- Seite 2 und 3:
�����������
- Seite 4 und 5:
1 Jahrtausendelang waren natürlich
- Seite 6 und 7:
1 1907 1916 1935 1938 1942 1943 194
- Seite 8 und 9:
1 1.06 WARUM FASERVERBUNDWERKSTOFFE
- Seite 10 und 11:
1 1.08 KONSTRUIEREN MIT FASERVERBUN
- Seite 12 und 13:
1 FVW sind im Prinzip vergleichbar
- Seite 14 und 15:
1 Polyaddition (z.B. Epoxyd-Harze)
- Seite 16 und 17:
1 Die Entwicklung der Hochleistungs
- Seite 18 und 19:
1 Konstruiert wird der Werkstoff, v
- Seite 20 und 21:
1 Kontinuumstheorie Voraussetzung:
- Seite 22 und 23:
1 LAMINATBERECHNUNG NACH DER KLASSI
- Seite 24 und 25:
1 Während die Werte des Längsmodu
- Seite 26 und 27:
1 Schritt 8: Summe der spannungswir
- Seite 28 und 29: 1 Wanddicken Ungüstige Bauteilgest
- Seite 30 und 31: 1 Versteifung durch Sicken oder auf
- Seite 32 und 33: 1 Klebstoffe auf Basis Cyanacrylat
- Seite 34 und 35: 1 * Sicherheitshinweis: Achten Sie
- Seite 36 und 37: 1 Messing Anschleifen und entfetten
- Seite 38 und 39: 1 Investitionskosten Capital costs
- Seite 40 und 41: 1 Geeignete Materialien Als Matrix
- Seite 42 und 43: 1 AUTOKLAV - VERFAHREN Das Autoklav
- Seite 44 und 45: 1 Für das Wickeln von Bauteilen -h
- Seite 46 und 47: 1 Naß-Preßverfahren Trockene Vers
- Seite 48 und 49: 1 Maximale Vorschubgeschwindigkeite
- Seite 50 und 51: 1 Faserverbundwerkstoffe und Beschi
- Seite 52 und 53: 1 Systeme Nach Anwendungsgebieten w
- Seite 54 und 55: 1 Lagerung EPOXYDHARZE EINE ÜBERSI
- Seite 56 und 57: 1 Es sollten flache Mischgefäße m
- Seite 58 und 59: 1 EPOXYDHARZE EINE ÜBERSICHT DER E
- Seite 60 und 61: 1 Fehler Problem EPOXYDHARZE EINE
- Seite 62 und 63: 1 Die richtige Temperatur ist ein e
- Seite 64 und 65: 1 DAS TEMPERN EPOXYDHARZE UND TEMPE
- Seite 66 und 67: 1 1.64 VOM RICHTIGEN, SICHEREN UMGA
- Seite 68 und 69: 1 Die Erfassung und Bestimmung sich
- Seite 70 und 71: 1 Epoxyd- und Polyesterharze haben
- Seite 72 und 73: 1 1. vor der Arbeit before work Ori
- Seite 74 und 75: 1 Leichtentzündlich Highly flammab
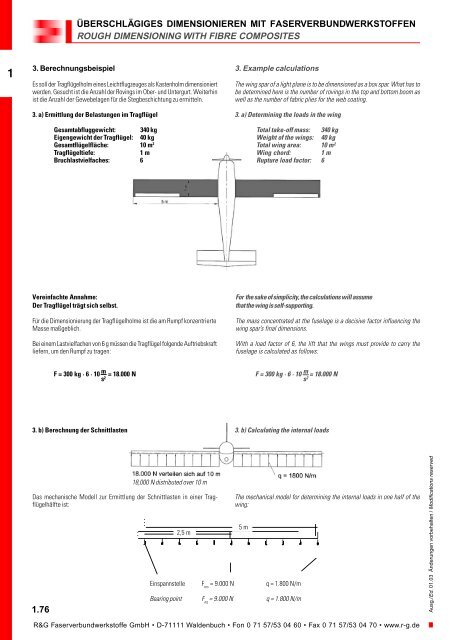
- Seite 76 und 77: 1 Das nachfolgende Beispiel zeigt,
- Seite 80 und 81: 1 In den Holmgurten wurde die mittl
- Seite 82 und 83: 1 Zur Fertigung von Bauteilen aus F
- Seite 84 und 85: 1 HERSTELLUNG EINER KUNSTSTOFF-FORM
- Seite 86 und 87: 1 2) Festlegung der Trennebenen und
- Seite 88 und 89: 1 Reste werden mit einem weichen Ba
- Seite 90 und 91: 1 4) Laminieren der Formteile Nach
- Seite 92 und 93: 1 Zum Schluß wird das Laminat noch
- Seite 94 und 95: 1 5) Nachbehandlung der Form Um ein
- Seite 96 und 97: 1 Ecken ausrunden und verstärken D
- Seite 98 und 99: 1 (Skizze 2) überstehendes Gewebe
- Seite 100 und 101: 1 Industriefußböden Industriefuß
- Seite 102 und 103: 1 Estriche/Mörtelbeläge Estriche
- Seite 104 und 105: 1 Bezugsquellen Füllstoffe Farbqua
- Seite 106 und 107: ������ �����
- Seite 108 und 109: Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 110 und 111: Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 112 und 113: Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 114 und 115: Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 116 und 117: Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 118 und 119: Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 120 und 121: Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 122 und 123: Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 124 und 125: Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 126 und 127: Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 128 und 129:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 130 und 131:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 132 und 133:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 134 und 135:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 136 und 137:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 138 und 139:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 140 und 141:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 142 und 143:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 144 und 145:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 146 und 147:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 148 und 149:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 150 und 151:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 152 und 153:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 154 und 155:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 156 und 157:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 158 und 159:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 160 und 161:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 162 und 163:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 164 und 165:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 166 und 167:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 168 und 169:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 170 und 171:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 172 und 173:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 174 und 175:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 176 und 177:
