Diseases and Management of Crops under Protected Cultivation
Diseases and Management of Crops under Protected Cultivation
Diseases and Management of Crops under Protected Cultivation
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
(<strong>Diseases</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Crops</strong> <strong>under</strong> <strong>Protected</strong> <strong>Cultivation</strong>)<br />
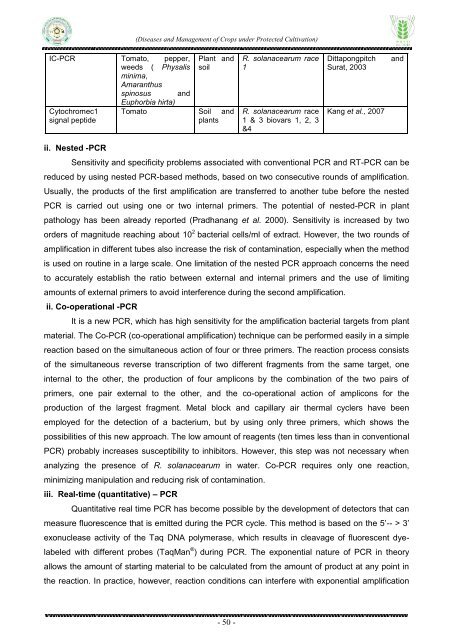
IC-PCR Tomato, pepper,<br />
weeds ( Physalis<br />
minima,<br />
Amaranthus<br />
spinosus <strong>and</strong><br />
Cytochromec1<br />
signal peptide<br />
Plant <strong>and</strong><br />
soil<br />
Euphorbia hirta)<br />
Tomato Soil <strong>and</strong><br />
plants<br />
R. solanacearum race<br />
1<br />
R. solanacearum race<br />
1 & 3 biovars 1, 2, 3<br />
&4<br />
Dittapongpitch<br />
Surat, 2003<br />
Kang et al., 2007<br />
<strong>and</strong><br />
ii. Nested -PCR<br />
Sensitivity <strong>and</strong> specificity problems associated with conventional PCR <strong>and</strong> RT-PCR can be<br />
reduced by using nested PCR-based methods, based on two consecutive rounds <strong>of</strong> amplification.<br />
Usually, the products <strong>of</strong> the first amplification are transferred to another tube before the nested<br />
PCR is carried out using one or two internal primers. The potential <strong>of</strong> nested-PCR in plant<br />
pathology has been already reported (Pradhanang et al. 2000). Sensitivity is increased by two<br />
orders <strong>of</strong> magnitude reaching about 10 2 bacterial cells/ml <strong>of</strong> extract. However, the two rounds <strong>of</strong><br />
amplification in different tubes also increase the risk <strong>of</strong> contamination, especially when the method<br />
is used on routine in a large scale. One limitation <strong>of</strong> the nested PCR approach concerns the need<br />
to accurately establish the ratio between external <strong>and</strong> internal primers <strong>and</strong> the use <strong>of</strong> limiting<br />
amounts <strong>of</strong> external primers to avoid interference during the second amplification.<br />
ii. Co-operational -PCR<br />
It is a new PCR, which has high sensitivity for the amplification bacterial targets from plant<br />
material. The Co-PCR (co-operational amplification) technique can be performed easily in a simple<br />
reaction based on the simultaneous action <strong>of</strong> four or three primers. The reaction process consists<br />
<strong>of</strong> the simultaneous reverse transcription <strong>of</strong> two different fragments from the same target, one<br />
internal to the other, the production <strong>of</strong> four amplicons by the combination <strong>of</strong> the two pairs <strong>of</strong><br />
primers, one pair external to the other, <strong>and</strong> the co-operational action <strong>of</strong> amplicons for the<br />
production <strong>of</strong> the largest fragment. Metal block <strong>and</strong> capillary air thermal cyclers have been<br />
employed for the detection <strong>of</strong> a bacterium, but by using only three primers, which shows the<br />
possibilities <strong>of</strong> this new approach. The low amount <strong>of</strong> reagents (ten times less than in conventional<br />
PCR) probably increases susceptibility to inhibitors. However, this step was not necessary when<br />
analyzing the presence <strong>of</strong> R. solanacearum in water. Co-PCR requires only one reaction,<br />
minimizing manipulation <strong>and</strong> reducing risk <strong>of</strong> contamination.<br />
iii. Real-time (quantitative) – PCR<br />
Quantitative real time PCR has become possible by the development <strong>of</strong> detectors that can<br />
measure fluorescence that is emitted during the PCR cycle. This method is based on the 5’-- > 3’<br />
exonuclease activity <strong>of</strong> the Taq DNA polymerase, which results in cleavage <strong>of</strong> fluorescent dyelabeled<br />
with different probes (TaqMan ® ) during PCR. The exponential nature <strong>of</strong> PCR in theory<br />
allows the amount <strong>of</strong> starting material to be calculated from the amount <strong>of</strong> product at any point in<br />
the reaction. In practice, however, reaction conditions can interfere with exponential amplification<br />
- 50 -