Third Day Poster Session, 17 June 2010 - NanoTR-VI
Third Day Poster Session, 17 June 2010 - NanoTR-VI
Third Day Poster Session, 17 June 2010 - NanoTR-VI
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Poster</strong> <strong>Session</strong>, Thursday, <strong>June</strong> <strong>17</strong><br />
Theme F686 - N1123<br />
Comparative Study of Humidity Sensing Properties of PVC-Bt6-Cu and PVC-Bt6-Hg Complex<br />
Films<br />
Mavişe ŞEKER 1 , Salih OKUR 1 , Nesli T. YAĞMURCUKARDEŞ 1 , Gülşah KURT 2 , Bedrettin MERCİMEK 3 , Mahmut KUŞ 4<br />
1Izmir Institute of Technology, Department of Physics Urla/Izmir/TURKEY<br />
2Aksaray University, Department of Chemistry, Aksaray/TURKEY<br />
3 Selçuk University, Department of Chemistry Education, Selçuklu/Konya/TURKEY<br />
4Selçuk University, Department of Chemical Engineering, Selçuklu/Konya/TURKEY<br />
Abstract: This study focuses on respectively the characterization of PVC-BT6-Cu complex and PVC-BT6-Hg complex films coated on a<br />
quartz surface by drop-casting method for humidity detection and comparison of these two thin films properties. The Resistance and quartz<br />
crystal microbalance (QCM) were employed for the characterization. The change of resistance and resonance frequency was monitored with<br />
different increasing and decreasing relative humidity (RH) values between 11% and 97%.The humidity adsorption and desorption kinetics<br />
of the PVC-Bt6-Cu complex and PVC-Bt6-Hg complex films was examined by QCM technique.<br />
Poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) was modified with<br />
benzoilizotiyosiyanat and amine derivative and PVC<br />
connected benzoylthiourea ligand (PVC-Bt6) was<br />
obtained.Then Cu and Hg complexes of this ligand were<br />
synthesized.[1] In Fig.1 molecular structure of (a) PVC-<br />
Bt6-Cu complex and (b) PVC-Bt6-Hg complex are shown.<br />
CH 2 -CH<br />
CH 2 -CH<br />
CH 2 -CH<br />
CH 2 -CH<br />
20<br />
20<br />
%11<br />
%11 RH<br />
%11<br />
%11 RH<br />
0<br />
0<br />
%22<br />
%22<br />
-20<br />
%43<br />
%43<br />
-20<br />
-40 %53<br />
%53<br />
-60<br />
%75<br />
Cu-PVC<br />
Cu-PVC<br />
-40<br />
%75<br />
(under %84 RH)<br />
%84<br />
%84<br />
-80<br />
%94<br />
-60<br />
%94<br />
-100<br />
Hg-PVC (a) -80<br />
Hg-PVC (b)<br />
%97<br />
(under %84 RH)<br />
-120<br />
200 400 600 800 1000 1200<br />
Time/sec<br />
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000<br />
Time/sec<br />
0<br />
dF/Hz<br />
1000<br />
dF/Hz<br />
N<br />
N<br />
N<br />
N<br />
y = 4.1948 * e^(0.032107x) R= 0.98952<br />
100<br />
HN<br />
N<br />
S<br />
O<br />
Cu<br />
S<br />
O<br />
NH<br />
N<br />
HN<br />
N<br />
S<br />
O<br />
Hg<br />
S<br />
O<br />
NH<br />
N<br />
- f(Hz)<br />
Hg<br />
downward<br />
10<br />
Cu<br />
Hg<br />
upward<br />
Cu<br />
(c)<br />
1<br />
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100<br />
Relative Humidity (%)<br />
(a)<br />
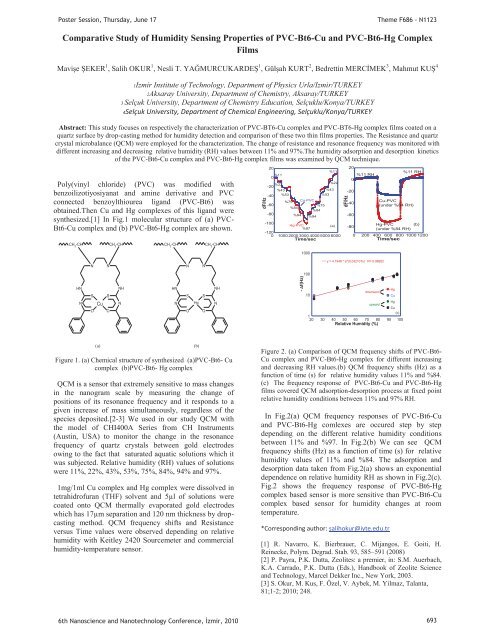
