Dismounted Reconnaissance Troop - Army Electronic Publications ...
Dismounted Reconnaissance Troop - Army Electronic Publications ...
Dismounted Reconnaissance Troop - Army Electronic Publications ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
CASUALTY RESPONSE PERSONNEL<br />
Sustainment<br />
8-81. Casualty response consists of a variety of tiered medical and leadership response personnel for<br />
medical care and assistance.<br />
First Response<br />
8-82. First response is defined as the initial, essential, stabilizing medical care rendered to wounded,<br />
injured, or ill Soldiers at the point of initial injury or illness. The first responder is the first individual to<br />
reach a casualty and provide first aid, enhanced first aid, or emergency medical treatment. First aid can be<br />
performed by the casualty (self-aid) or another individual (buddy-aid), while enhanced first aid is provided<br />
by the CLS. The individual who has medical military occupational specialty training is the combat medic<br />
(trauma specialist). He provides emergency medical treatment for life threatening trauma and stabilizes and<br />
prioritizes (triages) wounded for evacuation to the SAS. At the SAS, wounded Soldiers receive advanced<br />
trauma medicine by the treatment team composed of the surgeon, physician’s assistant, and a senior trauma<br />
specialist.<br />
Combat Lifesaver<br />
8-83. The CLS is a nonmedical Soldier trained to provide advanced first aid/lifesaving procedures beyond<br />
the level of self-aid or buddy-aid. The CLS is not intended to take the place of medical personnel, but to<br />
slow deterioration of a wounded Soldier's condition until treatment by medical personnel is possible. Each<br />
certified CLS is issued a CLS aid bag. Whenever possible, the troop commander ensures there is at least<br />
one combat lifesaver in each fire team. An emerging “first responder” program expands CLS trauma<br />
treatment with increased emphasis on combat and away from training injuries.<br />
8-84. Combat lifesavers are section members trained in emergency medical techniques. They are the “911”<br />
medical assets for the section until a medic or another more qualified medical person becomes available.<br />
Because combat lifesaving is an organic capability, the platoon and troop should make it a training priority.<br />
The combat lifesaver ensures the section CLS bag is packed, all IVs are present, and litters are properly<br />
packed, and identifies Class VIII shortages to the platoon medic. He participates in all casualty treatment<br />
and litter carry drills. The combat lifesaver must know the location of the CCP and the TACSOP for<br />
establishing them. He has a laminated quick reference nine-line MEDEVAC card.<br />
Senior Trauma Specialist<br />
8-85. The senior trauma specialist (troop senior medic) is both the troop's primary medical treatment<br />
practitioner and the supervisor of all battlefield medical operations. The latter role encompasses numerous<br />
responsibilities. The senior trauma specialist works closely with the DRT commander to ensure all<br />
members of the troop understand what to do to provide and obtain medical treatment in combat situations.<br />
He oversees the training of combat lifesavers. Once combat begins, he manages the troop CCP, provides<br />
medical treatment, and prepares patients for MEDEVAC. He helps the 1SG arrange CASEVAC. The senior<br />
trauma specialist also monitors the paperwork that is part of the medical treatment and evacuation process,<br />
including:<br />
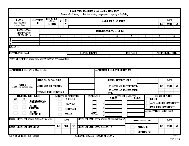
Ensuring that the casualty feeder report remains with each casualty until the Soldier reaches the<br />
squadron main aid station or field aid station.<br />
If a Soldier's remains cannot be recovered, completing DD Form 1380 (US Field Medical Card)<br />
and giving it to the 1SG for processing as soon as possible.<br />
Platoon Medic or Trauma Specialist<br />
8-86. Because platoon members commonly address their trauma specialist as “doc” or “medic,” shows his<br />
critical role in providing competent, life-saving care. During combat planning and preparation, he inspects<br />
platoon CLS bags, verifies that IVs are placed in litters, and fills Class VIII shortages. He recommends the<br />
location for the platoon CCPs and the TACSOP for establishing them. He rehearses casualty treatment and<br />
litter carries with all platoon members, not only aid and litter teams; and conducts CLS refresher training.<br />
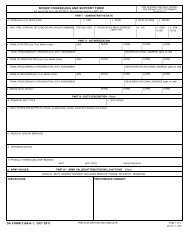
Designated medical personnel collect the DA Form 1156 (Casualty Feeder Card) at the aid station. They<br />
forward the form to the S1 section for further processing through administrative channels in the squadron<br />
field trains.<br />
16 November 2010 ATTP 3-20.97 8-15