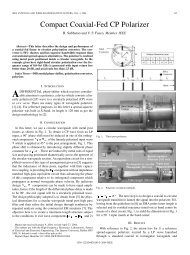
PPKE ITK PhD and MPhil Thesis Classes
PPKE ITK PhD and MPhil Thesis Classes
PPKE ITK PhD and MPhil Thesis Classes
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
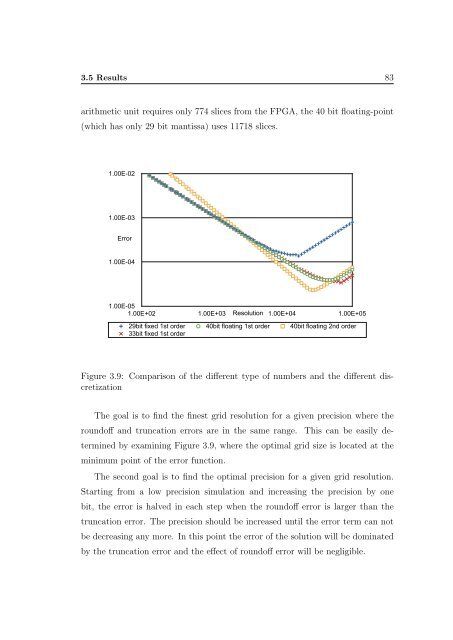
3.5 Results 83<br />
arithmetic unit requires only 774 slices from the FPGA, the 40 bit floating-point<br />
(which has only 29 bit mantissa) uses 11718 slices.<br />
1.00E-02<br />
1.00E-03<br />
Error<br />
1.00E-04<br />
1.00E-05<br />
1.00E+02 1.00E+03 Resolution 1.00E+04 1.00E+05<br />
29bit fixed 1st order 40bit floating 1st order 40bit floating 2nd order<br />
33bit fixed 1st order<br />
Figure 3.9: Comparison of the different type of numbers <strong>and</strong> the different discretization<br />
The goal is to find the finest grid resolution for a given precision where the<br />
roundoff <strong>and</strong> truncation errors are in the same range. This can be easily determined<br />
by examining Figure 3.9, where the optimal grid size is located at the<br />
minimum point of the error function.<br />
The second goal is to find the optimal precision for a given grid resolution.<br />
Starting from a low precision simulation <strong>and</strong> increasing the precision by one<br />
bit, the error is halved in each step when the roundoff error is larger than the<br />
truncation error. The precision should be increased until the error term can not<br />
be decreasing any more. In this point the error of the solution will be dominated<br />
by the truncation error <strong>and</strong> the effect of roundoff error will be negligible.





![optika tervezés [Kompatibilitási mód] - Ez itt...](https://img.yumpu.com/45881475/1/190x146/optika-tervezacs-kompatibilitasi-mad-ez-itt.jpg?quality=85)