Figure 1. (a) Chemical structure of synthesized (a)PVC-Bt6- Cu<br />
complex (b)PVC-Bt6- Hg complex<br />
QCM is a sensor that extremely sensitive to mass changes<br />
in the nanogram scale by measuring the change of<br />
positions of its resonance frequency and it responds to a<br />
given increase of mass simultaneously, regardless of the<br />
species deposited.[2-3] We used in our study QCM with<br />
the model of CHI400A Series from CH Instruments<br />
(Austin, USA) to monitor the change in the resonance<br />
frequency of quartz crystals between gold electrodes<br />
owing to the fact that saturated aquatic solutions which it<br />
was subjected. Relative humidity (RH) values of solutions<br />
were 11%, 22%, 43%, 53%, 75%, 84%, 94% and 97%.<br />
1mg/1ml Cu complex and Hg complex were dissolved in<br />
tetrahidrofuran (THF) solvent and 5μl of solutions were<br />
coated onto QCM thermally evaporated gold electrodes<br />
which has <strong>17</strong>μm separation and 120 nm thickness by dropcasting<br />
method. QCM frequency shifts and Resistance<br />
versus Time values were observed depending on relative<br />
humidity with Keitley 2420 Sourcemeter and commercial<br />
humidity-temperature sensor.<br />
(b)<br />
Figure 2. (a) Comparison of QCM frequency shifts of PVC-Bt6-<br />
Cu complex and PVC-Bt6-Hg complex for different increasing<br />
and decreasing RH values.(b) QCM frequency shifts (Hz) as a<br />
function of time (s) for relative humidity values 11% and %84.<br />
(c) The frequency response of PVC-Bt6-Cu and PVC-Bt6-Hg<br />
films covered QCM adsorption-desorption process at fixed point<br />
relative humidity conditions between 11% and 97% RH.<br />
In Fig.2(a) QCM frequency responses of PVC-Bt6-Cu<br />
and PVC-Bt6-Hg comlexes are occured step by step<br />
depending on the different relative humidity conditions<br />
between 11% and %97. In Fig.2(b) We can see QCM<br />
frequency shifts (Hz) as a function of time (s) for relative<br />
humidity values of 11% and %84. The adsorption and<br />
desorption data taken from Fig.2(a) shows an exponential<br />
dependence on relative humidity RH as shown in Fig.2(c).<br />
Fig.2 shows the frequency response of PVC-Bt6-Hg<br />
complex based sensor is more sensitive than PVC-Bt6-Cu<br />
complex based sensor for humidity changes at room<br />
temperature.<br />
*Corresponding author: salihokur@iyte.edu.tr<br />
[1] R. Navarro, K. Bierbrauer, C. Mijangos, E. Goiti, H.<br />
Reinecke, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 93, 585–591 (2008)<br />
[2] P. Payra, P.K. Dutta, Zeolites: a premier, in: S.M. Auerbach,<br />
K.A. Carrado, P.K. Dutta (Eds.), Handbook of Zeolite Science<br />
and Technology, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 2003.<br />
[3] S. Okur, M. Kus, F. Özel, V. Aybek, M. Yilmaz, Talanta,<br />
81;1-2; <strong>2010</strong>; 248.<br />
6th Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Conference, zmir, <strong>2010</strong> 693