198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Supramolecular Synthons and Pattern Recognition 77<br />
bond<strong>in</strong>g -OH group <strong>in</strong> picric acid 45 is capable of disrupt<strong>in</strong>g the recognition<br />
motif 49 of dibenzyli<strong>de</strong>ne ketones with tr<strong>in</strong>itrobenzenes. There is thus a limit to<br />
synthon robustness and an appreciation of these limits is advantageous <strong>in</strong> the<br />
<strong>de</strong>sign of newer crystal structures with<strong>in</strong> the same family.<br />
Two recent examples illustrate the consequences of N-H◊◊◊O and C-H◊◊◊O<br />
hydrogen bonds co-exist<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> a crystal structure. MacGillivray and Atwood<br />
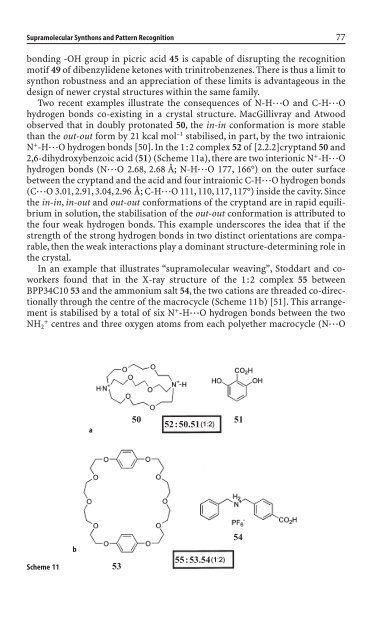
observed that <strong>in</strong> doubly protonated 50, the <strong>in</strong>-<strong>in</strong> conformation is more stable<br />
than the out-out form by 21 kcal mol –1 stabilised, <strong>in</strong> part, by the two <strong>in</strong>traionic<br />
N + -H◊◊◊O hydrogen bonds [50]. In the 1:2 complex 52 of [2.2.2]cryptand 50 and<br />
2,6-dihydroxybenzoic acid (51) (Scheme 11a), there are two <strong>in</strong>terionic N + -H◊◊◊O<br />
hydrogen bonds (N◊◊◊O 2.68, 2.68 Å; N-H◊◊◊O 177, 166°) on the outer surface<br />
between the cryptand and the acid and four <strong>in</strong>traionic C-H◊◊◊O hydrogen bonds<br />
(C◊◊◊O 3.01, 2.91, 3.04, 2.96 Å; C-H◊◊◊O 111, 110, 117, 117°) <strong>in</strong>si<strong>de</strong> the cavity. S<strong>in</strong>ce<br />
the <strong>in</strong>-<strong>in</strong>, <strong>in</strong>-out and out-out conformations of the cryptand are <strong>in</strong> rapid equilibrium<br />
<strong>in</strong> solution, the stabilisation of the out-out conformation is attributed to<br />
the four weak hydrogen bonds. This example un<strong>de</strong>rscores the i<strong>de</strong>a that if the<br />
strength of the strong hydrogen bonds <strong>in</strong> two dist<strong>in</strong>ct orientations are comparable,<br />
then the weak <strong>in</strong>teractions play a dom<strong>in</strong>ant structure-<strong>de</strong>term<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g role <strong>in</strong><br />
the crystal.<br />
In an example that illustrates “supramolecular weav<strong>in</strong>g”, Stoddart and coworkers<br />
found that <strong>in</strong> the X-ray structure of the 1:2 complex 55 between<br />
BPP34C10 53 and the ammonium salt 54, the two cations are threa<strong>de</strong>d co-directionally<br />
through the centre of the macrocycle (Scheme 11b) [51]. This arrangement<br />
is stabilised by a total of six N + -H◊◊◊O hydrogen bonds between the two<br />
NH 2 + centres and three oxygen atoms from each polyether macrocycle (N◊◊◊O<br />
b<br />
Scheme 11 53<br />
a<br />
50<br />
52:50.51<br />
55:53.54<br />
51<br />
54