P461–464.Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Theme F686 - N1123The Effect of TiCN Coat<strong>in</strong>gs on Frictional Properties of Orthodontic Archwires11111Uengül DanmanUP P*, Soner SavaP P, Gülfem IkP P, Tancan UysalP Pand Ahmet YacP1PErciyes University, Kayseri-TurkeyAbstract-One of the ma<strong>in</strong> problems <strong>in</strong> the orthodontic treatment is the frictional forces on the archwires. The geometry of an archwire and thecoat<strong>in</strong>gs applied on archwires affect these forces. In this study, the archwires were coated with TiCN by us<strong>in</strong>g dc reactive magnetron sputter<strong>in</strong>gmethod. It was found that the coefficient of frictions of the TiCN coated archwires were much lower than those of uncoated archwires.Hard ceramic coat<strong>in</strong>gs deposited by PVD (Physical VapourDeposition) techniques have been widely used <strong>in</strong> different<strong>in</strong>dustries because of their excellent coat<strong>in</strong>g properties: highhardness, good wear, corrosion and oxidation resistance,chemical resistance and good adhesion to the substrate. Today,<strong>in</strong> the field of biomedical applications - such as surgical tools,implants, lenses, stents, and materials used <strong>in</strong> dentistry - Ti,TiN, ZrN, TiAlN, DLC, etc. are successfully used as s<strong>in</strong>gle ormultilayered or nanolayered coat<strong>in</strong>gs. These coat<strong>in</strong>gs alsohave good bio-conformity with the human body [1-6].The objective of this study was to shorten the activetreatment time <strong>in</strong> the orthodontic treatment by reduc<strong>in</strong>g thestatic and dynamic friction between the brackets andarchwires. It was clearly seen that the friction was affected notonly archwire geometry and materials but also surface qualityof archwires. Today, esthetic brackets are preferred to thetraditional ones and, therefore, frictional forces on archwiresare <strong>in</strong>creased. These forces affect the movement of thearchwire and extend the duration of the treatment. Therefore,low frictional coat<strong>in</strong>gs are very important for orthodonticarchwires.In this study, the archwires were coated with TiCN by us<strong>in</strong>gdc reactive magnetron sputter<strong>in</strong>g method with the optimumdeposition parameters. The dynamic and static frictionalforces and surface roughnesses of the TiCN-coated anduncoated archwires (NiTi, BTi (TMA) and sta<strong>in</strong>less steelarchwires, 0.017"x0.025" and Ø0.016" <strong>in</strong> dimensions) weremeasured. Then, the friction coefficients of TiCN coated anduncoated archwires were determ<strong>in</strong>ed by us<strong>in</strong>g CSEM testerunder the frictional forces (10 mm/m<strong>in</strong> progress speed and 10N load were used as test parameters) and the results werediscussed comparatively.The friction tests showed that TiCN coated archwires hadlower coefficient of friction values than those of uncoatedarchwires. The coefficient of frictions of the TiCN coated B-Ti, Ni-Ti archwires as shown <strong>in</strong> the Fig.1b were foundsuperior to the sta<strong>in</strong>less steel <strong>in</strong> spite of the roughness ofsta<strong>in</strong>less steel was lower than the others (Figure 1a). In theliterature it was not encountered that friction and roughnesswas def<strong>in</strong>itely related each other [1-7].These f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>gs <strong>in</strong>dicate that TiCN coated B-Ti archwireshowed lowest friction coefficient but these results are nearthe values of TiCN coated Ni-Ti archwires. The obta<strong>in</strong>edresults are <strong>in</strong> good agreement with the literature.Figure 1. a) RRaR surface roughness, b) coefficient of friction values ofthe coated and uncoated archwires of different geometry.This study was supported by the Office of Scientific ResearchProjects <strong>in</strong> Erciyes University (Project no: FBT-09853).*Correspond<strong>in</strong>g author: sdanisman@erciyes.edu.trT[1] TProbst, J., Gbureck, UT., Thull, R., 2001, Surface and Coat<strong>in</strong>gsTTechnology, 148, 226-233.[2] Vadraj, A., Kamaraj, M., 2007T, Tribology International, 40, 82-88.T[3] TPaschoal, A.L., Vanânco, E.C., Canale L.C.F., Slva, O.L.,Huerta-Vlca, D., Motheo A.J., 2003T, 27 (5), T[4] Kobayashi, S., Ohgoe, Y., Ozeki, K., Sato, KT., Sumya, T.,Hrakur, K.K., H. Aok, H., 2005, 14, 1094– 1097.T[5] Ohgoe, Y. et al., T2006, Th<strong>in</strong> Solid Films, 497, 218–222.[6] Redlich, M., Katz, A., Rapoport, L., T Wagner, H.D., Feldman Y.,Tenne RT., T2008,T TDental Materials, Article <strong>in</strong> Pres.T[7] Kusy, R.P., Whitley, J.Q., Mayhew, M.J., Buckthal, J.E., 1988,Angle Orthod., 58 (1), 33-45.6th Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Conference, zmir, 2010 743
