198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
198 Topics in Current Chemistry Editorial Board: A. de Meijere KN ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
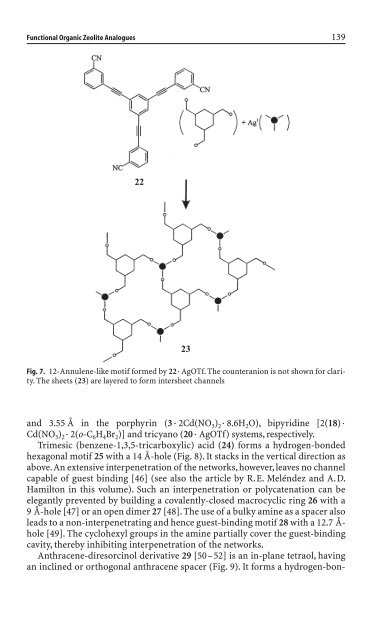
Functional Organic Zeolite Analogues 139<br />
22<br />
23<br />
Fig. 7. 12-Annulene-like motif formed by 22◊ AgOTf. The counteranion is not shown for clarity.<br />
The sheets (23) are layered to form <strong>in</strong>tersheet channels<br />
and 3.55 Å <strong>in</strong> the porphyr<strong>in</strong> (3 ◊ 2Cd(NO 3) 2◊ 8.6H 2O), bipyrid<strong>in</strong>e [2(18) ◊<br />
Cd(NO 3) 2◊ 2(o-C 6H 4Br 2)] and tricyano (20 ◊ AgOTf) systems, respectively.<br />
Trimesic (benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic) acid (24) forms a hydrogen-bon<strong>de</strong>d<br />
hexagonal motif 25 with a 14 Å-hole (Fig. 8). It stacks <strong>in</strong> the vertical direction as<br />
above.An extensive <strong>in</strong>terpenetration of the networks, however, leaves no channel<br />
capable of guest b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g [46] (see also the article by R.E. Melén<strong>de</strong>z and A.D.<br />
Hamilton <strong>in</strong> this volume). Such an <strong>in</strong>terpenetration or polycatenation can be<br />
elegantly prevented by build<strong>in</strong>g a covalently-closed macrocyclic r<strong>in</strong>g 26 with a<br />
9 Å-hole [47] or an open dimer 27 [48]. The use of a bulky am<strong>in</strong>e as a spacer also<br />
leads to a non-<strong>in</strong>terpenetrat<strong>in</strong>g and hence guest-b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g motif 28 with a 12.7 Åhole<br />
[49]. The cyclohexyl groups <strong>in</strong> the am<strong>in</strong>e partially cover the guest-b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g<br />
cavity, thereby <strong>in</strong>hibit<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>terpenetration of the networks.<br />
Anthracene-diresorc<strong>in</strong>ol <strong>de</strong>rivative 29 [50–52] is an <strong>in</strong>-plane tetraol, hav<strong>in</strong>g<br />
an <strong>in</strong>cl<strong>in</strong>ed or orthogonal anthracene spacer (Fig. 9). It forms a hydrogen-bon-