198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Functional Organic Zeolite Analogues 135<br />
cular O-H◊◊◊O hydrogen bonds <strong>in</strong> place of C-C covalent bonds as <strong>in</strong> diamond.<br />
The result<strong>in</strong>g ice is necessarily a porous and hence low-<strong>de</strong>nsity material, although<br />
the parent diamond is the high-<strong>de</strong>nsity har<strong>de</strong>st solid even known. Much<br />
larger diamondoid lattices, e.g. 7 [31], 8 [32], 9 [33], 10 [34], 11 [35], 12 [36] and<br />
13 [37] (Fig. 1) are obta<strong>in</strong>ed by us<strong>in</strong>g tetrahedral organic and <strong>in</strong>organic components<br />
such as 4,4¢,4¢¢,4¢¢¢-tetrasubstituted methane and 1,3,5,7-tetrasubstituted<br />
adamantane <strong>de</strong>rivatives and Cu I and Ag I centres, respectively. Rod-like spacers<br />
or connectors can also be used. The result<strong>in</strong>g diamondoid huge cavities <strong>in</strong><br />
9 and 11 <strong>in</strong>corporate two molecules of well-or<strong>de</strong>red butyric acid and > 7.7 molecules<br />
of disor<strong>de</strong>red nitrobenzene and counter anion (BF 4 – ), respectively. Guest<br />
b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g does not occur <strong>in</strong> other cases, where two or more networks overlap <strong>in</strong><br />
such a way as to fill the cavities with each other. Such a self-<strong>in</strong>clusion can be prevented,<br />
however, by modify<strong>in</strong>g the build<strong>in</strong>g blocks so that <strong>in</strong>terpenetration or<br />
catenation of the networks becomes sterically less likely to occur [38, 39].<br />
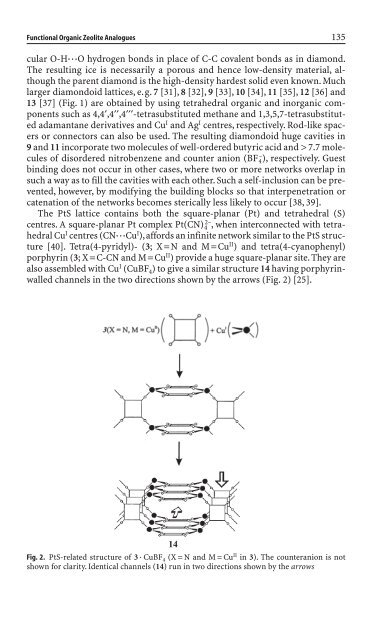
The PtS lattice conta<strong>in</strong>s both the square-planar (Pt) and tetrahedral (S)<br />
centres. A square-planar Pt complex Pt(CN) 4 2– , when <strong>in</strong>terconnected with tetrahedral<br />
Cu I centres (CN◊◊◊Cu I ),affords an <strong>in</strong>f<strong>in</strong>ite network similar to the PtS structure<br />
[40]. Tetra(4-pyridyl)- (3; X=N and M=Cu II ) and tetra(4-cyanophenyl)<br />
porphyr<strong>in</strong> (3; X=C-CN and M=Cu II ) provi<strong>de</strong> a huge square-planar site. They are<br />
also assembled with Cu I (CuBF 4) to give a similar structure 14 hav<strong>in</strong>g porphyr<strong>in</strong>walled<br />
channels <strong>in</strong> the two directions shown by the arrows (Fig. 2) [25].<br />
14<br />
Fig. 2. PtS-related structure of 3 ◊ CuBF 4 (X=N and M=Cu II <strong>in</strong> 3). The counteranion is not<br />
shown for clarity. I<strong>de</strong>ntical channels (14) run <strong>in</strong> two directions shown by the arrows