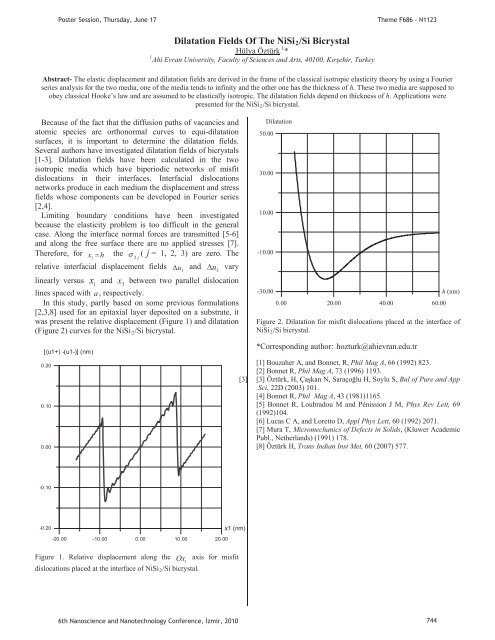
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17Theme F686 - N11231Dilatation Fields Of The NiSiR2R/Si Bicrystal1UHülya ÖztürkUP P*PAhi Evran University, Faculty of Sciences and Arts, 40100, Krehir, TurkeyAbstract- The elastic displacement and dilatation fields are derived <strong>in</strong> the frame of the classical isotropic elasticity theory by us<strong>in</strong>g a Fourierseries analysis for the two media, one of the media tends to <strong>in</strong>f<strong>in</strong>ity and the other one has the thickness of h. These two media are supposed toobey classical Hooke’s law and are assumed to be elastically isotropic. The dilatation fields depend on thickness of h. Applications werepresented for the NiSiR2R/Si bicrystal.Because of the fact that the diffusion paths of vacancies andatomic species are orthonormal curves to equi-dilatationsurfaces, it is important to determ<strong>in</strong>e the dilatation fields.Several authors have <strong>in</strong>vestigated dilatation fields of bi<strong>crystals</strong>[1-3]. Dilatation fields have been calculated <strong>in</strong> the twoisotropic media which have biperiodic networks of misfitdislocations <strong>in</strong> their <strong>in</strong>terfaces. Interfacial dislocationsnetworks produce <strong>in</strong> each medium the displacement and stressfields whose components can be developed <strong>in</strong> Fourier series[2,4].Limit<strong>in</strong>g boundary conditions have been <strong>in</strong>vestigatedbecause the elasticity problem is too difficult <strong>in</strong> the generalcase. Along the <strong>in</strong>terface normal forces are transmitted [5-6]and along the free surface there are no applied stresses [7].Therefore, for x 2h the 2 j( j = 1, 2, 3) are zero. Therelative <strong>in</strong>terfacial displacement fields u 1and u vary3l<strong>in</strong>early versus x and x between two parallel dislocation1 3l<strong>in</strong>es spaced with a , respectively.In this study, partly based on some previous formulations[2,3,8] used for an epitaxial layer deposited on a substrate, itwas present the relative displacement (Figure 1) and dilatation(Figure 2) curves for the NiSiR2R/Si bicrystal.-10.00Dilatation50.0030.0010.00-30.000.00 20. 00 40.00 60.00h (nm)Figure 2. Dilatation for misfit dislocations placed at the <strong>in</strong>terface ofNiSiR2R/Si bicrystal.[(u1+) -(u1-)] (nm)0.200.100.00*Correspond<strong>in</strong>g author: HThozturk@ahievran.edu.trTH[1] Bouzaher A, and Bonnet, R, Phil Mag A, 66 (1992) 823.[2] Bonnet R, Phil Mag A, 73 (1996) 1193.[3] [3] Öztürk, H, Çakan N, Saraçolu H, Soylu S, Bul of Pure and App.Sci, 22D (2003) 101.[4] Bonnet R, Phil Mag A, 43 (1981)1165.[5] Bonnet R, Loubradou M and Pénission J M, Phys Rev Lett, 69(1992)104.[6] Lucas C A, and Loretto D, Appl Phys Lett, 60 (1992) 2071.[7] Mura T, Micromechanics of Defects <strong>in</strong> Solids, (Kluwer AcademicPubl., Netherlands) (1991) 178.[8] Öztürk H, Trans Indian Inst Met, 60 (2007) 577.-0.10-0.20-20.00 -10.00 0.00 10.00 20.00x1 (nm)Figure 1. Relative displacement along the Ox axis for misfit1dislocations placed at the <strong>in</strong>terface of NiSiR2R/Si bicrystal.6th Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Conference, zmir, 2010 744
- Page 1:
Poster Presentations3rd Day17 June
- Page 4 and 5:
Determination of Dielectric Anisotr
- Page 7 and 8:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 9 and 10:
PP mPP vs.P =P,PP (1)P andPoster Se
- Page 11 and 12:
PP mPP vs.P =P,PP (1)P andPoster Se
- Page 13 and 14:
PP andPoster Session, Thursday, Jun
- Page 15 and 16:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 17 and 18:
PP and770 772 774 776 778 780 782 7
- Page 19 and 20:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 21 and 22:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 23 and 24:
P25,Poster Session, Thursday, June
- Page 25 and 26:
PP TOBBPoster Session, Thursday, Ju
- Page 27 and 28:
PisPPisisisP,PisPoster Session, Thu
- Page 29 and 30:
U NeslihanPPPPoster Session, Thursd
- Page 31 and 32:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 33 and 34:
PPPoster Session, Thursday, June 17
- Page 35 and 36:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 37 and 38:
P onP viaPP wereP upPoster Session,
- Page 39 and 40:
P ·cm.PVPPPsPPPPP andPoster Sessio
- Page 41 and 42:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 43 and 44:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 45 and 46:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 47 and 48:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 49 and 50:
PErkanPoster Session, Thursday, Jun
- Page 51 and 52:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 53 and 54:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 55 and 56:
