Australian Government Architecture Reference Models Version 3.0
Australian Government Architecture Reference Models Version 3.0
Australian Government Architecture Reference Models Version 3.0
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
88<br />
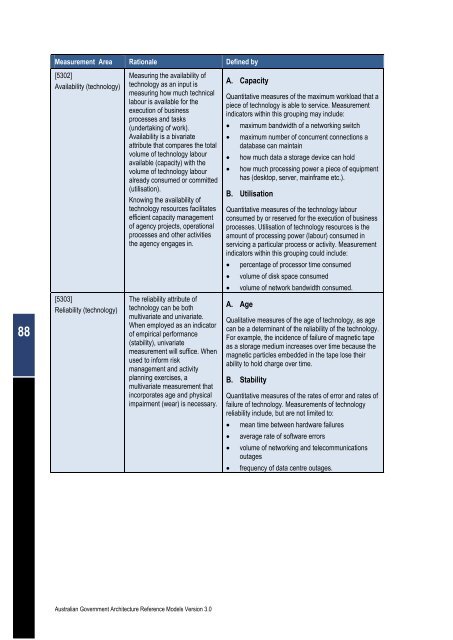
Measurement Area Rationale Defined by<br />
[5302]<br />
Availability (technology)<br />
[5303]<br />
Reliability (technology)<br />
Measuring the availability of<br />
technology as an input is<br />
measuring how much technical<br />
labour is available for the<br />
execution of business<br />
processes and tasks<br />
(undertaking of work).<br />
Availability is a bivariate<br />
attribute that compares the total<br />
volume of technology labour<br />
available (capacity) with the<br />
volume of technology labour<br />
already consumed or committed<br />
(utilisation).<br />
Knowing the availability of<br />
technology resources facilitates<br />
efficient capacity management<br />
of agency projects, operational<br />
processes and other activities<br />
the agency engages in.<br />
The reliability attribute of<br />
technology can be both<br />
multivariate and univariate.<br />
When employed as an indicator<br />
of empirical performance<br />
(stability), univariate<br />
measurement will suffice. When<br />
used to inform risk<br />
management and activity<br />
planning exercises, a<br />
multivariate measurement that<br />
incorporates age and physical<br />
impairment (wear) is necessary.<br />
<strong>Australian</strong> <strong>Government</strong> <strong>Architecture</strong> <strong>Reference</strong> <strong>Models</strong> <strong>Version</strong> <strong>3.0</strong><br />
A. Capacity<br />
Quantitative measures of the maximum workload that a<br />
piece of technology is able to service. Measurement<br />
indicators within this grouping may include:<br />
� maximum bandwidth of a networking switch<br />
� maximum number of concurrent connections a<br />
database can maintain<br />
� how much data a storage device can hold<br />
� how much processing power a piece of equipment<br />
has (desktop, server, mainframe etc.).<br />
B. Utilisation<br />
Quantitative measures of the technology labour<br />
consumed by or reserved for the execution of business<br />
processes. Utilisation of technology resources is the<br />
amount of processing power (labour) consumed in<br />
servicing a particular process or activity. Measurement<br />
indicators within this grouping could include:<br />
� percentage of processor time consumed<br />
� volume of disk space consumed<br />
� volume of network bandwidth consumed.<br />
A. Age<br />
Qualitative measures of the age of technology, as age<br />
can be a determinant of the reliability of the technology.<br />
For example, the incidence of failure of magnetic tape<br />
as a storage medium increases over time because the<br />
magnetic particles embedded in the tape lose their<br />
ability to hold charge over time.<br />
B. Stability<br />
Quantitative measures of the rates of error and rates of<br />
failure of technology. Measurements of technology<br />
reliability include, but are not limited to:<br />
� mean time between hardware failures<br />
� average rate of software errors<br />
� volume of networking and telecommunications<br />
outages<br />
� frequency of data centre outages.