- Page 1 and 2:
R 2.1 199^ ^.EN GINEERING DATA TRAN
- Page 3 and 4:
Date Received% • I INFORMATION RE
- Page 5 and 6:
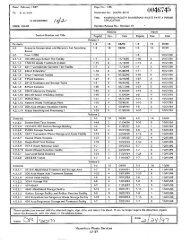
. SUPPORTING DOCUMENT 1. Total Page
- Page 7 and 8:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 EXECUTIVE
- Page 9 and 10:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 been achi
- Page 11 and 12:
__ _ _ MHC-SIL-yJ3,00-TI-D03 Rev. 0
- Page 13 and 14:
F`= WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 DESCR
- Page 15 and 16:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 LIST OF T
- Page 17 and 18:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 WASTE REC
- Page 19 and 20:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 1.2.1 Fee
- Page 21 and 22:
^s. WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 conta
- Page 23 and 24:
__-'°'2 WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0
- Page 25 and 26:
2.1 REGULATORY FRAMEWORK WHC-SD-W10
- Page 27 and 28:
^..." ;_:.. :.^ .^.y^ WHC-SD-W100-T
- Page 29 and 30:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 which the
- Page 31 and 32:
kIHC-S^u-Wi"v"u-Ti-u03 Rev. V ,--,,
- Page 33 and 34:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Type 1 wa
- Page 35 and 36:
3.3 TESTING APPROACH WHC-SD-W100-TI
- Page 37 and 38:
^.: fi WNC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Fi
- Page 39 and 40:
4.1 SCREENING TEST RESULTS WHC-SD-W
- Page 41 and 42:
,^. ----- -- WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev
- Page 43 and 44:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 4.1.3 The
- Page 45 and 46:
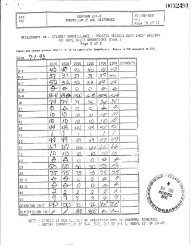
p Sam le Compressive Radiation stre
- Page 47 and 48:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Table 4-3
- Page 49 and 50:
..., TESTING RESULTS .^.CSSD-W-1OO-
- Page 51 and 52:
A I w ^^',; ^^ ;J ?1Fasf^.}: "q -?
- Page 53 and 54:
;..;: .^:. WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev.
- Page 55 and 56:
--- ....ti s..` WHC-SD-WI00-TI-003
- Page 57 and 58:
1.0 INTRODUCTION WHC-SD-W100-TI-003
- Page 59 and 60:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Waste For
- Page 61 and 62:
^-: -- ^ Component Waste Type 1 LET
- Page 63 and 64:
.^x. --1vHC-SD iii00- T i-003 Rev.
- Page 65 and 66:
WHC-SD-W: JV-TI-VVJ ^cv. v APPENDIX
- Page 67 and 68:
,..^ c:-- z ,.E ^=t ^^ln^l WHC-SD-W
- Page 69 and 70:
Scope WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Sup
- Page 71 and 72:
00 V F-' Activity and Miltstone Cha
- Page 73 and 74:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Laborator
- Page 75 and 76: WHC-SD-WIOO-TI-003 Rev. 0 APPENDIX
- Page 77 and 78: 16490 Chiaccothe Itoad Chagrin Fall
- Page 79 and 80: ca-. tY•^_E Q . - - StoGkE4uip+!n
- Page 81 and 82: ^.. WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 . , I
- Page 83 and 84: Waste Type: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev.
- Page 85 and 86: Stock E quipment Company A Unit of
- Page 87 and 88: G' ,.,. d,_ s WHC-0-W100-TI-003 Rev
- Page 89 and 90: Cx U: r°... .• , .ti Waste Type:
- Page 91 and 92: -. LeachantSolution: Specimen Diame
- Page 93 and 94: c^1, WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 THER
- Page 95 and 96: ..... lry" - Stock E a uipment Comp
- Page 97 and 98: ;=. .:^;. WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev< 0
- Page 99 and 100: (.7 ..^^ -„n f^. [Y^. Waste Type:
- Page 101 and 102: Date: _ Leachability Time Point Lea
- Page 103 and 104: 23 Ninety ( 90) Day Immersion Test
- Page 105 and 106: ty ,.. ='`F r...,, b Ly.. Specimen
- Page 107 and 108: 25 BIODEGRADATION TEST PROCEDURE St
- Page 109 and 110: Date: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 BIO
- Page 111 and 112: ^_... ..^^ C:i1 Date: WHC-SD-W100-T
- Page 113 and 114: Date: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 --
- Page 115 and 116: f-^ -- WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 2.
- Page 117 and 118: ^-..., 3•0 ASSAY FOR MEI'ALS 3.1
- Page 119 and 120: t..f f....,.. P....^ .-- ^ : .^ ^-.