PPPP andPoster Session, Thursday, J
- Page 57 and 58:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 59 and 60:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 61 and 62:
T PeptideTPP,PP,PP andTT2429TTTTTT
- Page 63 and 64:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 65 and 66:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 67 and 68:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 69 and 70:
PPPoster Session, Thursday, June 17
- Page 71 and 72:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 73 and 74:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 75 and 76:
PT AdditionalT ThePoster Session, T
- Page 77 and 78:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 79 and 80:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 81 and 82:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 83 and 84: PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 85 and 86: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 87 and 88: PPPoster Session, Thursday, June 17
- Page 89 and 90: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Hu
- Page 91 and 92: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 93 and 94: PPPPPPoster Session, Thursday, June
- Page 95 and 96: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 97 and 98: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 99 and 100: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 101 and 102: PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 103 and 104: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 105 and 106: PPPPPPPoster Session, Thursday, Jun
- Page 107 and 108: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 109 and 110: PPPR2R PIN(80)PPgPP OzlemPPoster Se
- Page 111 and 112: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 113 and 114: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 115 and 116: P onPP toP coordinatedPPoster Sessi
- Page 117 and 118: PPPPP,PP,P(PR RmPoster Session, Thu
- Page 119 and 120: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 121 and 122: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 123 and 124: PP InstitutePP DepartmentPoster Ses
- Page 125 and 126: andPCPPoster Session, Thursday, Jun
- Page 127 and 128: PP scatteringPYusufPP Corresponding
- Page 129 and 130: PP toPoster Session, Thursday, June
- Page 131 and 132: PP andPoster Session, Thursday, Jun
- Page 133: PPPPoster Session, Thursday, June 1
- Page 137 and 138: PPP andP (.cm).Poster Session, Thur
- Page 139 and 140: PP tiltP andP editionPoster Session
- Page 141 and 142: PP andPPoster Session, Thursday, Ju
- Page 143 and 144: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 145 and 146: PP forP forP edit.PPoster Session,
- Page 147 and 148: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 149 and 150: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 151 and 152: PP ionicPP ,PPoster Session, Thursd
- Page 153 and 154: PP lightPoster Session, Thursday, J
- Page 155 and 156: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 157 and 158: PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 159 and 160: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 161 and 162: PandPoster Session, Thursday, June
- Page 163 and 164: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17 T
- Page 165 and 166: PPPoster Session, Thursday, June 17
- Page 167 and 168: PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 169 and 170: PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 171 and 172: PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 173 and 174: PP DepartmentNanoscienceTPPoster Se
- Page 175 and 176: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 177 and 178: Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 179 and 180: PPPoster Session, Thursday, June 17
- Page 181 and 182: PPPPPoster Session, Thursday, June
- Page 183 and 184: PPPPoster Session, Thursday, June 1
- Page 185 and 186:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 187 and 188:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 189 and 190:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 191 and 192:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 193 and 194:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 195 and 196:
0T0T0T0T AsPPPP werePoster Session,
- Page 197 and 198:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 199 and 200:
PPPPPoster Session, Thursday, June
- Page 201 and 202:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 203 and 204:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 205 and 206:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Th
- Page 207 and 208:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 209 and 210:
PPoster Session, Thursday, June 17T
- Page 211:
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17AF