Diseases and Management of Crops under Protected Cultivation
Diseases and Management of Crops under Protected Cultivation
Diseases and Management of Crops under Protected Cultivation
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
(<strong>Diseases</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Crops</strong> <strong>under</strong> <strong>Protected</strong> <strong>Cultivation</strong>)<br />
with red worms, this includes composting with bacteria, fungi, insects, <strong>and</strong> other bugs.<br />
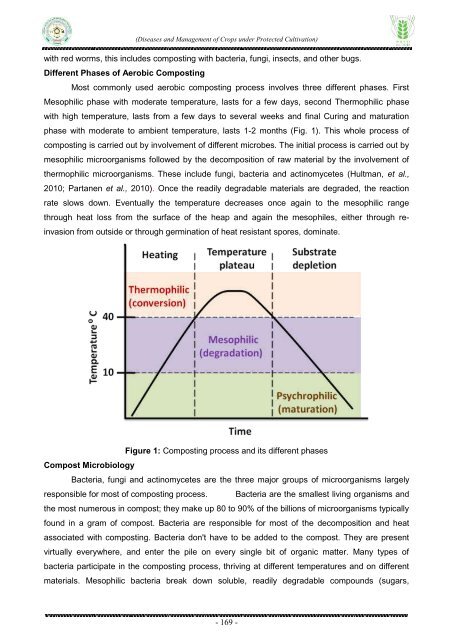
Different Phases <strong>of</strong> Aerobic Composting<br />
Most commonly used aerobic composting process involves three different phases. First<br />
Mesophilic phase with moderate temperature, lasts for a few days, second Thermophilic phase<br />
with high temperature, lasts from a few days to several weeks <strong>and</strong> final Curing <strong>and</strong> maturation<br />
phase with moderate to ambient temperature, lasts 1-2 months (Fig. 1). This whole process <strong>of</strong><br />
composting is carried out by involvement <strong>of</strong> different microbes. The initial process is carried out by<br />
mesophilic microorganisms followed by the decomposition <strong>of</strong> raw material by the involvement <strong>of</strong><br />
thermophilic microorganisms. These include fungi, bacteria <strong>and</strong> actinomycetes (Hultman, et al.,<br />
2010; Partanen et al., 2010). Once the readily degradable materials are degraded, the reaction<br />
rate slows down. Eventually the temperature decreases once again to the mesophilic range<br />
through heat loss from the surface <strong>of</strong> the heap <strong>and</strong> again the mesophiles, either through reinvasion<br />
from outside or through germination <strong>of</strong> heat resistant spores, dominate.<br />
Figure 1: Composting process <strong>and</strong> its different phases<br />
Compost Microbiology<br />
Bacteria, fungi <strong>and</strong> actinomycetes are the three major groups <strong>of</strong> microorganisms largely<br />
responsible for most <strong>of</strong> composting process. Bacteria are the smallest living organisms <strong>and</strong><br />
the most numerous in compost; they make up 80 to 90% <strong>of</strong> the billions <strong>of</strong> microorganisms typically<br />
found in a gram <strong>of</strong> compost. Bacteria are responsible for most <strong>of</strong> the decomposition <strong>and</strong> heat<br />
associated with composting. Bacteria don't have to be added to the compost. They are present<br />
virtually everywhere, <strong>and</strong> enter the pile on every single bit <strong>of</strong> organic matter. Many types <strong>of</strong><br />
bacteria participate in the composting process, thriving at different temperatures <strong>and</strong> on different<br />
materials. Mesophilic bacteria break down soluble, readily degradable compounds (sugars,<br />
- 169 -