Financial systems and development
Financial systems and development
Financial systems and development
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
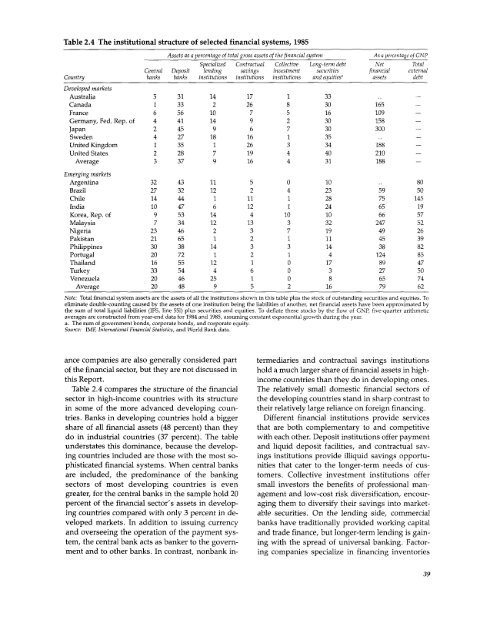
Table 2.4 The institutional structure of selected financial <strong>systems</strong>, 1985<br />
Assets as a percentage of total gross assets of the financial system<br />
As a percenztage of GNP<br />
Specialized Contractual Collective Long-term debt Net Total<br />
Central Deposit lending savings investment securities financial external<br />
Country banks banks institutions institutions institutionis <strong>and</strong> equities, assets debt<br />
Developed markets<br />
Australia 5 31 14 17 1 33<br />
Canada 1 33 2 26 8 30 165 -<br />
France 6 56 10 7 5 16 109 -<br />
Germany, Fed. Rep. of 4 41 14 9 2 30 158 -<br />
Japan 2 45 9 6 7 30 300 -<br />
Sweden 4 27 18 16 1 35<br />
United Kingdom 1 35 1 26 3 34 188<br />
United States 2 28 7 19 4 40 210<br />
Average 3 37 9 16 4 31 188 -<br />
Emerging markets<br />
Argentina 32 43 11 5 0 10 .. 80<br />
Brazil 27 32 12 2 4 23 59 50<br />
Chile 14 44 1 11 1 28 75 145<br />
India 10 47 6 12 1 24 65 19<br />
Korea, Rep. of 9 53 14 4 10 10 66 57<br />
Malaysia 7 34 12 13 3 32 247 52<br />
Nigeria 23 46 2 3 7 19 49 26<br />
Pakistan 21 65 1 2 1 11 45 39<br />
Philippines 30 38 14 3 3 14 38 82<br />
Portugal 20 72 1 2 1 4 124 85<br />
Thail<strong>and</strong> 16 55 12 1 0 17 89 47<br />
Turkey 33 54 4 6 0 3 27 50<br />
Venezuela 20 46 25 1 0 8 65 74<br />
Average 20 48 9 5 2 16 79 62<br />
Note: Total financial system assets are the assets of all the institutions shown in this table plus the stock of outst<strong>and</strong>ing securities <strong>and</strong> equities. To<br />
eliminate double-counting caused bv the assets of one institution being the liabilities of another, net financial assets have been approximated by<br />
the sum of total liquid liabilities (IFS, line 551) plus securities <strong>and</strong> equities. To deflate these stocks by the flow of GNP, five-quarter arithmetic<br />
averages are constructed from vear-end data for 1984 <strong>and</strong> 1985, assuming constant exponential growth during the year.<br />
a. The sum of government bonds, corporate bonds, <strong>and</strong> corporate equity.<br />
Source: IMF, International <strong>Financial</strong> Statistics, <strong>and</strong> World Bank data.<br />
ance companies are also generally considered part termediaries <strong>and</strong> contractual savings institutions<br />
of the financial sector, but they are not discussed in hold a much larger share of financial assets in highthis<br />
Report.<br />
income countries than they do in developing ones.<br />
Table 2.4 compares the structure of the financial The relatively small domestic financial sectors of<br />
sector in high-income countries with its structure the developing countries st<strong>and</strong> in sharp contrast to<br />
in some of the more advanced developing coun- their relatively large reliance on foreign financing.<br />
tries. Banks in developing countries hold a bigger Different financial institutions provide services<br />
share of all financial assets (48 percent) than they that are both complementary to <strong>and</strong> competitive<br />
do in industrial countries (37 percent). The table with each other. Deposit institutions offer payment<br />
understates this dominance, because the develop- <strong>and</strong> liquid deposit facilities, <strong>and</strong> contractual saving<br />
countries included are those with the most so- ings institutions provide illiquid savings opportuphisticated<br />
financial <strong>systems</strong>. When central banks nities that cater to the longer-term needs of cusare<br />
included, the predominance of the banking tomers. Collective investment institutions offer<br />
sectors of most developing countries is even small investors the benefits of professional mangreater,<br />
for the central banks in the sample hold 20 agement <strong>and</strong> low-cost risk diversification, encourpercent<br />
of the financial sector's assets in develop- aging them to diversify their savings into marketing<br />
countries compared with only 3 percent in de- able securities. On the lending side, commercial<br />
veloped markets. In addition to issuing currency banks have traditionally provided working capital<br />
<strong>and</strong> overseeing the operation of the payment sys- <strong>and</strong> trade finance, but longer-term lending is gaintem,<br />
the central bank acts as banker to the govern- ing with the spread of universal banking. Factorment<br />
<strong>and</strong> to other banks. In contrast, nonbank in- ing companies specialize in financing inventories<br />
39