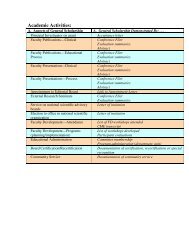
The SRA Symposium - College of Medicine
The SRA Symposium - College of Medicine
The SRA Symposium - College of Medicine
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Questions 4 and 5<br />
Papers<br />
<strong>The</strong> last two frequent questions flow together as research administrators wonder about what are<br />
the defense mechanisms and whether some are better than others. <strong>The</strong>re are defense mechanisms<br />
that can be categorized as defending by “withdrawal” such as: denial <strong>of</strong> reality that is refusing to<br />
recognize the threatening external event or piece <strong>of</strong> information. Examples include the tobacco<br />
addict who denies scientific evidence linking smoking to lung cancer. <strong>The</strong> “love is blind” perspective,<br />
the denial <strong>of</strong> death, and a “rose colored glasses” view <strong>of</strong> the world. Repression involves<br />
pushing unacceptable thoughts, feelings or impulses into the unconscious mind. Examples include<br />
“forgetting” dreams, dental appointments, childhood traumas, and repressing envious feelings.<br />
Regression is withdrawal into the past by readopting behaviors that previously brought satisfaction.<br />
Examples include a supervisor who has a temper tantrum when a subordinate makes a mistake,<br />
sulking when you do not get your way, or waiting to be “rescued”; acting childishly. Sublimation<br />
is placing unwanted impulses into socially acceptable behaviors. Examples include sexually<br />
forbidden desires being sublimated into creating works <strong>of</strong> art; an aggressive person redirecting<br />
that energy by going into the military or law enforcement pr<strong>of</strong>essions.<br />
<strong>The</strong>re are defense mechanisms that can be grouped into “defending by attacking”. <strong>The</strong>se include:<br />
displacement, which is discharging pent-up feelings <strong>of</strong> frustration onto weaker, less dangerous<br />
persons, animals, or objects rather than back to the real threat. An example would be picking an<br />
argument with a spouse when you are really angry with a supervisor or coworker. Projection is<br />
disowning personal responsibility by externalizing blame. Examples would include a person who<br />
is angry at their supervisor but acts friendly toward him or her and then complains that the same<br />
supervisor is angry with them, or “seeing” lust, fear, or hostility in others when it is really caused<br />
by one’s own unacceptable urges. Intellectualization is separating unpleasant emotions or personal<br />
responsibility from a threatening event or situation by thinking or talking about it in “intellectual”<br />
terms. Examples include using intellectual arguments as excuses, analyzing too much to avoid feelings,<br />
or pontificating. Rationalization is explaining shortcomings, lessening disappointments, or<br />
reducing guilt by justifying with reasons or excuses. Examples include when being passed over for<br />
an award and saying, “I did not really want it anyway” or having defensive explanations for poor<br />
performance.<br />
Finally, there are some defense mechanisms that defend by capitulation. Introjection helps to<br />
avoid rejection and external threats when a person internalizes the values and beliefs <strong>of</strong> others.<br />
An example is “group think” in organizations. Identification is boosting one’s own ego and esteem<br />
by identifying with powerful or desirable persons, groups, or organizations. Examples include<br />
name-dropping, taking on the latest fad, or joining a special group to bolster an insecure self-image.<br />
Reaction Formation prevents unacceptable urges from being expressed by exaggerating the<br />
opposite behavior or viewpoint. Examples are when one “dost protest too much” and “smother<br />
love” covering up hostility.<br />
All defense mechanisms distort reality so reality becomes less threatening to our self-image. If you<br />
are criticized for a project, you can control your anxiety by blaming others (projection), by giving<br />
excuses (rationalization), by getting angry and throwing something (displacement), and you could<br />
suppress your anxiety (repression).<br />
When under extreme stress a person’s psychological balance will shift and less mature defenses<br />
emerge. Vaillant (1971) suggested that there is a continuum <strong>of</strong> the defense mechanism. He proposed<br />
that defense maneuvers range from mature defenses <strong>of</strong> altruism, anticipation, humor,<br />
sublimation, and suppression to the neurotic defenses <strong>of</strong> displacement, intellectualization, reaction<br />
formation, and repression to the immature defenses <strong>of</strong> acting out, hypochondriasis, passive aggression,<br />
projection and finally to narcissistic defenses <strong>of</strong> delusion, distortions, and psychotic denial.<br />
2005 <strong>Symposium</strong> Proceedings Book 125