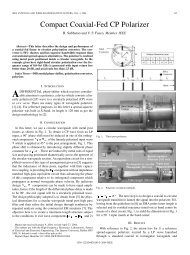
PPKE ITK PhD and MPhil Thesis Classes
PPKE ITK PhD and MPhil Thesis Classes
PPKE ITK PhD and MPhil Thesis Classes
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4 1. INTRODUCTION<br />
1.1 Cellular Neural/Nonlinear Network<br />
The basic building blocks of the Cellular Neural Networks, which was published in<br />
1988 by L. O. Chua <strong>and</strong> L. Yang [17], are the uniform structured analog processing<br />
elements, the cells. A st<strong>and</strong>ard CNN architecture consists of a rectangular 2Darray<br />
of cells as shown in Figure (1.1). With interconnection of many 2D arrays<br />
it can be extended to a 3-dimensional, multi-layer CNN structure. As it is in<br />
organic structures the simplest way to connect each cell is the connection of<br />
the local neighborhood via programmable weights. The weighted connections of<br />
a cell to its neighbors are called the cloning template. The CNN cell array is<br />
programmable by changing the cloning template. With the local connection of<br />
the cells difficult computational problems can be solved, like modeling biological<br />
structures [18] or the investigation of the systems which are based on partial<br />
differential equations [19].<br />
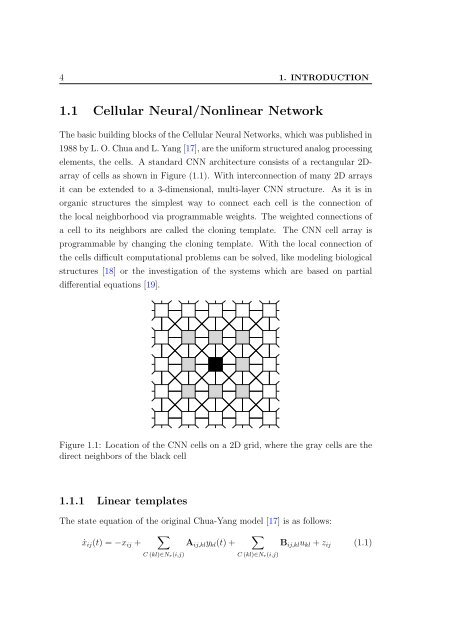
Figure 1.1: Location of the CNN cells on a 2D grid, where the gray cells are the<br />
direct neighbors of the black cell<br />
1.1.1 Linear templates<br />
The state equation of the original Chua-Yang model [17] is as follows:<br />
∑<br />
∑<br />
ẋ ij (t) = −x ij + A ij,kl y kl (t) + B ij,kl u kl + z ij (1.1)<br />
C (kl)∈N r(i,j)<br />
C (kl)∈N r(i,j)





![optika tervezés [Kompatibilitási mód] - Ez itt...](https://img.yumpu.com/45881475/1/190x146/optika-tervezacs-kompatibilitasi-mad-ez-itt.jpg?quality=85)