- Page 1 and 2:
\ m 5-7’. _ ! i‘ -‘ I I ’
- Page 3 and 4:
Correct citation." Intemationa] Ric
- Page 5 and 6:
llulrmflnn gamma Mimi
- Page 7 and 8:
CLIMATIC STRESS ON GROWTH AND YIELD
- Page 9 and 10:
4 CLINIATE mo) RICE agricultural an
- Page 11 and 12:
6 cuivnvri-i AND RICE R. N. Morse.
- Page 13 and 14:
8 CLItvhYfE an) RICE ice of agricul
- Page 15 and 16:
infill! IHNIQI Chill
- Page 17 and 18:
12 (JLLNLXTE AND rues In saving thi
- Page 19 and 20:
14 (ZLIh-L-XTE ant: RICE essential
- Page 21 and 22:
l 6 CLIlvLJtTE AND RICE Groin yield
- Page 23 and 24:
l8 CLIMATE AND RICE MANIPULATING LI
- Page 25 and 26:
20 (JLlMA'l‘E AND tour; Dcrkness
- Page 27 and 28:
22 CLIh-IATE AND RICE Photosynthesi
- Page 29 and 30:
24 cuivrxru AND rues temperature. l
- Page 31 and 32:
26 CLIh-IATE AND RICE REFERENCES BA
- Page 34 and 35:
Climatic environment 0f rice cultiv
- Page 36 and 37:
GEOGRAPHY mo) curt-tars OF RICE 31
- Page 38 and 39:
Gsooawm" .~'t.\1D CLIMATE or ates 3
- Page 40 and 41:
GEOGRAPHY AND CLINIATT-I OF RICE 35
- Page 42 and 43:
GEOGRJIPHH’ AND (jLlh-DYTE OF RIC
- Page 44 and 45:
GEOGRAPHY AND CLINIATE OF RICE 39 c
- Page 46 and 47:
oration-win‘ AND (ILIAIATE or RIC
- Page 48 and 49:
GEOGR.~'\PH\’ AND CLIlylATE OF RI
- Page 50 and 51:
GEOGRAPHY AND CLIMATE or RICE 45 No
- Page 52 and 53:
CIEOGRAPHY‘ AND (ILIh-LATE or RIC
- Page 54 and 55:
GEOGKAPIIH’ mo) CLIMATE OF RICE 4
- Page 56 and 57:
CROP PLANNING AND ILAINFALL 5i Clim
- Page 58 and 59:
(tRoP PLANNING mo RAINFImL 53 is al
- Page 60 and 61:
cnor PLANNING AND RAisFaLi. 55 the
- Page 62 and 63:
(IROP PLANNING AND RAINFALL 57 Tabl
- Page 64 and 65:
CROP PLANNING into RAINFALL 59 valu
- Page 66 and 67:
REFERENCES CROP PLANNING AND IL-XIN
- Page 68:
CROP PLANNING AND RAINFALL 63 the c
- Page 72 and 73:
PI-IY'SI(JL(')F1ICAL AND .\I(‘)RP
- Page 74 and 75:
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND NIORPIIOLOGICAL A
- Page 76 and 77:
l‘HYSl0L(_)(il(fi'\L AND .\IURPH(
- Page 78 and 79:
PHYSlOLt')GItT.=\I. AND l\tlORPHt')
- Page 80 and 81:
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICA]. AD
- Page 82 and 83:
PH‘t'SIOLOGI(,‘.+-\L AND tvltiR
- Page 84 and 85:
PHYSIOLOGICAL non) MORPHOLOGICAI. A
- Page 86 and 87:
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND NIORPI-IOIJJGKTAL
- Page 88 and 89:
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND IMIORPHOLIJGILTAL
- Page 90 and 91:
