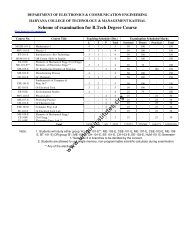
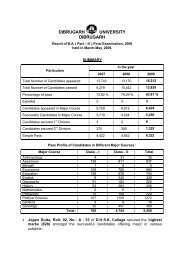
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ecoming) and self-fulfillment. Abraham Maslow surmised that until a person’s more<br />
basic needs are fulfilled, he or she will not strive to meet higher order needs. As each<br />
need is substantially satisfied, the next need becomes dominant. The needs when<br />
translated into an organizational context would mean wages, job-security, recognition,<br />
confidence and pride <strong>of</strong> excellence.<br />
Alderfer’s Existence, Relatedness and Growth Theory<br />
Clayton Alderfer through his ERG theory, reformulated Maslow’s theory by reducing the<br />
five level <strong>of</strong> needs into three namely Existence, Relatedness and Growth. Physiological<br />
and Security needs were combined under the label Existence, while love needs was<br />
renamed relatedness and self-esteem and self-actualization correspond to the growth<br />
needs. While the ERG theory accepted the usual movement from lower order to higher<br />
order needs, it also emphasizes the possibility <strong>of</strong> more than one need arising at a given<br />
time. Secondly, it states that if a higher order need is not satisfied, an employee may<br />
regress into the pursuit <strong>of</strong> lower order need.<br />
Alderfer suggested more <strong>of</strong> a continuum <strong>of</strong> needs than hierarchical levels <strong>of</strong> two<br />
factors <strong>of</strong> needs. Unlike Maslow and Herzberg, Alderfer did not contend that a lower level<br />
need has to be fulfilled before a higher-level need becomes motivating. According to the<br />
descriptions <strong>of</strong> the ERG theory, a person’s family background, upbringing or cultural<br />
atmosphere may dictate that the relatedness needs will take primacy over unfulfilled<br />
survival needs. Thus, there could be persons with genius qualities starving. Similarly in<br />
some cases the more the growth needs are satisfied, the more they will increase in<br />
intensity.<br />
Herzberg’s Two Factor Theory:<br />
Fredrick Herzberg and his associates’ recommendations are familiar to almost all<br />
managers. They had concluded in their prescriptive two-factor theory, also known as the<br />
motivation-hygiene theory that satisfaction and dissatisfaction with jobs occur because <strong>of</strong><br />
different set <strong>of</strong> factors. While dissatisfaction is caused if the hygiene factors such as pay,<br />
Job security, relationships with superior and peers, status, happiness in personal life,<br />
cordial relationships with peers and subordinates and physical working conditions are not<br />
possible or available in an adequate measure, but their mere presence would not be<br />
sufficient to motivate a person. Motivation at work occurs if another set <strong>of</strong> factors like<br />
recognition, challenging tasks, opportunity to use one’s talents and skills, demonstrate<br />
achievements, chances to learn and grow, are made possible or available to the employees.<br />
Herzberg’s theory has contributed to much <strong>of</strong> the enthusiasm towards job enrichment.