduction. Dev. Cell, 17, 49-61.Stilmann, M, Hinz, M, Cöl Arslan, S, Zimmer, A, Schreiber, V, Scheidereit, C,(2009). A nuclear poly(ADP-ribose) dependent signalosome confers DNAdamage induced IκB kinase activation. Mol Cell, in press.Cancer <strong>Research</strong> 81
- Page 1:
Research Report 2010MAX DELBRÜCK C
- Page 4 and 5:
ContentInhaltContentInhalt.........
- Page 6 and 7:
Surgical OncologyPeter M. Schlag...
- Page 11 and 12:
at the MDC. The role of the institu
- Page 13 and 14:
in discovering genes that contribut
- Page 16 and 17:
The ECRC offers research space and
- Page 18 and 19:
etween disciplines such as biology,
- Page 20 and 21:
approaches from bioinformatics/syst
- Page 23 and 24:
von Humboldt Foundation (AvH). The
- Page 25:
organization to a larger, multi-fac
- Page 28 and 29:
Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseas
- Page 30 and 31:
electrical signals. More recent wor
- Page 32 and 33:
Basic Cardiovascular FunctionStruct
- Page 34 and 35:
Figure 2: SORLA and sortilin in neu
- Page 36 and 37:
Annette Hammes(Delbrück Fellow)Str
- Page 38 and 39:
Ingo L. MoranoStructure of the Grou
- Page 40 and 41:
Figure 3. Membrane resealing assay
- Page 42 and 43:
Michael GotthardtStructure of the G
- Page 44 and 45:
Structure of the GroupSalim Seyfrie
- Page 46 and 47:
Structure of the GroupFerdinand le
- Page 48 and 49:
Francesca M. SpagnoliStructure of t
- Page 50 and 51:
Structure of the GroupKai M. Schmid
- Page 52 and 53:
Genetics and Pathophysiology of Car
- Page 54 and 55:
Figure 2. Planariato experimentally
- Page 56 and 57: Norbert HübnerStructure of the Gro
- Page 58 and 59: Structure of the GroupGroup LeaderF
- Page 60 and 61: Figure 2. Omega-3 fatty acids prote
- Page 62 and 63: Structure of the GroupDominik N. M
- Page 64 and 65: Rainer DietzStructure of the GroupG
- Page 66 and 67: Figure 2. Cardiac-restricted ablati
- Page 68 and 69: Ludwig ThierfelderStructure of the
- Page 70 and 71: standing of the molecular and cellu
- Page 72 and 73: Structure of the GroupThoralf Niend
- Page 74 and 75: Michael BaderStructure of the Group
- Page 76 and 77: Natriuretic peptide systemJens Butt
- Page 78 and 79: Structure of the GroupZsuzsanna Izs
- Page 80 and 81: Young-Ae LeeStructure of the GroupG
- Page 82 and 83: Structure of the GroupMatthias Selb
- Page 84 and 85: Matthew PoyStructure of the GroupGr
- Page 86 and 87: Jana WolfStructure of the GroupGrou
- Page 88 and 89: Structure of the GroupGroup LeaderD
- Page 91 and 92: Cancer Research ProgramKrebsforschu
- Page 93 and 94: are responsible for the emergence o
- Page 95 and 96: tral component of the canonical Wnt
- Page 97 and 98: lead to an aberrant constitutive ac
- Page 99 and 100: How Notch- and TGFβ signaling casc
- Page 101 and 102: tures of the chronic phase in human
- Page 103 and 104: oped a new safeguard that is based
- Page 105: Graduate StudentsSeda Cöl ArslanCa
- Page 109 and 110: Graduate StudentsÖzlem Akilli Özt
- Page 111 and 112: onment, the (cancer) stem cell nich
- Page 113 and 114: The pluripotent state of murine and
- Page 115 and 116: In the morula of the early mouse em
- Page 117 and 118: Graduate StudentsRami Hamscho*Qingb
- Page 119 and 120: esis and granulopoiesis. We showed
- Page 121 and 122: URE ∆/∆ mice regularly develope
- Page 123 and 124: PD Dr. Wolfgang Walther (GroupLeade
- Page 125 and 126: For the delivery of naked DNA into
- Page 127 and 128: ACBDMyc and FoxO transcription fact
- Page 129 and 130: Graduate StudentsKatrin BagolaHolge
- Page 131 and 132: Heinemann, we could also identify t
- Page 133 and 134: Above: Tip of chromosom3L showing t
- Page 135 and 136: Graduate StudentsSarbani Bhattachar
- Page 137 and 138: vesicle transport to the Golgi. Our
- Page 139 and 140: acbFigure 1a: EHD2 is tubulatingpho
- Page 141 and 142: KnowledgeProbabilitiesknownPossible
- Page 143 and 144: Graduate and undergraduatestudentsU
- Page 145 and 146: successive oncogenic mutations. We
- Page 147 and 148: CXCR5 drives the development of ect
- Page 149 and 150: Graduate and undergraduatestudentsW
- Page 151 and 152: Graduate andUndergraduate StudentsM
- Page 153 and 154: Angela MensenStefanie WittstockBjö
- Page 155 and 156: deficient mice, both major effector
