Sustainable Agriculture Literature Review - Boulder County
Sustainable Agriculture Literature Review - Boulder County
Sustainable Agriculture Literature Review - Boulder County
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
! ! !!<br />
"#$%&!'())!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!@+!A142!"#5#81B152!<br />
Glyphosate Resistance<br />
Glyphosate, first commercialized in 1974, has been extensively used for weed control. 599<br />
The first case of evolved resistance to glyphosate was reported in 1996 in rigid ryegrass<br />
(Lolium rigidum) 600 and approximately 18 species have now evolved resistance (Graph<br />
22). 601 According to the National Academy of Sciences, gene flow between herbicide<br />
resistant crops and closely related weed species does not explain the evolution of<br />
glyphosate resistance in U.S. fields because sexually compatible weeds are absent where<br />
corn, cotton, and soybean are grown in the United States. Instead, a number of studies<br />
have shown that the near exclusive use of glyphosate for weed control, a practice<br />
accelerated by the widespread introduction of glyphosate-resistant crop varieties, has<br />
caused substantial changes in weed communities. 602<br />
!<br />
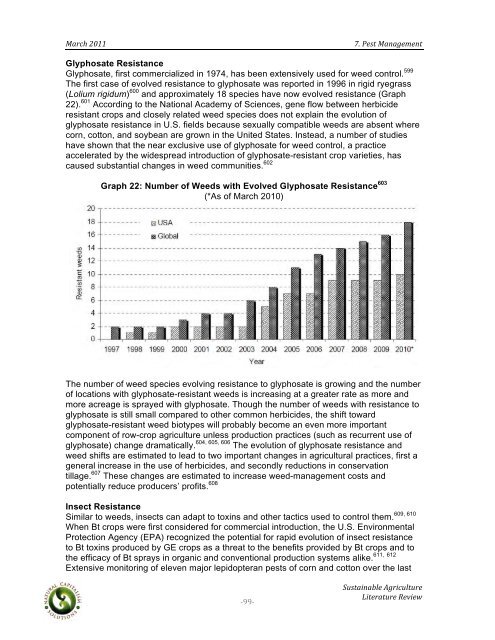
Graph 22: Number of Weeds with Evolved Glyphosate Resistance 603<br />
(*As of March 2010)<br />
The number of weed species evolving resistance to glyphosate is growing and the number<br />
of locations with glyphosate-resistant weeds is increasing at a greater rate as more and<br />
more acreage is sprayed with glyphosate. Though the number of weeds with resistance to<br />
glyphosate is still small compared to other common herbicides, the shift toward<br />
glyphosate-resistant weed biotypes will probably become an even more important<br />
component of row-crop agriculture unless production practices (such as recurrent use of<br />
glyphosate) change dramatically. 604, 605, 606 The evolution of glyphosate resistance and<br />
weed shifts are estimated to lead to two important changes in agricultural practices, first a<br />
general increase in the use of herbicides, and secondly reductions in conservation<br />
tillage. 607 These changes are estimated to increase weed-management costs and<br />
potentially reduce producers’ profits. 608<br />
Insect Resistance<br />
Similar to weeds, insects can adapt to toxins and other tactics used to control them.<br />
When Bt crops were first considered for commercial introduction, the U.S. Environmental<br />
Protection Agency (EPA) recognized the potential for rapid evolution of insect resistance<br />
to Bt toxins produced by GE crops as a threat to the benefits provided by Bt crops and to<br />
611, 612<br />
the efficacy of Bt sprays in organic and conventional production systems alike.<br />
Extensive monitoring of eleven major lepidopteran pests of corn and cotton over the last<br />
"$$"<br />
609, 610<br />
!,342#.5#6/1!78$.%3/23$1!<br />
9.21$#23$1!:1;.1