198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
68 A. Nangia · G.R. Desiraju<br />
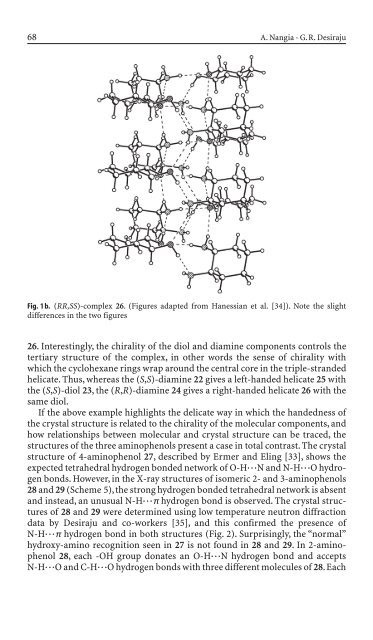
Fig. 1 b. (RR,SS)-complex 26. (Figures adapted from Hanessian et al. [34]). Note the slight<br />
differences <strong>in</strong> the two figures<br />
26. Interest<strong>in</strong>gly, the chirality of the diol and diam<strong>in</strong>e components controls the<br />
tertiary structure of the complex, <strong>in</strong> other words the sense of chirality with<br />
which the cyclohexane r<strong>in</strong>gs wrap around the central core <strong>in</strong> the triple-stran<strong>de</strong>d<br />
helicate. Thus, whereas the (S,S)-diam<strong>in</strong>e 22 gives a left-han<strong>de</strong>d helicate 25 with<br />
the (S,S)-diol 23, the (R,R)-diam<strong>in</strong>e 24 gives a right-han<strong>de</strong>d helicate 26 with the<br />
same diol.<br />
If the above example highlights the <strong>de</strong>licate way <strong>in</strong> which the han<strong>de</strong>dness of<br />
the crystal structure is related to the chirality of the molecular components, and<br />
how relationships between molecular and crystal structure can be traced, the<br />
structures of the three am<strong>in</strong>ophenols present a case <strong>in</strong> total contrast. The crystal<br />
structure of 4-am<strong>in</strong>ophenol 27, <strong>de</strong>scribed by Ermer and El<strong>in</strong>g [33], shows the<br />
expected tetrahedral hydrogen bon<strong>de</strong>d network of O-H◊◊◊N and N-H◊◊◊O hydrogen<br />
bonds. However, <strong>in</strong> the X-ray structures of isomeric 2- and 3-am<strong>in</strong>ophenols<br />
28 and 29 (Scheme 5),the strong hydrogen bon<strong>de</strong>d tetrahedral network is absent<br />
and <strong>in</strong>stead, an unusual N-H◊◊◊p hydrogen bond is observed. The crystal structures<br />
of 28 and 29 were <strong>de</strong>term<strong>in</strong>ed us<strong>in</strong>g low temperature neutron diffraction<br />
data by Desiraju and co-workers [35], and this confirmed the presence of<br />
N-H◊◊◊p hydrogen bond <strong>in</strong> both structures (Fig. 2). Surpris<strong>in</strong>gly, the “normal”<br />
hydroxy-am<strong>in</strong>o recognition seen <strong>in</strong> 27 is not found <strong>in</strong> 28 and 29. In 2-am<strong>in</strong>ophenol<br />
28, each -OH group donates an O-H◊◊◊N hydrogen bond and accepts<br />
N-H◊◊◊O and C-H◊◊◊O hydrogen bonds with three different molecules of 28.Each