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND IVIORPHOLOGILTAL
- Page 92 and 93:
(jtENETItT \’.-’\RI(_)L.'SNESS
- Page 94 and 95:
GENTETTIZT \".=\RIOLTS.\IFSS IN CLI
- Page 96 and 97:
GENETIC \"'.-\RI(,)l.'SI\'ESS IN t,
- Page 98 and 99:
GENETIC \';—\RIOLTS?\TESS IN FLIN
- Page 100 and 101:
GEYETIC INFORIv-LATTON ON CLIMATIC
- Page 102 and 103:
GENETIC VARIOUSNESS IN CLIMATTC ADA
- Page 104 and 105:
GENETIC VARIOIISNESS 1N ("LINIATTF
- Page 106 and 107:
GENETIC \';-\RIOL='S1\'lESS IN CLIM
- Page 108 and 109:
GENETIC‘ VARIOUSNESS IN (“LINIA
- Page 110 and 111:
GENETIC WXRIOLTSNESS IN cut-taut: A
- Page 112 and 113:
GENETIC \".=\R101.IS1\'ESS nv (ILIN
- Page 114 and 115:
GENETIC VstRlOLlSNESS IN CLIAIAIIC
- Page 116:
GENETIC VZARIOLISNESS m ClJlytNflC
- Page 119 and 120:
llmmwminh Quinlan mum
- Page 121 and 122:
116 CLIMATE AND RICE about the micr
- Page 123 and 124:
l l8 curt-ran; AND RICE xtinctm ooe
- Page 125 and 126:
i ~ I20 cLniATF. AND RIFF. [ml (g h
- Page 127 and 128:
122 cusiixrs mo RICE Albedo and rad
- Page 129 and 130:
124 cLuxiAnz AND RICE Relative reig
- Page 131 and 132:
126 curt-tyre AND RICE tribution. I
- Page 133 and 134:
I28 (‘LIMATE AND RICE 0d 56,855 .
- Page 135 and 136:
130 CLIAiL-YFE AND RICE temperature
- Page 137 and 138:
132 euixixna ma) RICE 0.19 for a ri
- Page 139 and 140:
134 Curt-tan; AND RICE solar elevat
- Page 141 and 142:
136 CLlk-LATE AND RICE REFERENCES C
- Page 143 and 144:
138 CLIMATE AND RICE UDAGAiwA, T..
- Page 145 and 146: 140 CLIMATE AND RICE estimated by t
- Page 147 and 148: 142 (rut-tars mo arcs closely relat
- Page 149 and 150: I44 CLINIATE am Rica we assume that
- Page 151 and 152: 146 CLlxL-Yfl-L AND RILTE DUPLICATI
- Page 153 and 154: 14S cumara mo RICE lamp type was su
- Page 155 and 156: 150 curtmrs AND RICE Table 5. Influ
- Page 157 and 158: 152 (tuners AND RICE amount of dama
- Page 159 and 160: 154 culture ANT) RICE enviromnent a
- Page 162: Environmental control 0f growth and
- Page 165 and 166: 160 CLIh-LATE AND RICE The effect o
- Page 167 and 168: 162 curt-LATE AND RICE Temperature
- Page 169 and 170: 164 curt-tare are) RICE (20°C) at
- Page 171 and 172: 166 cunt-ms AND RICE mersion at 25
- Page 173 and 174: 168 CLINLATE AND RICE Top growth To
- Page 175 and 176: 170 cur-airs ANT) RICE and dropped
- Page 177 and 178: 172 CLINIATE AND RICE Dividing cell
- Page 179 and 180: 174 CLIIMIATE AND RICE Rate of stre
- Page 181 and 182: 176 rim-tam AND RICE 60°—62°C.
