You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
5-2 Cómo usar la intersección (págs. 303–308)<br />
TEKS A.2.C, A.3.A, A.4.A, A.5.C, A.6.B, A.6.E<br />
EJEMPLO<br />
■ Halla las intersecciones con el eje x y con el eje y<br />
de 2x + 5y = 10.<br />
Sea y = 0. Sea x = 0.<br />
2x + 5 (0) = 10 2 (0)+ 5y = 10<br />
2x + 0 = 10 0 + 5y = 10<br />
2x = 10 5y = 10<br />
_ 2x<br />
2 = _ 10<br />
2<br />
5y _<br />
5<br />
= 10 _<br />
5<br />
x= 5 y = 2<br />
La intersección con La intersección con<br />
el eje x es 5. el eje y es 2.<br />
EJERCICIOS<br />
Halla las intersecciones con el eje x y con el eje y.<br />
13.<br />
<br />
<br />
14. <br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
15. 3x - y = 9 16. -2x + y = 1<br />
17. -x + 6y = 18 18. 3x - 4y = 1<br />
<br />
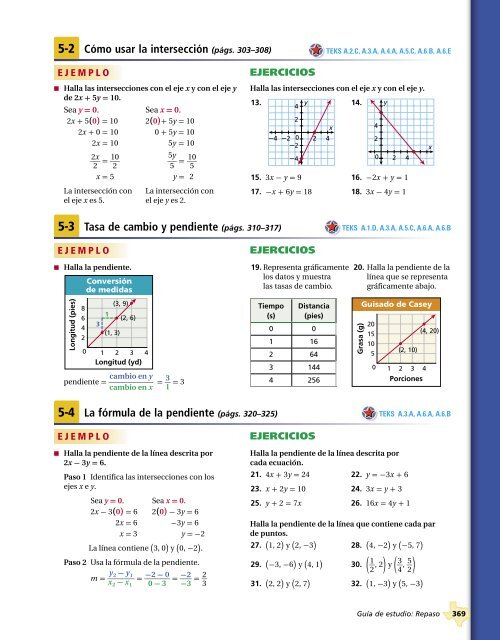
5-3 Tasa de cambio y pendiente (págs. 310–317)<br />
TEKS A.1.D, A.3.A, A.5.C, A.6.A, A.6.B<br />
EJEMPLO<br />
■ Halla la pendiente.<br />
Longitud (pies)<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
Conversión<br />
de medidas<br />
3<br />
1<br />
(1, 3)<br />
(3, 9)<br />
(2, 6)<br />
1 2 3 4<br />
Longitud (yd)<br />
cambio en y<br />
pendiente = __<br />
cambio en x = _ 3 1 = 3<br />
EJERCICIOS<br />
19. Representa gráficamente 20. Halla la pendiente de la<br />
los datos y muestra<br />
línea que se representa<br />
las tasas de cambio. gráficamente abajo.<br />
Tiempo<br />
(s)<br />
Distancia<br />
(pies)<br />
0 0<br />
1 16<br />
2 64<br />
3 144<br />
4 256<br />
Grasa (g)<br />
Guisado de Casey<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
(2, 10)<br />
1 2 3 4<br />
Porciones<br />
(4, 20)<br />
5-4 La fórmula de la pendiente (págs. 320–325)<br />
TEKS A.3.A, A.6.A, A.6.B<br />
EJEMPLO<br />
■ Halla la pendiente de la línea descrita por<br />
2x - 3y = 6.<br />
Paso 1 Identifica las intersecciones con los<br />
ejes x e y.<br />
Sea y = 0. Sea x = 0.<br />
2x - 3 (0) = 6 2 (0) - 3y = 6<br />
2x = 6 -3y = 6<br />
x = 3 y =-2<br />
La línea contiene (3, 0) y (0, -2) .<br />
Paso 2 Usa la fórmula de la pendiente.<br />
m = _ y 2 - y 1<br />
x2 - x<br />
= _ -2 - 0<br />
1 0 - 3 = _ -2<br />
-3 = _ 2 3<br />
EJERCICIOS<br />
Halla la pendiente de la línea descrita por<br />
cada ecuación.<br />
21. 4x + 3y = 24 22. y =-3x + 6<br />
23. x + 2y = 10 24. 3x = y + 3<br />
25. y + 2 = 7x 26. 16x = 4y + 1<br />
Halla la pendiente de la línea que contiene cada par<br />
de puntos.<br />
27. (1, 2) y (2, -3) 28. (4, -2) y (-5, 7)<br />
29. (-3, -6) y (4, 1) 30. (<br />
1_<br />
2 , 2 ) y _<br />
( 3 ,<br />
5_<br />
4 2)<br />
31. (2, 2) y (2, 7) 32. (1, -3) y (5, -3)<br />
Guía de estudio: Repaso 369