Prospective crime mapping in operational context Final report
Prospective crime mapping in operational context Final report
Prospective crime mapping in operational context Final report
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
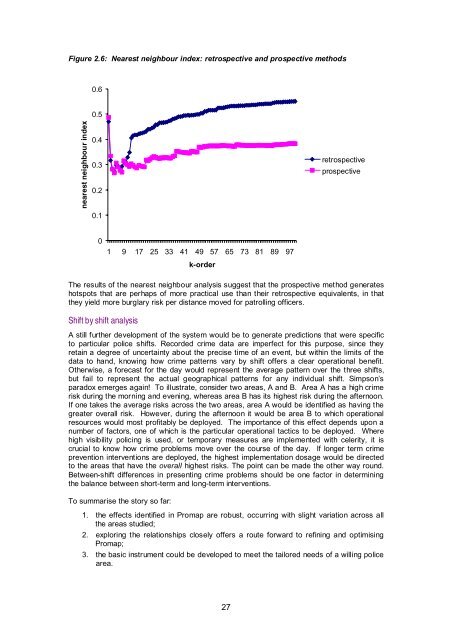
Figure 2.6: Nearest neighbour <strong>in</strong>dex: retrospective and prospective methods0.60.5nearest neighbour <strong>in</strong>dex0.40.30.20.1retrospectiveprospective01 9 17 25 33 41 49 57 65 73 81 89 97k-orderThe results of the nearest neighbour analysis suggest that the prospective method generateshotspots that are perhaps of more practical use than their retrospective equivalents, <strong>in</strong> thatthey yield more burglary risk per distance moved for patroll<strong>in</strong>g officers.Shift by shift analysisA still further development of the system would be to generate predictions that were specificto particular police shifts. Recorded <strong>crime</strong> data are imperfect for this purpose, s<strong>in</strong>ce theyreta<strong>in</strong> a degree of uncerta<strong>in</strong>ty about the precise time of an event, but with<strong>in</strong> the limits of thedata to hand, know<strong>in</strong>g how <strong>crime</strong> patterns vary by shift offers a clear <strong>operational</strong> benefit.Otherwise, a forecast for the day would represent the average pattern over the three shifts,but fail to represent the actual geographical patterns for any <strong>in</strong>dividual shift. Simpson’sparadox emerges aga<strong>in</strong>! To illustrate, consider two areas, A and B. Area A has a high <strong>crime</strong>risk dur<strong>in</strong>g the morn<strong>in</strong>g and even<strong>in</strong>g, whereas area B has its highest risk dur<strong>in</strong>g the afternoon.If one takes the average risks across the two areas, area A would be identified as hav<strong>in</strong>g thegreater overall risk. However, dur<strong>in</strong>g the afternoon it would be area B to which <strong>operational</strong>resources would most profitably be deployed. The importance of this effect depends upon anumber of factors, one of which is the particular <strong>operational</strong> tactics to be deployed. Wherehigh visibility polic<strong>in</strong>g is used, or temporary measures are implemented with celerity, it iscrucial to know how <strong>crime</strong> problems move over the course of the day. If longer term <strong>crime</strong>prevention <strong>in</strong>terventions are deployed, the highest implementation dosage would be directedto the areas that have the overall highest risks. The po<strong>in</strong>t can be made the other way round.Between-shift differences <strong>in</strong> present<strong>in</strong>g <strong>crime</strong> problems should be one factor <strong>in</strong> determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>gthe balance between short-term and long-term <strong>in</strong>terventions.To summarise the story so far:1. the effects identified <strong>in</strong> Promap are robust, occurr<strong>in</strong>g with slight variation across allthe areas studied;2. explor<strong>in</strong>g the relationships closely offers a route forward to ref<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and optimis<strong>in</strong>gPromap;3. the basic <strong>in</strong>strument could be developed to meet the tailored needs of a will<strong>in</strong>g policearea.27