- Page 183 and 184: 178 culture AND RICE REFERENCES ADA
- Page 185 and 186: 180 CLIMATE AND RICE LEE. H. S.. an
- Page 187 and 188: 182 CLINIATE AND RICE SAKAI. K. 194
- Page 189 and 190: 184 (TLlb-LYIE AND rucs DISCUSSION
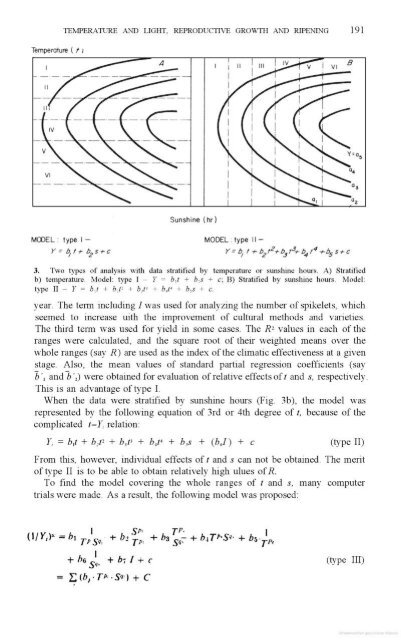
- Page 191 and 192: llulrmflnn gamma Mimi
- Page 193 and 194: 188 CLIMATE AND RICE reactions othe
- Page 195: 190 crux-tars AND RICE SD 0t temper
- Page 199 and 200: 194 trusarns imp RICE Spikeiets [no
- Page 201 and 202: 196 ems-tars AND RICE of tillers ha
- Page 203 and 204: 198 CLIh-LATE AND RICE Both of thes
- Page 205 and 206: 200 truatars AND RICE Ripemnq erode
- Page 207 and 208: 202 crux-tars AND RICE At such low
- Page 209 and 210: 204 CLIMATE AND RICE (l/Yflo‘? =
- Page 211 and 212: 206 tiLIMATE AND RICE Equations (T)
- Page 213 and 214: 208 cits-ems awn RICE DISCUSSION TA
- Page 215 and 216: 210 CLIh-LATE AND RICE hlANtJEL: So
- Page 217 and 218: 212 curt-tars AND RICE EFFECTS 0F C
- Page 219 and 220: 214 CLIMATE min RICE cOzlpnmt 35o 3
- Page 221 and 222: 2 l6 CLINIATE ANT) RICE may in part
- Page 223 and 224: 218 CLINIATE AND RICE could largely
- Page 225 and 226: 220 cuixiirrs AND RICE DISCUSSION T
- Page 228 and 229: 223 Climatic influence on photosynt
- Page 230 and 231: CLIMATIC INFLUENCE ON PHOTOSYNTTLES
- Page 232 and 233: (_'[.l\l.A'l'IC INFLUENCE ON PHOTOS
- Page 234 and 235: CLINIATIC mrurswca on Pnorosiwn. IE
- Page 236 and 237: CIJh-LATIC‘ [XTFTIFENCE ON PHOTOS
- Page 238 and 239: LTLIMAHC INFLUENCE ON PHOTOSYbTfHES
- Page 240 and 241: curt-write INFLUENCE cs PHtJTOSYNTH
- Page 242 and 243: 237 CLTNIATTC INFLUENCE ON PHOTOSYN
- Page 244 and 245: CLIhLATTC INFLUENCE OY PIIOTOSYNTHE
- Page 246 and 247:
cunmrs INFLUENCE ON PHOTOSYNTHESIS
- Page 248 and 249:
CIJMATTC HNTLUENCE ON PHOTOSYhTl-IE
- Page 250 and 251:
CLINIATIC INFLUENCE ON PHOTOSYNTI-I
- Page 252 and 253:
CLllvL-YTIC INFLUENCE ON Pl-lO'l‘
- Page 254 and 255:
249 Temperature and the chemical ki
- Page 256 and 257:
TENIPERATTIRE AND truss-nest. Kinet
- Page 258 and 259:
TEh-IPERi-KTITRE AND CHENHCAI. KINE
- Page 260 and 261:
TEMPERATURE AND CIIENHCAL KINETICS
- Page 262 and 263:
TEkIPEILATLRE AND CIIENHCAL KINETIC
- Page 264 and 265:
l l TEMPERATIIRE awn FHENfltX-U. KI
- Page 266 and 267:
TENIPERATLIRE ANT) CI-IENIICAL KINE
- Page 268:
TENIPERATLTRE AND CHEMICAL KINETICS
- Page 271 and 272:
266 (TLIINL-KTE two RICE _“ _'“
- Page 273 and 274:
268 ciriyrprna AND RICE the oxytgen
- Page 275 and 276:
270 FLINIATE AND RIPE Table 2. Effe
- Page 277 and 278:
272 CLltx-MTE AIMTD RICE Percent |2
- Page 279 and 280:
2'14 CLIMATE AND RICE Table 3. Reco
- Page 281 and 282:
276 (Tl.l.\t.»\"l1~‘. AND RICE I
- Page 283 and 284:
llnlznclvlzll wuzlnnnll-ul
- Page 285 and 286:
un-Iuuuzvtng-uml:usll
- Page 287 and 288:
282 CLIMATE AND RICE Brown rice yie
- Page 289 and 290:
284 CLIh-IATE AND RICE Susceptible
- Page 291 and 292:
286 cusutrs AhD RICE tillers were s
- Page 293 and 294:
288 CLIINIATE mo RICE Hoyuyuhi lNtl
- Page 295 and 296:
290 CLIh-IATE AND RICE us to make a
- Page 297 and 298:
292 curtrars AND RICE postulated th
- Page 299 and 300:
294 cummia am) RICE Cooling treatme
- Page 301 and 302:
296 eta-ctr]; AND RICE Isntztnza.
