Photonic crystals in biology - NanoTR-VI
Photonic crystals in biology - NanoTR-VI
Photonic crystals in biology - NanoTR-VI
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
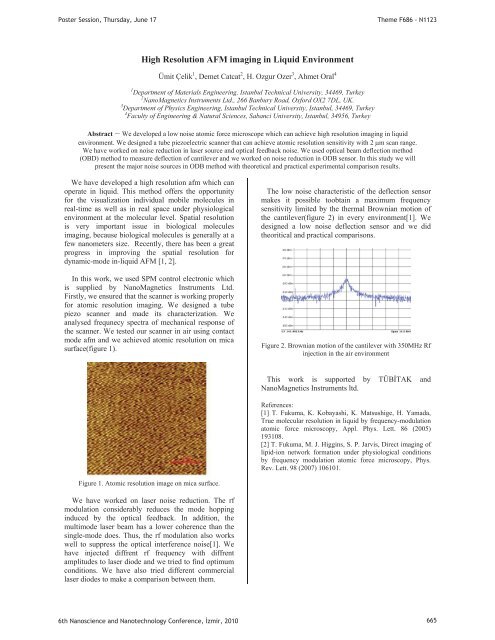
Poster Session, Thursday, June 17Theme F686 - N1123High Resolution AFM imag<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Liquid EnvironmentÜmit Çelik 1 , Demet Catcat 2 , H. Ozgur Ozer 3 , Ahmet Oral 41 Department of Materials Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Istanbul Technical University, 34469, Turkey2 NanoMagnetics Instruments Ltd., 266 Banbury Road, Oxford OX2 7DL, UK.3 Department of Physics Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul, 34469, Turkey4 Faculty of Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g & Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Istanbul, 34956, TurkeyAbstract – We developed a low noise atomic force microscope which can achieve high resolution imag<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> liquidenvironment. We designed a tube piezoelectric scanner that can achieve atomic resolution sensitivity with 2 m scan range.We have worked on noise reduction <strong>in</strong> laser source and optical feedback noise. We used optical beam deflection method(OBD) method to measure deflection of cantilever and we worked on noise reduction <strong>in</strong> ODB sensor. In this study we willpresent the major noise sources <strong>in</strong> ODB method with theoretical and practical experimental comparison results.We have developed a high resolution afm which canoperate <strong>in</strong> liquid. This method offers the opportunityfor the visualization <strong>in</strong>dividual mobile molecules <strong>in</strong>real-time as well as <strong>in</strong> real space under physiologicalenvironment at the molecular level. Spatial resolutionis very important issue <strong>in</strong> biological moleculesimag<strong>in</strong>g, because biological molecules is generally at afew nanometers size. Recently, there has been a greatprogress <strong>in</strong> improv<strong>in</strong>g the spatial resolution fordynamic-mode <strong>in</strong>-liquid AFM [1, 2].In this work, we used SPM control electronic whichis supplied by NanoMagnetics Instruments Ltd.Firstly, we ensured that the scanner is work<strong>in</strong>g properlyfor atomic resolution imag<strong>in</strong>g. We designed a tubepiezo scanner and made its characterization. Weanalysed frequnecy spectra of mechanical response ofthe scanner. We tested our scanner <strong>in</strong> air us<strong>in</strong>g contactmode afm and we achieved atomic resolution on micasurface(figure 1).The low noise characteristic of the deflection sensormakes it possible toobta<strong>in</strong> a maximum frequencysensitivity limited by the thermal Brownian motion ofthe cantilever(figure 2) <strong>in</strong> every environment[1]. Wedesigned a low noise deflection sensor and we didtheoritical and practical comparisons.Figure 2. Brownian motion of the cantilever with 350MHz Rf<strong>in</strong>jection <strong>in</strong> the air environmentThis work is supported by TÜBTAK andNanoMagnetics Instruments ltd.References:[1] T. Fukuma, K. Kobayashi, K. Matsushige, H. Yamada,True molecular resolution <strong>in</strong> liquid by frequency-modulationatomic force microscopy, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 (2005)193108.[2] T. Fukuma, M. J. Higg<strong>in</strong>s, S. P. Jarvis, Direct imag<strong>in</strong>g oflipid-ion network formation under physiological conditionsby frequency modulation atomic force microscopy, Phys.Rev. Lett. 98 (2007) 106101.Figure 1. Atomic resolution image on mica surface.We have worked on laser noise reduction. The rfmodulation considerably reduces the mode hopp<strong>in</strong>g<strong>in</strong>duced by the optical feedback. In addition, themultimode laser beam has a lower coherence than thes<strong>in</strong>gle-mode does. Thus, the rf modulation also workswell to suppress the optical <strong>in</strong>terference noise[1]. Wehave <strong>in</strong>jected diffrent rf frequency with diffrentamplitudes to laser diode and we tried to f<strong>in</strong>d optimumconditions. We have also tried different commerciallaser diodes to make a comparison between them.6th Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Conference, zmir, 2010 665