- Page 121 and 122: ^c. v 3 0 w.3 cn a v t[ACeRUtIIY IO
- Page 123 and 124: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 APPENDIX
- Page 125: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 STOCK EQU
- Page 129 and 130: L:^3 ll Q. 4 AA :'ILTEP.S WHC-0-W10
- Page 131 and 132: 4_T tJrD o,...Ys j ^,.,. WHC-SD-W10
- Page 133 and 134: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 -, Proced
- Page 135 and 136: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Procedure
- Page 137 and 138: (FM WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Proce
- Page 139 and 140: C... 6 Wet Waste Sample Contains no
- Page 141 and 142: ^..., . ,.y^ h:.r WHC-SD-WI00-Ti-00
- Page 143 and 144: :. WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 TA3i.E
- Page 145 and 146: ^' . WHC-SD-W100-T1-003 Rev. 0 TABL
- Page 147 and 148: ^- ^-> ^ C^Jl I I^t ^.: l WHC-St]-W
- Page 149 and 150: c. 03 00 r=3 ^t C^' II 6.0 II Calib
- Page 151 and 152: LY; ^ C=l . ^.^ .^,..,, €:^. MHC-
- Page 153 and 154: R: C=1 rIj s^ ^ ^.. WHC-SD-YlI00-TI
- Page 155 and 156: .,,_..1 ---^ - - i-•_E ?*^^ Mater
- Page 157 and 158: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Dow Chemi
- Page 159 and 160: ^ ±.£:a [7.p -;^ --- --------- WH
- Page 161 and 162: WHC-S®-hi1.00-T'.-00?, Rev. Dow Ch
- Page 163 and 164: t;7_7 ,...:: ----------- WHC-SD-W10
- Page 165 and 166: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Daw M.. u
- Page 167 and 168: ^ ^..rYfl VF •UIYb 1 1 AGA GllS.
- Page 169 and 170: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 APPENDIX
- Page 171 and 172: CHARACTERIZATION DATA Part A: Overv
- Page 173 and 174: Grit Specie or MaterialOverall Cont
- Page 175 and 176: WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 The incin
- Page 177 and 178:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 183-H BAS
- Page 179 and 180:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 June - Se
- Page 181 and 182:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 BASINS 3
- Page 183 and 184:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 BASINS 3
- Page 185 and 186:
^- WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 BASIN
- Page 187 and 188:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 ---------
- Page 189 and 190:
J. L. Westcott Page 3 June 1, 1992
- Page 191 and 192:
u...^^, WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 I
- Page 193 and 194:
•N`^C-Sf1-"d100-71-003 Rev. 0 ,S'
- Page 195 and 196:
CONTAINER /NFORMATlO N: `d"-C-Sn-'w
- Page 197 and 198:
ONTANVER BVFORMA SI7 E: AMOUN=i 8 G
- Page 199 and 200:
LOT WRAP 2A.4 SHEET 7.XLS RECOMMEND
- Page 201 and 202:
LOT WRAP 2A.5 SHEET 8.XLS RECOMMEND
- Page 203 and 204:
.:•n-,,, LOT WRAP 2A.6 SHEET 9.XL
- Page 205 and 206:
LOT WRAP 2A.7 SHEET 10.XLS RECOMMEN
- Page 207 and 208:
PHYSICAL DESCR/PTTON: V-r-S?-W100-T
- Page 209 and 210:
,.: Westinoause Harlford COMM WHC-S
- Page 211 and 212:
O I tA SHEETII.XLS ;, LOT WRAP2A.2
- Page 213 and 214:
CONTAINER /NFORMAT/ON: DOSE: SIZE:
- Page 215 and 216:
PU33-11-1992 09:48 FROM EDS/qRI$ir
- Page 217 and 218:
LOT WRAP 2A 10 Slf-EET 14.)C,S RECO
- Page 219 and 220:
qN i: 105N-89-1097 105N-89-1098 105
- Page 221 and 222:
SIZE: DOSE: 5 GAL 1 1@15 Mr 30 GAL
- Page 223 and 224:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Westtngho
- Page 225 and 226:
LOT WRAP A2.14 SHEET 18.XLS RECOMME
- Page 227 and 228:
---- - LOT WRAP ZA.13 SHEET 17.XLS
- Page 229 and 230:
n .-.^..-n..^^- .. ... .dJ. ^ ShIEE
- Page 231 and 232:
--^ WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 APPEN
- Page 233 and 234:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Westingho
- Page 235 and 236:
Table 1 Candidate Waste Forms Absor
- Page 237 and 238:
--- -Aauaspt and Pe-liroset WHC-SD-
- Page 239 and 240:
- '^ - qev. r' Literature Search WR
- Page 241 and 242:
Dow Polymer WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev.
