- Page 3:
ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONSBAUB/CCBA
- Page 7 and 8:
TABLESTable 2.1 Financial analysis
- Page 9:
FIGURESFigure 1.1 Project cost spre
- Page 12 and 13:
Cohesion Fund, and through the leve
- Page 14 and 15:
or the plant will not reveal excess
- Page 17 and 18:
CHAPTER ONEPROJECT APPRAISAL IN THE
- Page 19 and 20:
Some specifications for financial t
- Page 21 and 22:
FOCUS: INFORMATION REQUIREDGeneral
- Page 23 and 24:
In particular, CBA results should p
- Page 25 and 26:
CHAPTER TWOAN AGENDA FOR THE PROJEC
- Page 27 and 28:
objectives, are, as far as possible
- Page 29 and 30: considered the appropriate shadow p
- Page 31 and 32: 2.3.2 Feasibility analysisFeasibili
- Page 34 and 35: This approach will be presented in
- Page 36 and 37: Current assets include:- receivable
- Page 38 and 39: The following items are usually not
- Page 40 and 41: Mainly, the examiner uses the FRR(C
- Page 42 and 43: The dynamics of the incoming flows
- Page 44 and 45: eturn on their own capital (Kp). Th
- Page 46 and 47: While the approach presented in thi
- Page 48 and 49: 2.5.1 Conversion of market to accou
- Page 50 and 51: Table 2.9 Electricity price dispers
- Page 52 and 53: 2.5.1.2 Fiscal correctionsSome item
- Page 54 and 55: previously estimated in projects wi
- Page 56 and 57: FOCUS: ENPV VS. FNPVThe difference
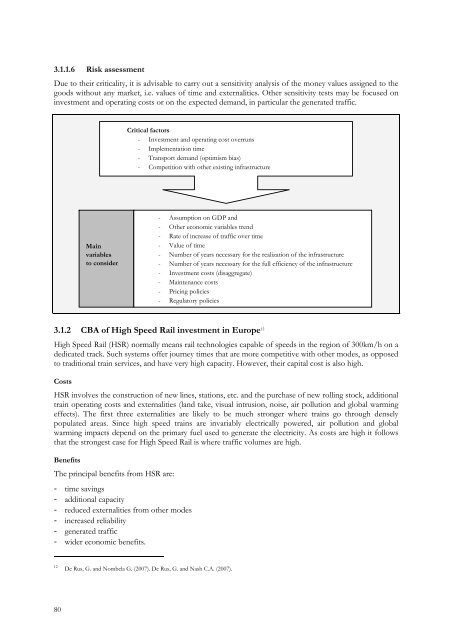
- Page 58 and 59: 2.6 Risk assessmentProject appraisa
- Page 60 and 61: Table 2.14 Impact analysis of criti
- Page 62 and 63: Figure 2.6 Probability distribution
- Page 64 and 65: eneficiary. The project proposer sh
- Page 66 and 67: There are many ways to design an MC
- Page 68 and 69: PROJECT APPRAISAL CHECK-LISTCONTEXT
- Page 70 and 71: - reduction of congestion by elimin
- Page 72 and 73: - the methods applied to estimate e
- Page 74 and 75: - the marginal external costs: cong
- Page 76 and 77: - the benefits for the existing tra
- Page 78 and 79: The following tables show some refe
- Page 82 and 83: As shown in Figure 3.1, only under
- Page 84 and 85: 3.1.3.7 Other project evaluation ap
- Page 87 and 88: - Waste Management Hierarchy rules
- Page 89 and 90: The time horizon for a project anal
- Page 91 and 92: 3.2.1.7 Other project evaluation ap
- Page 93 and 94: every user support the total costs
- Page 95 and 96: Territorial reference frameworkIf t
- Page 97 and 98: Cycle and phases of the projectGrea
- Page 99 and 100: One of the most important aims of t
- Page 101 and 102: projects, as in other sectors in wh
- Page 103 and 104: 3.2.3.2 Project identificationBasic
- Page 105 and 106: 3.2.3.7 Other project evaluation ap
- Page 107 and 108: In order to evaluate the overall im
- Page 109 and 110: for regassification plants, number
- Page 111 and 112: Examples of objectives are:- change
- Page 113 and 114: decontamination if any;- the techni
- Page 115 and 116: 3.3.3.6 Risk AnalysisCritical facto
- Page 117 and 118: 3.3.4.6 Risk assessmentCritical fac
- Page 119 and 120: 3.4.1.5 Economic analysisThe follow
- Page 121 and 122: Financial inflows• Admission fees
- Page 123 and 124: expectancy suitably adjusted by the
- Page 125 and 126: The time horizon for project analys
- Page 127 and 128: A Cost-Benefit Analysis should cons
- Page 129 and 130: CHAPTER FOURCASE STUDIESOverviewThi
- Page 131 and 132:
- finally, there is the traffic tha
- Page 134 and 135:
c) Road users producer’s surplus:
