Photonic crystals in biology
Photonic crystals in biology
Photonic crystals in biology
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Poster Session, Tuesday, June 15<br />
Theme A1 - B702<br />
Preparation and Characterization of Zn-Rice Husk Char<br />
Esra Alt <strong>in</strong>tig 1 *<br />
1 Department of Chemistry, Sakarya University, Sakarya 54180, Turkey<br />
Abstract- In this study, rice husk was used as precursor for the preparation of activated carbon by chemical activation with ZnCl 2 . Rice husk<br />
charcoal support<strong>in</strong>g z<strong>in</strong>c (RH/Zn) was prepared by activation and chemical reduction. The RH/Zn composites were characterized by FTIR,<br />
XRD, EDS, z<strong>in</strong>c particle size and distribution, z<strong>in</strong> ion (Zn +2 ). Scann<strong>in</strong>g electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the Z n particles were<br />
distributed uniformly on the RH matrix. The Zn content and surface morphology of the RH/Zn composites depended on the <strong>in</strong>itial concentration<br />
of ZnNO 3 , and the higher the Zn content, the smaller the specific surface area obta<strong>in</strong>ed on the RH.<br />
Rice is one of the major crops grown throughout the world,<br />
shar<strong>in</strong>g equal importance with wheat as the pr<strong>in</strong>cipal staple<br />
food and a provider of nourishment for the world's population<br />
Concern about environmental protection has aroused over the<br />
years from a global viewpo<strong>in</strong>t. Rice husk ash, the most<br />
appropriate representative of the high ash biomass waste, is<br />
currently obta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g sufficient attraction, own<strong>in</strong>g to its wide<br />
usefulness and potentiality <strong>in</strong> environmental conservation. [1].<br />
Activated carbons are produced through physical or<br />
chemical activation. Chemical activation can be accomplished<br />
<strong>in</strong> a s<strong>in</strong>gle step by carry<strong>in</strong>g out thermal decomposition of raw<br />
material with chemical reagents. The most widely used<br />
chemicals <strong>in</strong>clude z<strong>in</strong>c chloride (ZnCl 2 ), phosphoric acid<br />
(H 3 PO 4 ), and potassium hydroxide/carbonate (KOH/K 2 CO 3 )<br />
[2].<br />
In this study, rice husk was used as precursor for the<br />
preparation of activated carbon by chemical activation and<br />
Zn-RH active carbon was prepared by exchang<strong>in</strong>g Na ions<br />
with Zn ions <strong>in</strong> active carbon.<br />
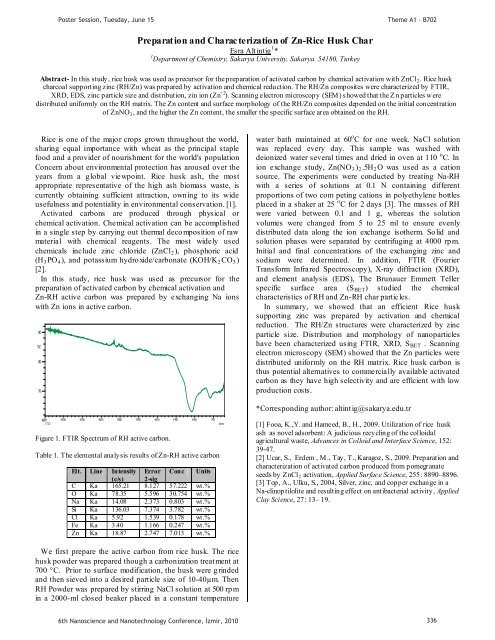
90<br />
%T<br />
80<br />
70<br />
water bath ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>ed at 60 o C for one week. NaCl solution<br />
was replaced every day. This sample was washed with<br />
deionized water several times and dried <strong>in</strong> oven at 110 o C. In<br />
ion exchange study, Zn(NO 3 ) 2 .5H 2 O was used as a cation<br />
source. The experiments were conducted by treat<strong>in</strong>g Na-RH<br />
with a series of solutions at 0.1 N conta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g different<br />
proportions of two com pet<strong>in</strong>g cations <strong>in</strong> polyethylene bottles<br />
placed <strong>in</strong> a shaker at 25 o C for 2 days [3]. The masses of RH<br />