- Page 157 and 158:
ant of CD3 delta coding for a 45-me
- Page 159 and 160:
Robert KudernatschLi-Min LiuAna Mil
- Page 161 and 162:
Sebastian GüntherTechnical Assista
- Page 163 and 164:
Graduate StudentsJana RolffAnnika W
- Page 165:
with murine hepatocytes showed morp
- Page 168 and 169:
Function and Dysfunction of the Ner
- Page 170 and 171:
The Neuroscience Department also es
- Page 172 and 173:
the coming years, Björn Schröder
- Page 174 and 175:
mice. Further analysis of the funct
- Page 176 and 177:
Signaling Pathways and Mechanisms i
- Page 178 and 179:
Control Olig3 -/-ABFigure 2. Geneti
- Page 180 and 181:
Thomas J. JentschStructure of the G
- Page 182 and 183:
Figure 2. Cellular model for ionic
- Page 184 and 185:
Structure of the GroupGroup LeaderF
- Page 186 and 187:
paired-pulse facilitation, less dep
- Page 188 and 189:
Gary R. LewinStructure of the Group
- Page 190 and 191:
Model summarizing the three waves o
- Page 192 and 193:
Structure of the GroupInes Ibañez-
- Page 194 and 195:
Jochen C. MeierStructure of the Gro
- Page 196 and 197:
Björn Christian SchroederStructure
- Page 198 and 199:
Structure of the GroupJan Siemens(S
- Page 200 and 201:
Structure of the GroupGroup LeaderD
- Page 202 and 203:
Imaging of the Living BrainStructur
- Page 204 and 205:
Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Ne
- Page 206 and 207:
Figure 2. Iba1 positive microglia c
- Page 208 and 209:
Erich E. WankerStructure of the Gro
- Page 210 and 211:
Scientific-Technical StaffAnja Frit
- Page 212 and 213:
Structure of the GroupJan Bieschke(
- Page 215 and 216:
Berlin Institute of Medical Systems
- Page 217 and 218:
etes, metabolic diseases and neurod
- Page 219 and 220:
A number of MDC investigators have
- Page 221 and 222:
Technical AssistantsClaudia Langnic
- Page 223 and 224:
has become a standardized data flow
- Page 225:
Phylogeny of cellulase genes from P
- Page 228 and 229:
Experimental and Clinical Research
- Page 230 and 231:
his patients, and a basic research
- Page 232 and 233:
The ultrahigh field MR facility was
- Page 234 and 235:
Structure of the GroupSimone Spuler
- Page 236 and 237:
Ralph KettritzStructure of the Grou
- Page 238 and 239:
Structure of the GroupJeanette Schu
- Page 240 and 241:
Maik GollaschStructure of the Group
- Page 243 and 244:
Technology PlatformsComputational B
- Page 245 and 246:
projects/ard/] to detect repeats li
- Page 247 and 248:
Simulation of line-scan images of C
- Page 249 and 250:
Development of an MRM method for qu
- Page 251 and 252:
mobility or turnover of the underly
- Page 253 and 254:
Left: Inside view of a FACSAria2 (f
- Page 255 and 256:
Examples fort the use of EM methods
- Page 257:
Oviducts lined up in pre-implantati
- Page 260 and 261:
Academic Appointments 2008-2009Beru
- Page 262 and 263:
Buch which is part of the Excellenc
- Page 264 and 265:
“Bioinformatics in Quantitative B
- Page 266 and 267:
Delbrück FellowsDelbrück-Stipendi
- Page 268 and 269:
Yinth Andrea Bernal-Sierra, a PhD s
- Page 270 and 271:
Congresses and Scientific MeetingsK
- Page 272 and 273:
SeminarsSeminare2008Speaker Institu
- Page 274 and 275:
Speaker Institute TitleKiyoshi Mori
- Page 276 and 277:
2009Speaker Institute TitleDavid G.
- Page 278 and 279:
Speaker Institute TitleJuri Rappsil
- Page 280 and 281:
The Helmholtz AssociationDie Helmho
- Page 282 and 283:
The Berlin-Buch CampusDer Campus Be
- Page 284:
the MDC, the existing collaboration
- Page 287 and 288:
Prof. Dr. Gary R. LewinMDC Berlin-B
- Page 289 and 290:
Prof. Dr. Renato ParoCenter of Bios
- Page 291 and 292:
Staff CouncilThe Staff Council is i
- Page 293 and 294:
Type of Financing/Art der Finanzier
- Page 295 and 296:
Research Projects 2008-2009Forschun
- Page 297 and 298:
CIC-5 Regulation und Endocytose am
- Page 299 and 300:
MDCMAX-DELBRÜCK-CENTRUMFÜR MOLEKU
- Page 301 and 302:
Index 275Bröske, A. . . . . . . .
- Page 303 and 304:
Index 277Gross, V. . . . . . . . .
- Page 305 and 306:
Index 279Kur, E. . . . . . . . . .
- Page 307 and 308:
Index 281Piano, F. . . . . . . . .
- Page 309 and 310:
Index 283Smink, J. . . . . . . . .
- Page 312 and 313:
Campus MapCampusplanRobert-Rössle-
- Page 314:
How to find your way to the MDCDer