- Page 303 and 304:
298 (fLllt-iitTE AND RICE TORIYAMA.
- Page 305 and 306:
300 curaaTF. AND RICE and the toler
- Page 307 and 308:
302 CLllt-IATE AND RICE the low-lyi
- Page 309 and 310:
304 cuxmn: AND RICE Water depth ter
- Page 311 and 312:
306 (tux-tats AND RICE Fertilizer i
- Page 313 and 314:
308 CLINIATE AND RICE of the plant
- Page 315 and 316:
3 l0 CLIMATE ANT) RICE The floating
- Page 317 and 318:
312 cuxranz AND RICE Branching does
- Page 319 and 320:
314 culture AND RICE variety would
- Page 321 and 322:
316 CLIMATE AND RICE [in Japanese,
- Page 323 and 324:
318 CLIMATE AND RICE by adventitiou
- Page 325 and 326:
LhflklfllillrxfiibMill
- Page 327 and 328:
322 cLnuArE AND RICE fied in the se
- Page 329 and 330:
324 CLIMATE AND RICE Photosynthesis
- Page 331 and 332:
326 CLIMATE AND RICE maize was grow
- Page 333 and 334:
328 CLIMATE AND RICE sunflower. It
- Page 335 and 336:
330 (fLlIvlATE am: RICE maze m“ (
- Page 337 and 338:
332 cLix-L-vra AND RICE and ‘wate
- Page 339 and 340:
334 CIIXIATE AND RICE IMPROVEMENT O
- Page 341 and 342:
336 cusmnz Ann RICE cell elongation
- Page 343 and 344:
338 CLINIATE AND RICE REFERENCES AC
- Page 345 and 346:
340 Cl.l.\t.-'\'l'E AND RICE DIS CL
- Page 347 and 348:
342 CLINLATE AND RICE ALLURI: Could
- Page 349 and 350:
""1133"lflhllll “IIIII
- Page 351 and 352:
UlljiflllijlllhfiHid
- Page 353 and 354:
348 crLnuATs AND RICE Experimental
- Page 355 and 356:
350 CLIMAtTE AND RICE constant.”
- Page 357 and 358:
352 CLINIATE AND RICE Scamens (1923
- Page 359 and 360:
354 CLIMATE AND RICE constant-facto
- Page 361 and 362:
356 criixinrs Aim RICE sider how th
- Page 363 and 364:
358 CLIMAJE AND RICE BIOCLINLNPIC I
- Page 365 and 366:
