PPKE ITK PhD and MPhil Thesis Classes
PPKE ITK PhD and MPhil Thesis Classes
PPKE ITK PhD and MPhil Thesis Classes
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
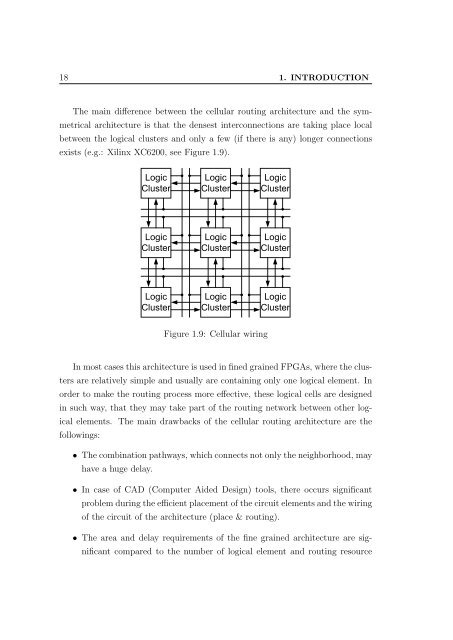
18 1. INTRODUCTION<br />
The main difference between the cellular routing architecture <strong>and</strong> the symmetrical<br />
architecture is that the densest interconnections are taking place local<br />
between the logical clusters <strong>and</strong> only a few (if there is any) longer connections<br />
exists (e.g.: Xilinx XC6200, see Figure 1.9).<br />
Figure 1.9: Cellular wiring<br />
In most cases this architecture is used in fined grained FPGAs, where the clusters<br />
are relatively simple <strong>and</strong> usually are containing only one logical element. In<br />
order to make the routing process more effective, these logical cells are designed<br />
in such way, that they may take part of the routing network between other logical<br />
elements. The main drawbacks of the cellular routing architecture are the<br />
followings:<br />
• The combination pathways, which connects not only the neighborhood, may<br />
have a huge delay.<br />
• In case of CAD (Computer Aided Design) tools, there occurs significant<br />
problem during the efficient placement of the circuit elements <strong>and</strong> the wiring<br />
of the circuit of the architecture (place & routing).<br />
• The area <strong>and</strong> delay requirements of the fine grained architecture are significant<br />
compared to the number of logical element <strong>and</strong> routing resource





![optika tervezés [Kompatibilitási mód] - Ez itt...](https://img.yumpu.com/45881475/1/190x146/optika-tervezacs-kompatibilitasi-mad-ez-itt.jpg?quality=85)