3 R&G führt eine Auswahl ungesätt
- Seite 178 und 179:
3 Lagerung UNGESÄTTIGTE POLYESTERH
- Seite 180 und 181:
3 UNGESÄTTIGTE POLYESTERHARZE, FOR
- Seite 182 und 183:
3 3.08 UNGESÄTTIGTE POLYESTERHARZE
- Seite 184 und 185:
3 Beschreibung 3.10 UNGESÄTTIGTE P
- Seite 186 und 187:
3 4 UNGESÄTTIGTE POLYESTERHARZE, P
- Seite 188 und 189:
3 Einfärbungen UP-Gießharz Glaskl
- Seite 190 und 191:
3 DER SCHWABBELLACK UND SEINE VERAR
- Seite 192 und 193:
3 Bevor Epoxydharz aufgebracht werd
- Seite 194 und 195:
3 Beschreibung Weißes / farbloses
- Seite 196 und 197:
3 Beschreibung Hochkonzentrierte, l
- Seite 198 und 199:
3 Beschreibung Dünnflüssig, leich
- Seite 200 und 201:
3 Daten für MEKP-Härter Specifica
- Seite 202 und 203:
������ �����
- Seite 204 und 205:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 206 und 207:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 208 und 209:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 210 und 211:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 212 und 213:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 214 und 215:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 216 und 217:
5 Die R&G Laminierkeramik ist ein v
- Seite 218 und 219:
5 Beschreibung Besondere Vorteile:
- Seite 220 und 221:
5 Fotos: H. Funke FORMENBAU MIT LAM
- Seite 222 und 223:
������ �����
- Seite 224 und 225:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 226 und 227:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 228 und 229:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 230 und 231:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 232 und 233:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 234 und 235:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 236 und 237:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 238 und 239:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 240 und 241:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 242 und 243:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 244 und 245:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 246 und 247:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 248 und 249:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 250 und 251:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 252 und 253:
7 Lieferbare Produkte Lieferform De
- Seite 254 und 255:
7 GRUNDIERWACHS PRIMING WAX Beschre
- Seite 256 und 257:
7 Beschreibung Milde Polierpaste zu
- Seite 258 und 259:
7 Beschreibung Hochwärmefestes Tre
- Seite 260 und 261:
7 Beschreibung Enthält Butylacetat
- Seite 262 und 263:
������ �����
- Seite 264 und 265:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 266 und 267:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 268 und 269:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 270 und 271:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 272 und 273:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 274 und 275:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 276 und 277:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 278 und 279:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 280 und 281:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 282 und 283:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 284 und 285:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 286 und 287:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 288 und 289:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 290 und 291:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 292 und 293:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 294 und 295:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 296 und 297:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 298 und 299:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 300 und 301:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 302 und 303:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 304 und 305:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 306 und 307:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 308 und 309:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 310 und 311:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 312 und 313:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 314 und 315:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 316 und 317:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 318 und 319:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 320 und 321:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 322 und 323:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 