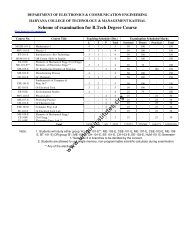
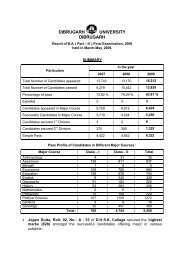
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4.1 Introduction<br />
Human resource activities are based on the propositions that highest goals can be achieved<br />
only by developing and maintaining a loyal, efficient group <strong>of</strong> employees, who believe in<br />
the company, who gain satisfaction from their work, and from whom extraordinary<br />
achievement is an individual ambition. In order to achieve these conditions a pr<strong>of</strong>essional<br />
would need a strong foundation on the variables like morale, motivation, compensation<br />
and Quality <strong>of</strong> Work Life, which are being elaborated upon in this unit. In the absence <strong>of</strong><br />
an amiable and cohesive human resource environment, an organization’s activities would<br />
see a gradual decline, even if the organization is provided all resources. Organizations that<br />
focus their energies on achieving reasonably satisfying levels <strong>of</strong> Human Resource<br />
Development indicators tend to be more stable and healthy.<br />
4.2 Principal compensation Issues and Management and Basic Concepts in<br />
Compensation<br />
The total <strong>of</strong> all rewards provided employees in return for their labor is called by the<br />
generic term “Compensation”. Monetary compensation includes both direct and indirect<br />
components. Direct compensation consists <strong>of</strong> the base wage and incentives. Job-based pay<br />
and competency-based pay are two methods <strong>of</strong> determining the base wage or salary.<br />
Indirect compensation includes benefits that are mandated by law and those that<br />
employers provide voluntarily. Social security, unemployment compensation, and<br />
workers’ compensation are benefits that employers provide. Allowances for house rent or<br />
to meet escalating cost <strong>of</strong> living, Insurance and vacation pay are commonly <strong>of</strong>fered<br />
benefits and perquisites that are not required by laws. Factors like minimum wage<br />
specified by legislation, the market rate for different qualifications, an organization’s<br />
ability to pay and the compensatory factors other than pay that an organization could <strong>of</strong>fer<br />
to its employees are some <strong>of</strong> the determinants <strong>of</strong> compensation levels.<br />
4.3 Wage and Salary<br />
Wage and Salary is together known as pay. While wage specifies the worth <strong>of</strong> the job,<br />
salary specifies the worth <strong>of</strong> the person. Salary is usually paid on a monthly basis while<br />
wage could be paid daily, weekly or fortnightly. Wage is usually associated with manual<br />
work and comes with provisions for overtime work, while the word salary is used to refer<br />
the remuneration for white-collar staff, pr<strong>of</strong>essionals and managers. Wages and salaries<br />
have also been used interchangeably. Both wage and salary help to achieve effective<br />
employee performance.<br />
Wage is the part <strong>of</strong> total production that is the return to labor as earned income as<br />
distinct from the remuneration received by capital as unearned income. Wage freeze