360 CLIh-IATE awn RICE faster rate.
- Page 367 and 368:
362 CLIIvLATE AND RICE REFERENCES A
- Page 369 and 370:
364 CLINIATE AND RICE —. 1959. Ef
- Page 371 and 372:
366 crumars AND RICE rliferrenger:
- Page 373 and 374:
368 (ILlh-IATE AND RICE Moreover. i
- Page 375 and 376:
370 curt-i-rra AND RICE caused tl1e
- Page 377 and 378:
372 CLIMATE Am) RICE Insects oftrop
- Page 379 and 380:
374 CLIMATE awn RICE Amaini. in the
- Page 381 and 382:
376 CLIMATE AND RICE former outbrea
- Page 383 and 384:
378 CLItvLATE AND RICE 1965. All bu
- Page 385 and 386:
380 CLlhiXfE AND RICE Future work I
- Page 387 and 388:
382 cuzxrars AND RICE Tsuruoka. 196
- Page 389 and 390:
384 crux-LATE AND RICJF. Wind direc
- Page 391 and 392:
386 CLIMATE AND RICE in June and Ju
- Page 393 and 394:
388 cur-ran: AND RICE JOHN. V. T..
- Page 395 and 396:
390 CLINIATE AND RICE PRADHAN. S. 1
- Page 397 and 398:
unmmmmnq-um-u-u
- Page 399 and 400:
394 (‘LIA-LATE AND RICE in that y
- Page 401 and 402:
396 CLIMATE AND RICE 26 inches long
- Page 403 and 404:
398 crnxrara AND RICE the 0.001 lev
- Page 405 and 406:
400 ci.ixi.»\'r|-: AND Rjtfl-I Ano
- Page 407 and 408:
402 euxiivrs AND RICE ation periods
- Page 409 and 410:
404 CLIMATE AND RICE Disease onset
- Page 411 and 412:
406 ctnvrara AND RICE If subsequent
- Page 413 and 414:
408 (fLlN-LAII-i AND RICE Spores ob
- Page 415 and 416:
410 CLINLATE AND RICE 29.900/aere L
- Page 417 and 418:
412 CLIMATE AND RICE Synthesis of d
- Page 419 and 420:
414 CLINIATE ma) RICE REFERENCES HY
- Page 421 and 422:
mnnnmmmrumanumrd
- Page 423 and 424:
418 (TLIMATE AND RICfE: Lesimlrrwnl
- Page 425 and 426:
420 cuMATE AND RICE COHIGIO |5 [I03
- Page 427 and 428:
422 CLL\-IATE AND RICE less than l
- Page 429 and 430:
424 CLIMATE AND RICE under field co
- Page 432 and 433:
Climate and crop productivity
- Page 434 and 435:
429 Comparisons of rice growth in d
- Page 436 and 437:
RICE (iROWFH IN DIFFERENT EI\'\"IR(
- Page 438 and 439:
RICE oaowrn m DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENT
- Page 440 and 441:
RICE GROWTH l.\l DII~'FERE.\IT' ENV
- Page 442 and 443:
RICE GROWTH IN DIFFERENT Emotions-i
- Page 444 and 445:
RICE GROWTH IN DIFFERENT EBFVIRONNI
- Page 446 and 447:
RICE GROWTH IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONMEN
- Page 448 and 449:
RICE oaoyvnr n; DIFFERENT ENVIRONIN
- Page 450 and 451:
RICE cRowni as DIFFERENT Eminomunst
- Page 452 and 453:
RICE GROWTH IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONNIE
- Page 454 and 455:
449 Productivity of rice in differe
- Page 456 and 457:
RICE PRODIlCTH-TTY IN ("IAlh“i|AT
- Page 458 and 459:
RICE PRODUCTIVITY IN CLIMATIC REGIO
- Page 460 and 461:
RICE PR()[)t.t(’l‘I\"l'I‘Y IN
- Page 462 and 463:
RICE PRODUCTIVITY IN CLINIATIC REGI
- Page 464 and 465:
RICE PR()I>t.T(.'Tl\-"lT‘t' m tru
- Page 466 and 467:
RICE PRODUCTIVITY I.\I CLIMATIL" RE
- Page 468 and 469:
RICE PRODLYt“.TI\-"'ITY' IN ('3I.