- Page 243 and 244:
L im e Literature Search WRAP 2A Pa
- Page 245 and 246:
The report compares the 7eachabilit
- Page 247 and 248:
J. L. Westcott Page 2 May 29, 1992
- Page 249 and 250:
Package #1: Package #2: WHC-SD-W100
- Page 251 and 252:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 SURVEY OF
- Page 253 and 254:
f ..;' WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 A
- Page 255 and 256:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 SURVEY OF
- Page 257 and 258:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 commercia
- Page 259 and 260:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Revo 0 Bibliogra
- Page 261 and 262:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 A. P. Tos
- Page 263 and 264:
OAK R1DGE NATIONAL LABORATORY OPERA
- Page 265 and 266:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 SURVEY OF
- Page 267 and 268:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 commercia
- Page 269 and 270:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Revo 0 A report
- Page 271 and 272:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 impermeab
- Page 273 and 274:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 reprocess
- Page 275 and 276:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 STR?.THGI
- Page 277 and 278:
Contained under four reports: WHC-S
- Page 279 and 280:
^.yo F-SD-W"00-7-003 Rev. 0 THERMOS
- Page 281 and 282:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 The techn
- Page 283 and 284:
loomi^^lC& 111111111111F .^^.\ West
- Page 285 and 286:
^u9^c ?fi. ...^ .._-, WHC-SD-W100-T
- Page 287 and 288:
Stock Equipment Company WHC-SD-WI00
- Page 289 and 290:
^ i w STOCK EOUIPMENT COMPANY 14-OC
- Page 291 and 292:
\. . 1 .: lh,lf^ LEACH / IMMERSIONI
- Page 293 and 294:
^;- v.4'? Sampls ID L781 Elsment CO
- Page 295 and 296:
4.a
- Page 297 and 298:
Sanp)a ID L781 Elamant STRONTIUM Ma
- Page 299 and 300:
.^ "-; SampI81D L3B2 Z e"- ^.;;. Sa
- Page 301 and 302:
Sample 10 L3B1 Elsmant CESIUM Matri
- Page 303 and 304:
Sample ID W B1 Elemant STRONIIUM Ma
- Page 305 and 306:
Westinghouse Hanford Company 2355 S
- Page 307 and 308:
--- - ftCR-e4Uip1P1eFf Company WHC-
- Page 309 and 310:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 Russ Czel
- Page 311 and 312:
Stock Equipment Company 3:0 -SCFIED
- Page 313 and 314:
THERMAL CYCLING SAMPLES BEFORE THE
- Page 315 and 316:
BIODEGRADATION SAMPLES BEFORE THE S
- Page 317 and 318:
C/ 0D OC M1 0, ^yII i..) d tl ^ a I
- Page 319 and 320:
T 1 A w ^ • $ ^py yf ; pp V ^ py
- Page 321 and 322:
T 1 A ^ !^^ + ^ i •^^w^:rwwwwrpR^
- Page 323 and 324:
'i A v lf^. j^^ u e e - - I I I a i
- Page 325 and 326:
0 > d C.) O O F- 0 0 3 G NI U 3 ^ c
- Page 327 and 328:
en a-. p g aQ i ^ rr it - l r rF e^
- Page 329 and 330:
' iO`F*'P\^ Westinghouse Hanford Co
- Page 331 and 332:
Stock Equipment Company 1.0 SUMMARY
- Page 333 and 334:
Stock Equipment Company WHC-SD-W100
- Page 335 and 336:
2a0 SCHEDULE Activitv - Prepare Wor
- Page 337 and 338:
T 1 o+ THERMAL CYCLWG SAMPLES BEFOR
- Page 339 and 340:
T 1 OI 80 70 U 60 VJ w 50 w 0 40 30
- Page 341 and 342:
^ °' cn l .:. U CD w a: w r' i ^ I
- Page 343 and 344:
SAMPLE ID Li-117 L1-118 L1-19 L3-17
- Page 345 and 346:
T °,w ^ - : C s 0 n a ^^ s ^ i ^-
- Page 347 and 348:
71 I V y,,} ^ • 5il i ^ ^^ ^ ^ ^
- Page 349 and 350:
0 a^ on O O M F- 1OCD 3 1 G N^ U il
- Page 351 and 352:
O > W C f.) O O 1-- ^ O HI 6./ 3 ^
- Page 353 and 354:
0 > ar oe M 0 c C3, I O c V 3 ^I d
- Page 355 and 356:
TI V 40 IN s i s : s ^l l i " p p l
- Page 357 and 358:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 APPENDIX
- Page 359 and 360:
WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev. 0 _QVrDvrru
- Page 361 and 362:
^-_- .,:... WHC-SD-W100-TI-003 Rev.
- Page 363 and 364:
Ceramics and glass WHC-SD-W200-TI-0
- Page 365 and 366:
,. ., Extruder/melter WHC-SD-W100-T