Photonic crystals in biology - NanoTR-VI
Photonic crystals in biology - NanoTR-VI
Photonic crystals in biology - NanoTR-VI
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
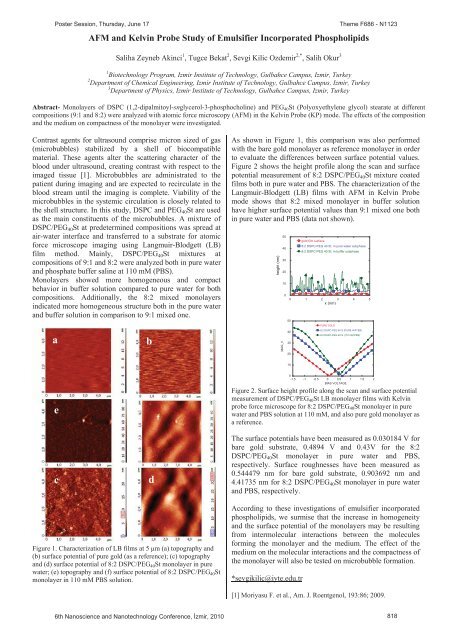
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17AFM and Kelv<strong>in</strong> Probe Study of Emulsifier Incorporated PhospholipidsSaliha Zeyneb Ak<strong>in</strong>ci 1 , Tugce Bekat 2 , Sevgi Kilic Ozdemir 2,* , Salih Okur 3Theme F686 - N11231 Biotechnology Program, Izmir Institute of Technology, Gulbahce Campus, Izmir, Turkey2 Department of Chemical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Izmir Institute of Technology, Gulbahce Campus, Izmir, Turkey3 Department of Physics, Izmir Institute of Technology, Gulbahce Campus, Izmir, TurkeyAbstract- Monolayers of DSPC (1,2-dipalmitoyl-snglycerol-3-phosphochol<strong>in</strong>e) and PEG 40 St (Polyoxyethylene glycol) stearate at differentcompositions (9:1 and 8:2) were analyzed with atomic force microscopy (AFM) <strong>in</strong> the Kelv<strong>in</strong> Probe (KP) mode. The effects of the compositionand the medium on compactness of the monolayer were <strong>in</strong>vestigated.Contrast agents for ultrasound comprise micron sized of gas(microbubbles) stabilized by a shell of biocompatiblematerial. These agents alter the scatter<strong>in</strong>g character of theblood under ultrasound, creat<strong>in</strong>g contrast with respect to theimaged tissue [1]. Microbubbles are adm<strong>in</strong>istrated to thepatient dur<strong>in</strong>g imag<strong>in</strong>g and are expected to recirculate <strong>in</strong> theblood stream until the imag<strong>in</strong>g is complete. Viability of themicrobubbles <strong>in</strong> the systemic circulation is closely related tothe shell structure. In this study, DSPC and PEG 40 St are usedas the ma<strong>in</strong> constituents of the microbubbles. A mixture ofDSPC/PEG 40 St at predeterm<strong>in</strong>ed compositions was spread atair-water <strong>in</strong>terface and transferred to a substrate for atomicforce microscope imag<strong>in</strong>g us<strong>in</strong>g Langmuir-Blodgett (LB)film method. Ma<strong>in</strong>ly, DSPC/PEG 40 St mixtures atcompositions of 9:1 and 8:2 were analyzed both <strong>in</strong> pure waterand phosphate buffer sal<strong>in</strong>e at 110 mM (PBS).Monolayers showed more homogeneous and compactbehavior <strong>in</strong> buffer solution compared to pure water for bothcompositions. Additionally, the 8:2 mixed monolayers<strong>in</strong>dicated more homogeneous structure both <strong>in</strong> the pure waterand buffer solution <strong>in</strong> comparison to 9:1 mixed one.As shown <strong>in</strong> Figure 1, this comparison was also performedwith the bare gold monolayer as reference monolayer <strong>in</strong> orderto evaluate the differences between surface potential values.Figure 2 shows the height profile along the scan and surfacepotential measurement of 8:2 DSPC/PEG 40 St mixture coatedfilms both <strong>in</strong> pure water and PBS. The characterization of theLangmuir-Blodgett (LB) films with AFM <strong>in</strong> Kelv<strong>in</strong> Probemode shows that 8:2 mixed monolayer <strong>in</strong> buffer solutionhave higher surface potential values than 9:1 mixed one both<strong>in</strong> pure water and PBS (data not shown).height (nm)5040302010050gold film surface8:2 DSPC-PEG 40 St. <strong>in</strong> pure water subphase8:2 DSPC-PEG 40 St. <strong>in</strong> buffer subphase0 1 2 3 4 5x (nm)PURE GOLDabMAG_V40308:2 DSPC-PEG 40 S (PURE WATER)8:2 DSPC-PEG 40 S (110 mM PBS)2010e0-1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2BIAS VOLTAGEFigure 2. Surface height profile along the scan and surface potentialmeasurement of DSPC/PEG 40 St LB monolayer films with Kelv<strong>in</strong>probe force microscope for 8:2 DSPC/PEG 40 St monolayer <strong>in</strong> purewater and PBS solution at 110 mM, and also pure gold monolayer asa reference.cdThe surface potentials have been measured as 0.030184 V forbare gold substrate, 0.4894 V and 0.43V for the 8:2DSPC/PEG 40 St monolayer <strong>in</strong> pure water and PBS,respectively. Surface roughnesses have been measured as0.544479 nm for bare gold substrate, 0.903692 nm and4.41735 nm for 8:2 DSPC/PEG 40 St monolayer <strong>in</strong> pure waterand PBS, respectively.Figure 1. Characterization of LB films at 5 m (a) topography and(b) surface potential of pure gold (as a reference); (c) topographyand (d) surface potential of 8:2 DSPC/PEG 40 St monolayer <strong>in</strong> purewater; (e) topography and (f) surface potential of 8:2 DSPC/PEG 40 Stmonolayer <strong>in</strong> 110 mM PBS solution.Accord<strong>in</strong>g to these <strong>in</strong>vestigations of emulsifier <strong>in</strong>corporatedphospholipids, we surmise that the <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> homogeneityand the surface potential of the monolayers may be result<strong>in</strong>gfrom <strong>in</strong>termolecular <strong>in</strong>teractions between the moleculesform<strong>in</strong>g the monolayer and the medium. The effect of themedium on the molecular <strong>in</strong>teractions and the compactness ofthe monolayer will also be tested on microbubble formation.*sevgikilic@iyte.edu.tr[1] Moriyasu F. et al., Am. J. Roentgenol, 193:86; 2009.6th Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Conference, zmir, 2010 818