324 und 325:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 326 und 327:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 328 und 329:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 330 und 331:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 332 und 333:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 334 und 335:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 336 und 337:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 338 und 339:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 340 und 341:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 342 und 343:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 344 und 345:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 346 und 347:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 348 und 349:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 350 und 351:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 352 und 353:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 354 und 355:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 356 und 357:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 358 und 359:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 360 und 361:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 362 und 363:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 364 und 365:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 366 und 367:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 368 und 369:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 370 und 371:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 372 und 373:
9 9.02 STÜTZSTOFFE SANDWICH MATERI
- Seite 374 und 375:
9 Welche Materialkombinationen sind
- Seite 376 und 377:
9 Fläche einer Halbschale Surface
- Seite 378 und 379:
9 Wie wird ein Wabensandwich herges
- Seite 380 und 381:
9 Was kann man tun, um die Delamina
- Seite 382 und 383:
9 Auch im Formenbau werden mittlerw
- Seite 384 und 385:
9 WABEN IM MODELLBAU HERSTELLUNG EI
- Seite 386 und 387:
9 16 17 18 Auftragen von Harz und E
- Seite 388 und 389:
9 STÜTZSTOFF FÜR LEICHTE SANDWICH
- Seite 390 und 391:
9 Literaturhinweis Systematische En
- Seite 392 und 393:
9 Verarbeitung Die Verarbeitung unt
- Seite 394 und 395:
9 DIMENSIONIERUNG VON FLÄCHENSTECK
- Seite 396 und 397:
9 Gebrauch der Tabellen Die Werte i
- Seite 398 und 399:
9 Leichte Segelflugmodelle, langsam
- Seite 400 und 401:
9 Hotliner, Speedmodelle, Kunstflug
- Seite 402 und 403:
9 HALBZEUGE SEMI-FINISHED PRODUCTS
- Seite 404 und 405:
9 HALBZEUGE SEMI-FINISHED PRODUCTS
- Seite 406 und 407:
9 Beschreibung HALBZEUGE SEMI-FINIS
- Seite 408 und 409:
9 HALBZEUGE SEMI-FINISHED PRODUCTS
- Seite 410 und 411:
9 WEICHGEGLÜHTES ALUMINIUM FÜR SC
- Seite 412 und 413:
9 WEICHES ALUMINIUM-STRECKMETALL F
- Seite 414 und 415:
9 FORMETAL ® FLEXMETAL ® Strecken
- Seite 416 und 417:
9 Hauptbegriffe Unterbereiche Categ
- Seite 418 und 419:
9 Hauptbegriffe Unterbereiche Categ
- Seite 420 und 421:
9 Hauptbegriffe Unterbereiche Categ
- Seite 422 und 423:
������ �����
- Seite 424 und 425:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 426 und 427:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 428 und 429:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 430 und 431:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 432 und 433:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 434 und 435:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 436 und 437:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 438 und 439:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 440 und 441:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 442 und 443:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 444 und 445:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 446 und 447:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 448 und 449:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 450 und 451:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 452 und 453:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 454 und 455:
������ �����
- Seite 456 und 457:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 458 und 459:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 460 und 461:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 462 und 463:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 464 und 465:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 466 und 467:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 468 und 469:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 470 und 471:
Ausg./Ed. 01.03 Änderungen vorbeha
- Seite 472 und 473:
12 Copyright ANHANG APPENDIX © bei
- Seite 474 und 475:
12 ANHANG APPENDIX Fachtermini (in
- Seite 476 und 477:
12 ANHANG APPENDIX Harzansatz Rezep
- Seite 478 und 479:
12 ANHANG APPENDIX quasiiotrop nahe