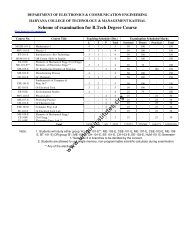
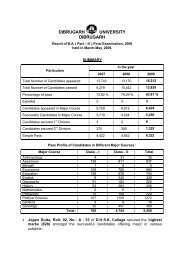
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
UNIT – I Lesson 1 HRM – AN OVERVIEW Lesson Outline Nature of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Peter Drucker (2002), the renowned Management Guru identified different types <strong>of</strong><br />
productivity such as plant productivity, material productivity, financial and capital<br />
productivity, machine productivity and human productivity. Human productivity is further<br />
classified as managerial and labor productivity. He has emphasized productivity through<br />
the following statement “A productivity measurement is the only yardstick that can<br />
actually gauge the competence <strong>of</strong> management and allow comparison between<br />
managements <strong>of</strong> different units within the enterprise, and <strong>of</strong> different enterprises”.<br />
Poor productivity is the result <strong>of</strong> several factors like lack <strong>of</strong> adequate planning,<br />
failure to be proactive in preparing for alternatives, incompetence, insufficient training,<br />
weak discipline, low standards and disharmonious relationship between employer<br />
employees. Other phenomena that could result in productivity problems include demotivation,<br />
lack <strong>of</strong> commitment towards job and organization, tolerance towards wasteful<br />
practices, bloated human power, nepotism, impeding bureaucracy, dysfunctional<br />
competition, conflicts and alienation among employees. Inadequate <strong>of</strong>fice support, lack <strong>of</strong><br />
proper equipments, shortages <strong>of</strong> supplies, excessive reporting requirements and<br />
unpredictable workloads are also common situational constraints.<br />
Productivity could also be affected by certain restrictive practices which might be<br />
in the form <strong>of</strong> outmoded, irrational or unreasonable rules or customs which unduly hinder<br />
the efficient use <strong>of</strong> labor. At times, work groups might seek to maintain traditional rights<br />
and prerogatives in the context <strong>of</strong> changed circumstances and technological advance.<br />
Some times, wage-productivity linkage might have to be examined for commensurability.<br />
Hence it might not be worthwhile for any manager to aim straightaway at productivity<br />
improvement without addressing these underlying impeding factors.<br />
Productivity in certain cases might also be impaired due to human causes. This<br />
might include pressures from coworkers to limit one’s performance in orders to check<br />
work targets from shooting up or prevent downsizing. Inadequate performance by<br />
coworkers could also affect a person’s productivity if the latter is an internal customer <strong>of</strong><br />
the former. There could be situational constraints due to colleagues in the form <strong>of</strong> turnover<br />
<strong>of</strong> key personnel and absenteeism. Elton Mayo, the father <strong>of</strong> Human Relations School <strong>of</strong><br />
management thought concluded that behavior and sentiments were closely related. He<br />
established that group influences significantly affected individual behavior, that groups’<br />
standards established individual worker’s output and that money was les a factor in<br />
determining output and productivity than aspects like group standards, group sentiments<br />
and groups’ security.