- Page 1 and 2:
TMIC 9486Information Circular/2006H
- Page 3 and 4:
ORDERING INFORMATIONCopies of Natio
- Page 5 and 6:
ILLUSTRATIONS—ContinuedPage4-6. U
- Page 8:
HANDBOOK FOR METHANE CONTROL IN MIN
- Page 11 and 12:
4Below 5%, called the lower explosi
- Page 13 and 14:
6reduced pressure, except at very l
- Page 15 and 16:
8Static electricity. Protection aga
- Page 17 and 18:
10Figure 1-4.—Estimated methane c
- Page 19 and 20:
12LAYERING OF METHANE AT THE MINE R
- Page 21 and 22:
14good eyesight. 24methane level.Ot
- Page 23 and 24:
16a material balance indicated that
- Page 25 and 26:
18As an example, assume that themet
- Page 27 and 28:
20Figure 1-10.—Relative frequency
- Page 29 and 30:
22Davies AW, Isaac AK, Cook PM [200
- Page 31 and 32:
24Margerson SNA, Robinson H, Wilkin
- Page 33 and 34:
CHAPTER 2.—SAMPLING FOR METHANE I
- Page 35 and 36:
29USING PORTABLE METHANE DETECTORST
- Page 37 and 38:
Out-of-range gas concentrations in
- Page 39 and 40:
Figure 2-3.—Recorder chart from a
- Page 41 and 42:
35Industrial Scientific Corp. [2004
- Page 43 and 44:
38peaks, not the overallmethane lev
- Page 45 and 46:
40hung on J-hook assemblies, which
- Page 47 and 48:
42Methane dilution effectiveness.Th
- Page 49 and 50:
44found that effective scrubber ope
- Page 51 and 52:
46When the scrubber exhaust is not
- Page 53 and 54:
48Methane monitors are usually moun
- Page 55 and 56:
50to use radial bits instead of con
- Page 57 and 58:
52Mott ML, Chuhta EJ [1991]. Face v
- Page 59 and 60: 54Service, Centers for Disease Cont
- Page 61 and 62: 56Methane accumulationsaround thesh
- Page 63 and 64: 58corner and by 43% at supportNo. 4
- Page 65 and 66: 60When using water sprays to reduce
- Page 67 and 68: 62Cecala AB, Zimmer JA, Thimons ED
- Page 69 and 70: 64DESIGNING BLEEDER SYSTEMSAs part
- Page 71 and 72: 66Caved area characteristics. The c
- Page 73 and 74: 68then move this gas into the activ
- Page 75 and 76: 70perform tests to determine whethe
- Page 77 and 78: 72A major purpose of the bleeder sy
- Page 79 and 80: 74• Inlets to the pillared area n
- Page 81 and 82: 76REFERENCESCFR. Code of federal re
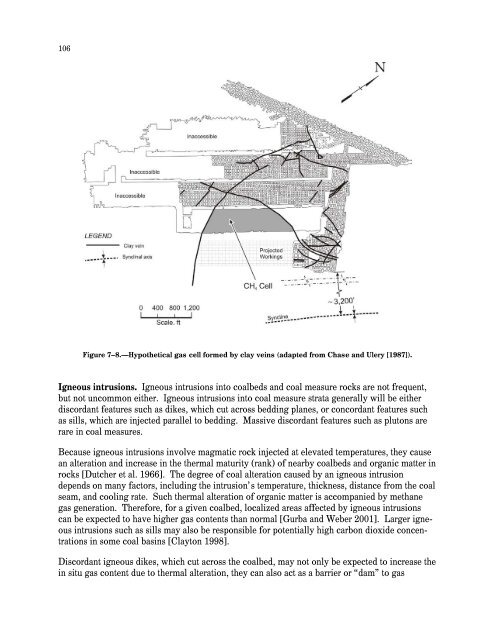
- Page 83 and 84: 78Methane is released into each min
- Page 85 and 86: 80Figure 6-1.—Gas content of coal
- Page 87 and 88: 82Figure 6-3.—Simplified illustra
- Page 89 and 90: 842. In-mine inclined or vertical b
- Page 91 and 92: 861. Packed cavity method and its v
- Page 93 and 94: 88Table 6-3.—Methane capture rati
- Page 95 and 96: 90Early experiences with this metho
- Page 97 and 98: 9211. At the surface installation (
- Page 99 and 100: 94• Estimated cost for moderately
- Page 101 and 102: 96Thakur PC [1981]. Methane control
- Page 103 and 104: 98Anomalous, unanticipated methane
- Page 105 and 106: 100Vertical methane drainage boreho
- Page 107 and 108: 102Figure 7-2 shows a mine entry ap
- Page 109: 104obvious solution to this problem
- Page 113 and 114: 108Lama and Bodziony [1998] compile
- Page 115 and 116: 110In-mine methane drainage systems
- Page 117 and 118: 112Iannacchione AT, Ulery JP, Hyman
- Page 119 and 120: 114More sophisticated reservoir eng
- Page 121 and 122: 116coal lithotype on gas content is
- Page 123 and 124: 118FORECASTING REMAINING GAS-IN-PLA
- Page 125 and 126: 120⎛ y⎞⎜⎛⎞ ⎛ ⎞= ⎜
- Page 127 and 128: 122emissions. The geometry and size
- Page 129 and 130: 124Reservoir models require a subst
- Page 131 and 132: 126King GR, Ertekin T [1989a]. A su
- Page 133 and 134: 128an area of 314 ft 2 would requir
- Page 135 and 136: 130In the case of the abovementione
- Page 137 and 138: 132FILLING SHAFTS AT CLOSED MINESFi
- Page 139 and 140: 134Hinderfeld G [1995]. Ventilation
- Page 141 and 142: 136To calculate the effectiveinert,
- Page 143 and 144: 138exhaust. The remaining diesel ex
- Page 145 and 146: 140required only 4 min. As a result
- Page 147 and 148: 142Figure 11-1.—Desorption test a
- Page 149 and 150: 144enclosed in a tunnel-like struct
- Page 151 and 152: 146Kolada RJ [1985]. Investigation
- Page 153 and 154: 148air in a 6-ft by 9-ft by 6.5-ft
- Page 155 and 156: 150represents flammable mixtures. F
- Page 157 and 158: 152• In Eastern Europe, petroleum
- Page 159 and 160: 154Category II applies to domal sal
- Page 161 and 162:
1562. Monitoring for gas and taking
- Page 163 and 164:
158These mines typically have large
- Page 165 and 166:
160Dave Graham is the safety and he
- Page 167 and 168:
162Figure 13-2.—Examples of metha
- Page 169 and 170:
164REFERENCESAndrews JN [1987]. Nob
- Page 171 and 172:
166APPENDIX A.—ONTARIO OCCUPATION
- Page 174 and 175:
169CHAPTER 14.—PREVENTING METHANE
- Page 176 and 177:
Ways to confirm the presence of gas
- Page 178 and 179:
173The tunnel face is usually venti
- Page 180 and 181:
175Figure 14-5.—TBM ventilation s
- Page 182 and 183:
face. While one of these elements a
- Page 184 and 185:
179ELIMINATING IGNITION SOURCESElec
- Page 186 and 187:
181INDEXAAbnormally gassy faces....
- Page 188 and 189:
183NNatural ventilation, coal silos
- Page 190 and 191:
Delivering on the Nation’s Promis