The SRA Symposium - College of Medicine
The SRA Symposium - College of Medicine
The SRA Symposium - College of Medicine
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
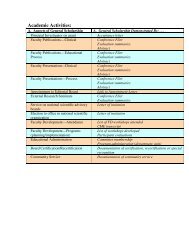
Nine keys to the essentials financial management include: 1. Administration <strong>of</strong> Finance - the quality<br />
<strong>of</strong> financial management (A multi-year financial plan, Debt management policies, Investment<br />
policies, Budgeting and monitoring the budget and Growth and vision.) 2. Sources <strong>of</strong> Revenue<br />
- Student Fees, (Institutional philosophy-Price vs. Cost, How are price increases determined?<br />
Tuition as a percentage <strong>of</strong> education and general expenditures, Special fees-Student activity fees,<br />
Athletic and Others, Investments, Grants, gifts & contracts, and Auxiliary enterprises.) 3. Expenditures<br />
(academic, auxiliary and athletic.) 4. Accounting and Reporting (Monthly financial reports,<br />
Budget reports, financial aid budgets, financial aid reports, and Auxiliary enterprise reports.) 5.<br />
Budgeting – Planning (Establish clearly state institutional objectives and Develop clearly defined<br />
philosophy <strong>of</strong> institutional finance), Preparation – (Establish policy on tuition and fees charged,<br />
Enrollment objectives, Faculty student ratios) and +Compensation (Fringe benefits, full and part<br />
time positions.) 6. Debt Management - Debt management reports (Short term, Long term, Interest<br />
due per year, and Principal per year.) 7. Audits - Annual audits (A-133 Audit <strong>of</strong> Federal Programs<br />
and Internal.) 8. Endowments: investment, spending formula, and reporting.) 9. Administration <strong>of</strong><br />
Financial Aid.<br />
A financial checklist for new college presidents includes questions such as has the institution generated<br />
operating deficits? What is the size <strong>of</strong> unrestricted endowment per FTE, per faculty? Are<br />
there funds functioning as endowment? At what level, and with what certainty, will the primary<br />
source continue to provide funding – tuition and fees? What is the status <strong>of</strong> debt serviced payments?<br />
Which institutional assets can be liquidated? Federal Grants-To what extent are faculty<br />
salaries funded by grants? How will the future be impacted by grants? What is the reimbursed<br />
indirect cost rate? Are federal funds reimbursed timely and in compliance with federal requirements?<br />
What is the status <strong>of</strong> cash and short-term investments? What is the actual cost <strong>of</strong> fringe<br />
benefits? To what extent are monies borrowed from current restricted funds, endowment or<br />
outside sources to pay normal operating expenses? Are receivables converted to cash on a timely<br />
basis? Are vendor payments made on time? Is there adequate working capital and are there shortterm<br />
loans? and What is the status <strong>of</strong> the annual audit?<br />
A financial aid checklist for new college presidents may include questions such as: Who is the senior<br />
administrator responsible for monitoring financial aid? Who establishes and approves policies<br />
for awarding financial aid? What is the composition <strong>of</strong> the institutions’ financial aid by source and<br />
by type (loan, scholarship, employment, etc.)? How do peer group institutions’ student financial<br />
expenditures compare? To what extent are unrestricted funds used to finance student aid? What is<br />
the distribution <strong>of</strong> financial aid by class? What are the potential changes in federal or state policies<br />
that will affect the availability <strong>of</strong> financial aid? What is the number and percentages <strong>of</strong> students<br />
who receive financial aid? What are the default rates for Perkins loans and the cohort default rate<br />
for FFEL loans?<br />
RESOURCES FOR HISTORICALLY BLACK COLLEGES AND UNIVERSITIES<br />
Papers<br />
Founded after the Civil War during a period when African-Americans were denied admission<br />
to colleges nationwide, black colleges naturally awarded most <strong>of</strong> the degrees earned by African-<br />
Americans. However, following integration efforts <strong>of</strong> the 1950s and 60s, new educational opportunities<br />
were extended to African Americans within predominantly white schools, resulting in<br />
migration to these white schools, thus weakening many black colleges. <strong>The</strong>y lost students, faculty,<br />
their best athletes and <strong>of</strong> course a large portion <strong>of</strong> their revenue base – student tuition.<br />
According to the Christian Science Monitor, since 2000, more than 25% <strong>of</strong> the black college presidents<br />
have resigned in recent years, with most citing the stresses and strains <strong>of</strong> fundraising as their<br />
primary obstacle.<br />
2005 <strong>Symposium</strong> Proceedings Book 49