Elementary New Testament Greek, 2014a
Elementary New Testament Greek, 2014a
Elementary New Testament Greek, 2014a
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
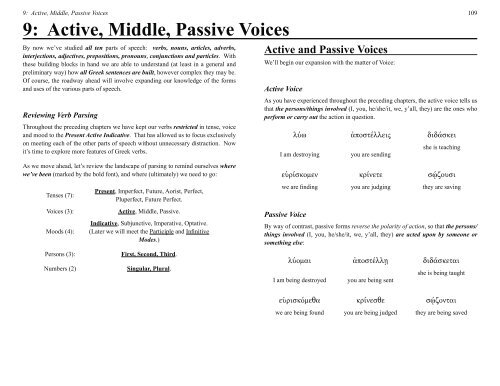
9: Active, Middle, Passive Voices<br />
9: Active, Middle, Passive Voices<br />
By now we’ve studied all ten parts of speech: verbs, nouns, articles, adverbs,<br />
interjections, adjectives, prepositions, pronouns, conjunctions and particles. With<br />
these building blocks in hand we are able to understand (at least in a general and<br />
preliminary way) how all <strong>Greek</strong> sentences are built, however complex they may be.<br />
Of course, the roadway ahead will involve expanding our knowledge of the forms<br />
and uses of the various parts of speech.<br />
Reviewing Verb Parsing<br />
Throughout the preceding chapters we have kept our verbs restricted in tense, voice<br />
and mood to the Present Active Indicative. That has allowed us to focus exclusively<br />
on meeting each of the other parts of speech without unnecessary distraction. Now<br />
it’s time to explore more features of <strong>Greek</strong> verbs.<br />
As we move ahead, let’s review the landscape of parsing to remind ourselves where<br />
we’ve been (marked by the bold font), and where (ultimately) we need to go:<br />
Tenses (7):<br />
Voices (3):<br />
Moods (4):<br />
Persons (3):<br />
Numbers (2)<br />
Present, Imperfect, Future, Aorist, Perfect,<br />
Pluperfect, Future Perfect.<br />
Active, Middle, Passive.<br />
Indicative, Subjunctive, Imperative, Optative.<br />
(Later we will meet the Participle and Innitive<br />
Modes.)<br />
First, Second, Third.<br />
Singular, Plural.<br />
Active and Passive Voices<br />
We’ll begin our expansion with the matter of Voice:<br />
Active Voice<br />
109<br />
As you have experienced throughout the preceding chapters, the active voice tells us<br />
that the personsthings involved (I, you, he/she/it, we, y’all, they) are the ones who<br />
perform or carry out the action in question.<br />
<br />
I am destroying<br />
you are sending<br />
she is teaching<br />
μ <br />
we are nding you are judging they are saving<br />
Passive Voice<br />
By way of contrast, passive forms reverse the polarity of action, so that the persons<br />
things involved (I, you, he/she/it, we, y’all, they) are acted upon by someone or<br />
something else:<br />
μ <br />
I am being destroyed<br />
you are being sent<br />
she is being taught<br />
μ <br />
we are being found you are being judged they are being saved