were varied between 0.1 and 1 g, whereas the solution<br />
volumes were changed from 5 to 25 ml to ensure evenly<br />
distributed data along the ion exchange isotherm. Solid and<br />
solution phases were separated by centrifug<strong>in</strong>g at 4000 rpm.<br />
Initial and f<strong>in</strong>al concentrations of the exchang<strong>in</strong>g z<strong>in</strong>c and<br />
sodium were determ<strong>in</strong>ed. In addition, FTIR (Fourier<br />
Transform Infrared Spectroscopy), X-ray diffraction (XRD),<br />
and element analysis (EDS), The Brunauer Emmett Teller<br />
specific surface area (S BET ) studied the chemical<br />
characteristics of RH and Zn-RH char particles.<br />
In summary, we showed that an efficient Rice husk<br />
support<strong>in</strong>g z<strong>in</strong>c was prepared by activation and chemical<br />
reduction. The RH/Zn structures were characterized by z<strong>in</strong>c<br />
particle size. Distribution and morphology of nanoparticles<br />
have been characterized us<strong>in</strong>g FTIR, XRD, SBET . Scann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the Zn particles were<br />
distributed uniformly on the RH matrix. Rice husk carbon is<br />
thus potential alternatives to commercially available activated<br />
carbon as they have high selectivity and are efficient with low<br />
production costs.<br />
*Correspond<strong>in</strong>g author: alt<strong>in</strong>tig@sakarya.edu.tr<br />
4000<br />
FTIR<br />
3500<br />
3000<br />
2500<br />
Figure 1. FTIR Spectrum of RH active carbon.<br />
2000<br />
1750<br />
1500<br />
1250<br />
1000<br />
750<br />
1/cm<br />
Table 1. The elemental analysis results of Zn-RH active carbon<br />
El t. L<strong>in</strong>e Intensity Error Conc Units<br />
(c/s) 2-sig<br />
C Ka 165.21 8.127 57.222 wt.%<br />
O Ka 78.35 5.596 30.754 wt.%<br />
Na Ka 14.08 2.373 0.803 wt.%<br />
Si Ka 136.03 7.374 3.782 wt.%<br />
Cl Ka 5.92 1.539 0.178 wt.%<br />
Fe Ka 3.40 1.166 0.247 wt.%<br />
Zn Ka 18.87 2.747 7.013 wt.%<br />
[1] Fooa, K.,Y. and Hameed, B., H., 2009. Utilization of rice husk<br />
ash as novel adsorbent: A judicious recycl<strong>in</strong>g of the colloidal<br />
agricultural waste, Advances <strong>in</strong> Colloid and Interface Science, 152:<br />
39-47.<br />
[2] Ucar, S., Erdem , M., Tay, T., Karagoz, S., 2009. Preparation and<br />
characterization of activated carbon produced from pomegranate<br />
seeds by ZnCl 2 activation, Applied Surface Science, 255: 8890–8896.<br />
[3] Top, A., Ulku, S., 2004, Silver, z<strong>in</strong>c, and copper exchange <strong>in</strong> a<br />
Na-cl<strong>in</strong>op tilolite and result<strong>in</strong>g effect on antibacterial activity, Applied<br />
Clay Science, 27: 13– 19.<br />
We first prepare the active carbon from rice husk. The rice<br />
husk powder was prepared though a carbonization treatment at<br />
700 °C. Prior to surface modification, the husk were gr<strong>in</strong>ded<br />
and then sieved <strong>in</strong>to a desired particle size of 10-40μm. Then<br />
RH Powder was prepared by stirr<strong>in</strong>g NaCl solution at 500 rpm<br />
<strong>in</strong> a 2000-ml closed beaker placed <strong>in</strong> a constant temperature<br />
6th Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Conference, zmir, 2010 336