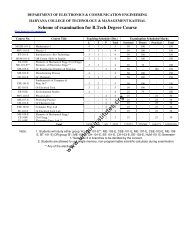
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Analyzing the conceptualizations <strong>of</strong> the main authors who investigated the theme,<br />
it is possible to identify three main groups that had developed common basic points in its<br />
statements <strong>of</strong> QWL. The common conceptions were:<br />
1. Emphasis on well-being and worker satisfaction, concomitant with the concern<br />
with the productivity increase, effectiveness and the organizational effectiveness<br />
2. Valuation <strong>of</strong> workers’ participation in decision taking process, at work and<br />
questions related to the reformulation <strong>of</strong> positions<br />
3. Emphasis on humanist perspective to think on the people, their work and the<br />
organization.<br />
QWL is also referred to as an important Organization Development (OD)<br />
intervention technique to be used along with other techniques like team building, process<br />
consultation and role analysis technique. QWL as an OD technique is designed to improve<br />
organizational functioning by helping to humanizing the workplace, making it more<br />
democratic and involving employees in making decisions affecting them. The conditions<br />
that contribute to motivation such as equitable salaries, activities such as job enrichment<br />
and job rotation would also contribute QWL. Thus, QWL clearly exhibits features that<br />
have also been associated with the very basic objectives <strong>of</strong> Human Resources<br />
Management, Employee Relations and Labor Welfare.<br />
Jurisdiction <strong>of</strong> QWL initiatives includes task-related issues, managementemployee<br />
communication, team working, work restructuring, redesigning <strong>of</strong> compensation<br />
and benefits, and workers’ active participation in management. The underlying importance<br />
<strong>of</strong> QWL <strong>of</strong> human capital, lies in the fact that most people who work for a living are<br />
spending a significant amount <strong>of</strong> their waking hours at the workplace executing the<br />
requirements, duties and functions <strong>of</strong> their job and that their satisfactions and<br />
dissatisfactions at workplace are carried over to the home as well. By improving the QWL,<br />
the workers feel better about themselves when they are working in a plant.<br />
In the middle phases <strong>of</strong> the QWL debate in the 1970s, the idea was put forth that<br />
greater individual control over work, through genuine participatory decision making,<br />
would have positive outcomes for employees and employers alike. By the early 1980s,<br />
such advocates <strong>of</strong> worker involvement and labor-management cooperation identified<br />
increased participation with workplace empowerment. In the past, management assumed<br />
an attitude <strong>of</strong> passivity when solving their subordinates’ problems. But when employees<br />
are encouraged to solve their own problems using the managers as resources, a sea change<br />
is at hand. On the employee side, the act <strong>of</strong> taking on power and responsibility is equally<br />
momentous”