- Page 470 and 471:
RICF. PRt)l')L.'(f‘l‘t\r'lTY 1N
- Page 472 and 473:
RICE PRODUCTIVITY IN (TLIINLATIC RE
- Page 474 and 475:
RICE PRODUCTIVITY IN CLIMATIC REGIO
- Page 476 and 477:
471 Climatic influence on yield and
- Page 478 and 479:
‘ITELI? AND YIELD (‘Ol\'[PONEN'
- Page 480 and 481:
YIELD AND ‘FIELD (‘(’J.\lPt'J
- Page 482 and 483:
Table. 2. YIELD AND ‘KIRLD (‘Tt
- Page 484 and 485:
‘HELD AND YIELD (,7()l\-ll‘()l\
- Page 486 and 487:
YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENTS 0F LOVtL
- Page 488 and 489:
YIELD .-’\.\lD YlELD ("OMPONERWS
- Page 490 and 491:
YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENTS 0F LOWLA
- Page 492 and 493:
‘ITELD AND YIELD COMPONENTS OF LO
- Page 494 and 495:
YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENTS OF LO\\"
- Page 496 and 497:
YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENTS OF LOVfL
- Page 498 and 499:
YIELD AND YIELD (.‘.(IJl\rfP()NEl
- Page 500 and 501:
495 Climate and crop productivity i
- Page 502 and 503:
CLIMATE AND CROP PRODUCTIVITY IN AL
- Page 504 and 505:
CLlMikTl-i AND CROP PRODUCTTVYTX’
- Page 506 and 507:
CIJMATTZ AND CROP PROI)LI(TI"IVI'I'
- Page 508 and 509:
cunt-yrs AND tutor PR()[)tJ(,"l‘l
- Page 510 and 511:
(TLIMATE AND CROP PRODLFCTR-‘YTY
- Page 512 and 513:
(tin-acre mo) can? PRODU(J'l'lV1'1
- Page 514 and 515:
509 Nitrogen response of lowland an
- Page 516 and 517:
Gruinviefl (t/hal IO NITROGEN RESPO
- Page 518 and 519:
NITROGEN RESPONSE OF RICE IN 'l'R()
- Page 520 and 521:
NITROGEN RESPONSE or RICE IN TROPIC
- Page 522 and 523:
NITROGEN RESPONSE OF RICE IN 'I'ROP
- Page 524 and 525:
NITROGEN RESPONSE or RICE IN TROPIC
- Page 526 and 527:
NITROGEN RESPONSE or RICE l.\‘ TR
- Page 528 and 529:
NITROGEN sssmnsr: 0F lure m raoiatr
- Page 530 and 531:
NITROGEN RESPONSE OF RICE IN TROPIC
- Page 532 and 533:
NITROGEN RESPONSE or RICE [N TROPIC
- Page 534 and 535:
NITROGEN RESPONSE OF Rltflrl 1N TRO
- Page 536 and 537:
NITROGEN RESPONSE or RIPE IN TROPKT
- Page 538 and 539:
NITROGEN RESPONSE or RICE IN TROPIC
- Page 540 and 541:
xmzoonn RESPONSE or RICE I.\I TROPI
- Page 542 and 543:
NITROGEN RESPONSE OF RICE IN TROPIC
- Page 544 and 545:
NITROGEN RESPONSE OF RICE IN TROPIC
- Page 546 and 547:
CONCLUDING REMARKS 541 Their influe
- Page 548 and 549:
Ui#- b) List 0f Participants AHN. S
- Page 550 and 551:
tune); 545 Index Abnonnalities, cyt
- Page 552 and 553:
INDEX 547 fixation in photosynthesi
- Page 554 and 555:
INDEX 549 mean. and net production.
- Page 556 and 557:
moex S51 Gene analysis, components
- Page 558 and 559:
INDEX 553 water soluble. elTect of
- Page 560 and 561:
INDEX 555 Millhr-QZ) variety, 521 h
- Page 562 and 563:
INDEX 557 Photosynthesis and leaf a
- Page 564 and 565:
INDEX 559 Reproductive cycles, cont
- Page 566 and 567:
INDEX 561 Solar elevation and albed
- Page 568 and 569:
INDEX 563 stetilitv (See Sterility}
- Page 570:
INDEX 565 breeding. Mexico. 102 nit