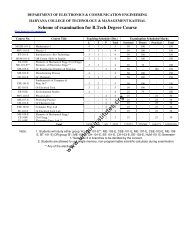
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
the odds are high because they get no achievement satisfaction from happenstance<br />
success. Similarly they dislike low odds which have high probability <strong>of</strong> success,<br />
because there would be no challenge to their skills.<br />
• Individuals <strong>of</strong> the second type, namely those with high need for power enjoy being<br />
“in-charge” and striving for influence over others. They tend to prefer to be<br />
competitive in status-oriented situations. Need for power may be further divided<br />
into institutional powers and personal powers. People seeking personal power like<br />
to inspire subordinates and expect the latter to respect than obey them. Other<br />
managers seeking institutional power tend to use authority, regulations and other<br />
such formal mechanisms and get things done in the interests <strong>of</strong> the organization.<br />
• Affiliation, the third need identified by McClelland is the desire to be liked and<br />
accepted by others. Individuals with high need for affiliation would constantly tend<br />
to strive for friendships, prefer cooperative situations rather than competitive ones<br />
and desire relationships involving a high degree <strong>of</strong> mutual sensitivity,<br />
understanding and appreciation.<br />
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory<br />
This is a process theory <strong>of</strong> motivation that helps managers to appreciate the complexities<br />
<strong>of</strong> motivation. Victor Vroom (1964) made an important contribution to managers’<br />
understanding <strong>of</strong> motivation through his Expectancy Theory, which is an alternative to the<br />
content theories. According to Vroom’s theory, individuals’ effort is based on their<br />
perceptions <strong>of</strong> certain factors in the work environment. They are termed as Expectancy,<br />
Instrumentality and Valence. The strength <strong>of</strong> the motivation to perform a certain act will<br />
depend on the combination <strong>of</strong> the three factors.<br />
Valence means attraction or repulsion <strong>of</strong> an outcome to an individual. In order for<br />
the valence to be positive, the person must prefer attaining the outcome to not attaining it.<br />
A valence <strong>of</strong> zero occurs when the individual is indifferent towards the outcome. The<br />
valence is negative when the individual prefers not attaining the outcome to attaining it.<br />
Expectancy is the expected relationship between effort and successful performance. It is<br />
the probability that a particular action or effort will lead to a particular first level outcome,<br />
such as production or quality. Instrumentality is the performance-reward linkage. It is the<br />
degree to which a first-level outcome will lead to a desired second-level outcome such as<br />
money, recognition, job security or career growth.