- Page 136 and 137:
4.1.5 Scenario analysisTwo scenario
- Page 138 and 139:
The financial performance indicator
- Page 140 and 141:
Table 4.10 Economic analysis (Milli
- Page 142 and 143:
Table 4.12 Financial return on capi
- Page 144 and 145:
4.2 Case Study: investment in a rai
- Page 146 and 147:
4.2.4 Economic analysisThe benefits
- Page 148 and 149:
Financial investment costs have bee
- Page 150 and 151:
Figure 4.6 Results of the risk anal
- Page 152 and 153:
Table 4.22 Economic analysis (Milli
- Page 154 and 155:
Table 4.24 Financial return on capi
- Page 156 and 157:
4.3 Case Study: investment in an in
- Page 158 and 159:
ate of 0.6% per year is assumed for
- Page 160 and 161:
The shadow price of the CO 2 avoide
- Page 162 and 163:
As a result, the probability distri
- Page 164 and 165:
Table 4.36 Financial return on capi
- Page 166 and 167:
16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
- Page 168 and 169:
4.4 Case Study: investment in a was
- Page 170 and 171:
4.4.2 Financial analysisAlthough in
- Page 172 and 173:
THE CALCULATION OF REVENUESReferrin
- Page 174 and 175:
0.15 m 3 /m 2 a depreciation of 20%
- Page 176 and 177:
As result, the probability distribu
- Page 178 and 179:
Figure 4.13 Probability distributio
- Page 180 and 181:
Table 4.48 Financial return on nati
- Page 182 and 183:
Table 4.50 Financial return on priv
- Page 184 and 185:
16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
- Page 186 and 187:
4.5 Case Study: industrial investme
- Page 188 and 189:
4.5.4.1 Investment costsThe total i
- Page 190 and 191:
Finally, a residual value was estim
- Page 192 and 193:
This analysis shows the need to pay
- Page 194 and 195:
Table 4.62 Financial return on inve
- Page 196 and 197:
Table 4.64 Return on private equity
- Page 198 and 199:
Table 4.66 Economic analysis (thous
- Page 200 and 201:
ANNEX ADEMAND ANALYSISDemand foreca
- Page 202 and 203:
The method applied for the forecast
- Page 204 and 205:
Furthermore, travel demand depends
- Page 206 and 207:
This Guide supports a unique refere
- Page 208 and 209:
A higher discount rate for countrie
- Page 210 and 211:
Figure C.1 Project ranking by NPV v
- Page 212 and 213:
The main problems with this indicat
- Page 214 and 215:
EXAMPLE OF SHADOW WAGE IN DUAL MARK
- Page 216 and 217:
Another exhaustive way to include d
- Page 218 and 219:
Figure E.2 Percentage of low income
- Page 220 and 221:
ANNEX FEVALUATION OF HEALTH &ENVIRO
- Page 222 and 223:
Figure F.1 Main evaluation methodsS
- Page 224 and 225:
- expenditure on capital equipment
- Page 226 and 227:
due to air pollution or water conta
- Page 228 and 229:
BENEFIT TRANSFER - SELECTED REFEREN
- Page 230 and 231:
ANNEX GEVALUATION OF PPP PROJECTSIt
- Page 232 and 233:
adjustments for Competitive Neutral
- Page 234 and 235:
ANNEX HRISK ASSESSMENTIn ex-ante pr
- Page 236 and 237:
Reference ForecastingThe question o
- Page 238 and 239:
Figure H.5 Levels of risks in diffe
- Page 240 and 241:
ANNEX IDETERMINATION OF THE EU GRAN
- Page 242 and 243:
A.4. Technological Alternatives and
- Page 244 and 245:
GLOSSARYAccounting period: the inte
- Page 246 and 247:
Market price: the price at which a
- Page 248 and 249:
BIBLIOGRAPHY1. ReferencesBelli, P.,
- Page 250 and 251:
Ray, A. 1984, Cost-benefit analysis
- Page 252 and 253:
EnvironmentGeneralAtkinson, G., 200
- Page 254 and 255:
European Commission, DG Tren, 2003,