198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Hydrogen-Bon<strong>de</strong>d Ribbons, Tapes and Sheets as Motifs for Crystal Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 123<br />
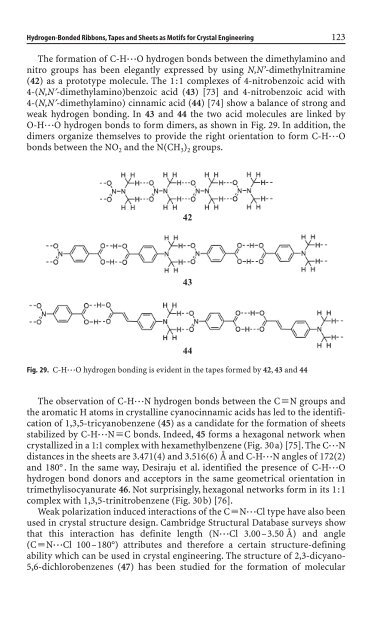
The formation of C-H◊◊◊O hydrogen bonds between the dimethylam<strong>in</strong>o and<br />
nitro groups has been elegantly expressed by us<strong>in</strong>g N,N’-dimethylnitram<strong>in</strong>e<br />
(42) as a prototype molecule. The 1:1 complexes of 4-nitrobenzoic acid with<br />
4-(N,N¢-dimethylam<strong>in</strong>o)benzoic acid (43) [73] and 4-nitrobenzoic acid with<br />
4-(N,N¢-dimethylam<strong>in</strong>o) c<strong>in</strong>namic acid (44) [74] show a balance of strong and<br />
weak hydrogen bond<strong>in</strong>g. In 43 and 44 the two acid molecules are l<strong>in</strong>ked by<br />
O-H◊◊◊O hydrogen bonds to form dimers, as shown <strong>in</strong> Fig. 29. In addition, the<br />
dimers organize themselves to provi<strong>de</strong> the right orientation to form C-H◊◊◊O<br />
bonds between the NO 2 and the N(CH 3) 2 groups.<br />
Fig. 29. C-H◊◊◊O hydrogen bond<strong>in</strong>g is evi<strong>de</strong>nt <strong>in</strong> the tapes formed by 42, 43 and 44<br />
42<br />
43<br />
44<br />
The observation of C-H◊◊◊N hydrogen bonds between the CN groups and<br />
the aromatic H atoms <strong>in</strong> crystall<strong>in</strong>e cyanoc<strong>in</strong>namic acids has led to the i<strong>de</strong>ntification<br />
of 1,3,5-tricyanobenzene (45) as a candidate for the formation of sheets<br />
stabilized by C-H◊◊◊NC bonds. In<strong>de</strong>ed, 45 forms a hexagonal network when<br />
crystallized <strong>in</strong> a 1:1 complex with hexamethylbenzene (Fig. 30a) [75]. The C◊◊◊N<br />
distances <strong>in</strong> the sheets are 3.471(4) and 3.516(6) Å and C-H◊◊◊N angles of 172(2)<br />
and 180° . In the same way, Desiraju et al. i<strong>de</strong>ntified the presence of C-H◊◊◊O<br />
hydrogen bond donors and acceptors <strong>in</strong> the same geometrical orientation <strong>in</strong><br />
trimethylisocyanurate 46. Not surpris<strong>in</strong>gly, hexagonal networks form <strong>in</strong> its 1:1<br />
complex with 1,3,5-tr<strong>in</strong>itrobenzene (Fig. 30b) [76].<br />
Weak polarization <strong>in</strong>duced <strong>in</strong>teractions of the CN◊◊◊Cl type have also been<br />
used <strong>in</strong> crystal structure <strong>de</strong>sign. Cambridge Structural Database surveys show<br />
that this <strong>in</strong>teraction has <strong>de</strong>f<strong>in</strong>ite length (N◊◊◊Cl 3.00–3.50 Å) and angle<br />
(CN◊◊◊Cl 100–180°) attributes and therefore a certa<strong>in</strong> structure-<strong>de</strong>f<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g<br />
ability which can be used <strong>in</strong> crystal eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g. The structure of 2,3-dicyano-<br />
5,6-dichlorobenzenes (47) has been studied for the formation of molecular