book1
book1
book1
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
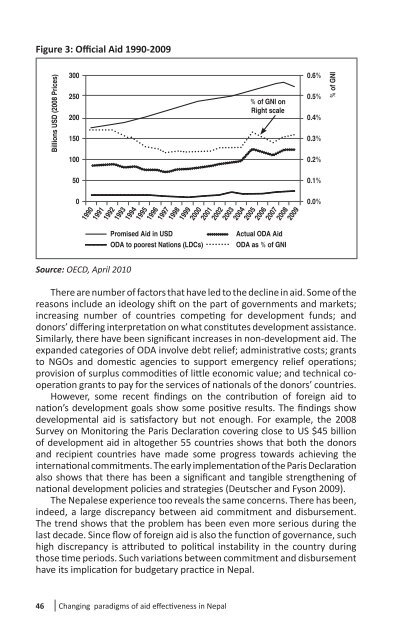
Figure 3: Offi cial Aid 1990-2009<br />
46<br />
Billions USD (2008 Prices)<br />
300<br />
250<br />
200<br />
1990<br />
1991<br />
1992<br />
1993<br />
1994<br />
1995<br />
1996<br />
1997<br />
1998<br />
1999<br />
2000<br />
2001<br />
2002<br />
2003<br />
2004<br />
2005<br />
2006<br />
2007<br />
2008<br />
2009<br />
150<br />
100<br />
50<br />
0<br />
Source: OECD, April 2010<br />
Promised Aid in USD Actual ODA Aid<br />
ODA to poorest Nations (LDCs) ODA as % of GNI<br />
Changing paradigms of aid eff ec� veness in Nepal<br />
% of GNI on<br />
Right scale<br />
There are number of factors that have led to the decline in aid. Some of the<br />
reasons include an ideology shi� on the part of governments and markets;<br />
increasing number of countries compe� ng for development funds; and<br />
donors’ diff ering interpreta� on on what cons� tutes development assistance.<br />
Similarly, there have been signifi cant increases in non-development aid. The<br />
expanded categories of ODA involve debt relief; administra� ve costs; grants<br />
to NGOs and domes� c agencies to support emergency relief opera� ons;<br />
provision of surplus commodi� es of li� le economic value; and technical coopera�<br />
on grants to pay for the services of na� onals of the donors’ countries.<br />
However, some recent fi ndings on the contribu� on of foreign aid to<br />
na� on’s development goals show some posi� ve results. The fi ndings show<br />
developmental aid is sa� sfactory but not enough. For example, the 2008<br />
Survey on Monitoring the Paris Declara� on covering close to US $45 billion<br />
of development aid in altogether 55 countries shows that both the donors<br />
and recipient countries have made some progress towards achieving the<br />
interna� onal commitments. The early implementa� on of the Paris Declara� on<br />
also shows that there has been a signifi cant and tangible strengthening of<br />
na� onal development policies and strategies (Deutscher and Fyson 2009).<br />
The Nepalese experience too reveals the same concerns. There has been,<br />
indeed, a large discrepancy between aid commitment and disbursement.<br />
The trend shows that the problem has been even more serious during the<br />
last decade. Since fl ow of foreign aid is also the func� on of governance, such<br />
high discrepancy is a� ributed to poli� cal instability in the country during<br />
those � me periods. Such varia� ons between commitment and disbursement<br />
have its implica� on for budgetary prac� ce in Nepal.<br />
0.6%<br />
0.5%<br />
0.4%<br />
0.3%<br />
0.2%<br />
0.1%<br />
0.0%<br />
% of GNI