ISQ User Guide - Write Frame of Mind
ISQ User Guide - Write Frame of Mind
ISQ User Guide - Write Frame of Mind
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4 Creating a Method<br />
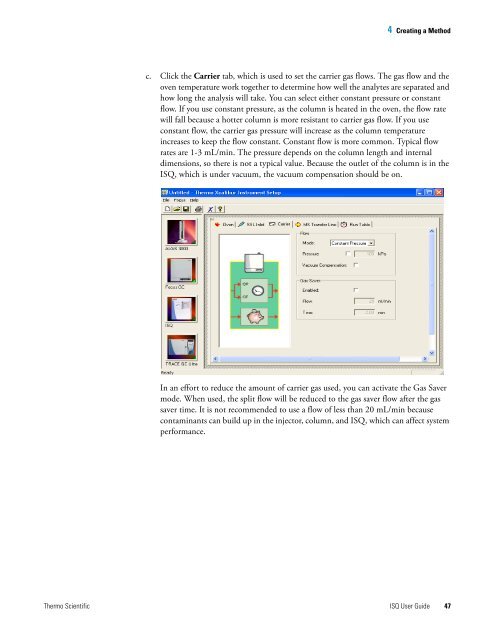
c. Click the Carrier tab, which is used to set the carrier gas flows. The gas flow and the<br />
oven temperature work together to determine how well the analytes are separated and<br />
how long the analysis will take. You can select either constant pressure or constant<br />
flow. If you use constant pressure, as the column is heated in the oven, the flow rate<br />
will fall because a hotter column is more resistant to carrier gas flow. If you use<br />
constant flow, the carrier gas pressure will increase as the column temperature<br />
increases to keep the flow constant. Constant flow is more common. Typical flow<br />
rates are 1-3 mL/min. The pressure depends on the column length and internal<br />
dimensions, so there is not a typical value. Because the outlet <strong>of</strong> the column is in the<br />
<strong>ISQ</strong>, which is under vacuum, the vacuum compensation should be on.<br />
In an effort to reduce the amount <strong>of</strong> carrier gas used, you can activate the Gas Saver<br />
mode. When used, the split flow will be reduced to the gas saver flow after the gas<br />
saver time. It is not recommended to use a flow <strong>of</strong> less than 20 mL/min because<br />
contaminants can build up in the injector, column, and <strong>ISQ</strong>, which can affect system<br />
performance.<br />
Thermo Scientific <strong>ISQ</strong> <strong>User</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> 47