Third Day Poster Session, 17 June 2010 - NanoTR-VI
Third Day Poster Session, 17 June 2010 - NanoTR-VI
Third Day Poster Session, 17 June 2010 - NanoTR-VI
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
P<br />
P<br />
<strong>Poster</strong> <strong>Session</strong>, Thursday, <strong>June</strong> <strong>17</strong><br />
Theme F686 - N1123<br />
Investigation of Crystal Structure of 4-(3-Benzylpiperidino)-propionylamino benzenesulfonamide by<br />
X-ray Powder Diffraction Method<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
erife YalçinP P, UHasan TürkmenUP P*, Mehmet AkkurtP<br />
PDepartment of Physics,Harran University, anlurfa 63000,Turkey<br />
PDepartment of Chemistry,Harran University, anlurfa 63000,Turkey<br />
3<br />
PDepartment of Physics,Erciyes University, Kayseri 38039,Turkey<br />
P<br />
2<br />
1<br />
Abstract-The Crystal Structure of 4-(3-Benzylpiperidino)-propionylamino benzenesulfonamide [1] was synthesised by the reaction of 3-<br />
chloropropionylamino benzenesulfonamide and Benzylpiperidine, was characterised by X-ray powder diffraction method. Crystal Structure of<br />
this compound by X-ray powder diffraction method has not been studied before. In this study, we found crystal system of title compound as<br />
triclinic. We also investigated unit cell parameters, grain size analysis of the title compound (1). We hope that the results obtained in this study<br />
would give some ideas about electrical, magnetical and optical features of this compound.<br />
CA inhibition with sulfanilamide discovered by Mann and<br />
Keilin [2] was the beginning of a great scientific adventure<br />
that led to important drugs, such as the antihypertensives of<br />
benzothiadiazine and high-ceiling diuretics type, [3] the<br />
sulfonamides with CA inhibitory properties mainly used as<br />
antiglaucoma agents, [4,3,5] some antithyroid drugs, [3] the<br />
hypoglycemic sulfonamides, [6] and, ultimately, some novel<br />
types of anticancer agents.[7] The report of Krebs [8] that<br />
mainly the unsubstituted aromatic sulfonamides of type<br />
ArSOR2RNHR2R act as strong CAIs, and that the potency of such<br />
compounds is drastically reduced by N-substitution of the<br />
sulfonamide moiety, constituted the beginning of extensive<br />
structure–activity correlations, which led to some valuable<br />
drugs during a short period of time.<br />
FW(S)*Cos(Theta)<br />
0.128<br />
* Fit Size Only: XS(nm) = 86.6 (130.0), Strain(%) = 0.0, ESD of Fit = 0.0, LC = 1.0<br />
(1)<br />
Figure 1. The scheme of the title compound<br />
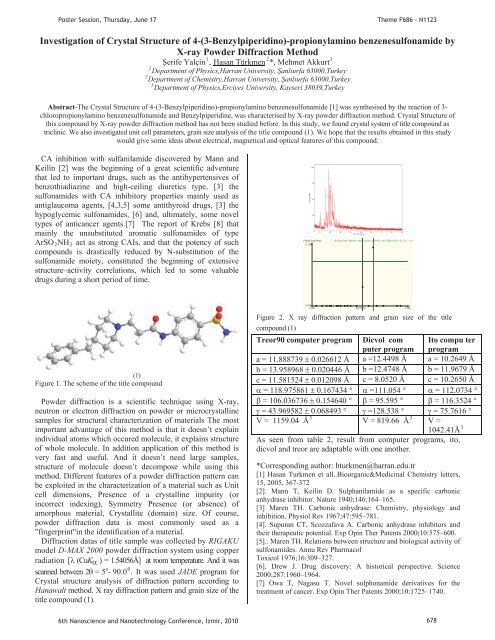
Powder diffraction is a scientific technique using X-ray,<br />
neutron or electron diffraction on powder or microcrystalline<br />
samples for structural characterization of materials The most<br />
important advantage of this method is that it doesn’t explain<br />
individual atoms which occured molecule, it explains structure<br />
of whole molecule. In addition application of this method is<br />
very fast and useful. And it doesn’t need large samples,<br />
structure of molecule doesn’t decompose while using this<br />
method. Different features of a powder diffraction pattern can<br />
be exploited in the characterization of a material such as Unit<br />
cell dimensions, Presence of a crystalline impurity (or<br />
incorrect indexing), Symmetry Presence (or absence) of<br />
amorphous material, Crystallite (domain) size. Of course,<br />
powder diffraction data is most commonly used as a<br />
"fingerprint"in the identification of a material.<br />
Diffraction datas of title sample was collected by RIGAKU<br />
model D-MAX 2000 powder diffraction system using copper<br />
radiation [ (CuK ) = 1.54056Å] at room temperature. And it was<br />
o 0<br />
scanned between 2 = 5P P- 90.0 P P. It was used JADE program for<br />
Crystal structure analysis of diffraction pattern according to<br />
Hanawalt method. X ray diffraction pattern and grain size of the<br />
title compound (1).<br />
0.000<br />
0.080 Sin(Theta)<br />
0.396<br />
Figure 2. X ray diffraction pattern and grain size of the title<br />
compound (1)<br />
Treor90 computer program Dicvol com Ito compu ter<br />
puter program program<br />
a = 11.888739 0.026612 Å a =12.4498 Å a = 10.2649 Å<br />
b = 13.958968 0.020446 Å b =12.4748 Å b = 11.9679 Å<br />
c = 11.581524 0.012098 Å c = 8.0520 Å c = 10.2650 Å<br />
= 118.975861 0.167434 ° =111.054 ° = 112.0734 °<br />
= 106.036736 0.154640 ° = 95.595 ° = 116.3524 °<br />
= 43.969582 0.068493 ° =128.538 ° = 75.7616 °<br />
3<br />
V = 1159.04 ÅP<br />
3<br />
V = 819.66 ÅP V =<br />
1042.41ÅP<br />
As seen from table 2, result from computer programs, ito,<br />
dicvol and treor are adaptable with one another.<br />
*Corresponding author: hturkmen@harran.edu.tr<br />
[1] Hasan Turkmen et all..Bioorganic&Medicinal Chemistry letters,<br />
15, 2005, 367-372<br />
[2]. Mann T, Keilin D. Sulphanilamide as a specific carbonic<br />
anhydrase inhibitor. Nature 1940;146:164–165.<br />
[3] Maren TH. Carbonic anhydrase: Chemistry, physiology and<br />
inhibition. Physiol Rev 1967;47:595–781.<br />
[4]. Supuran CT, Scozzafava A. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and<br />
their therapeutic potential. Exp Opin Ther Patents 2000;10:575–600.<br />
[5].. Maren TH. Relations between structure and biological activity of<br />
sulfonamides. Annu Rev Pharmacol<br />
Toxicol 1976;16:309–327.<br />
[6]. Drew J. Drug discovery: A historical perspective. Science<br />
2000;287:1960–1964.<br />
[7] Owa T, Nagasu T. Novel sulphonamide derivatives for the<br />
treatment of cancer. Exp Opin Ther Patents 2000;10:<strong>17</strong>25–<strong>17</strong>40.<br />
3<br />
6th Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Conference, zmir, <strong>2010</strong> 678