Handbook for Methane Control in Mining - AMMSA
Handbook for Methane Control in Mining - AMMSA
Handbook for Methane Control in Mining - AMMSA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
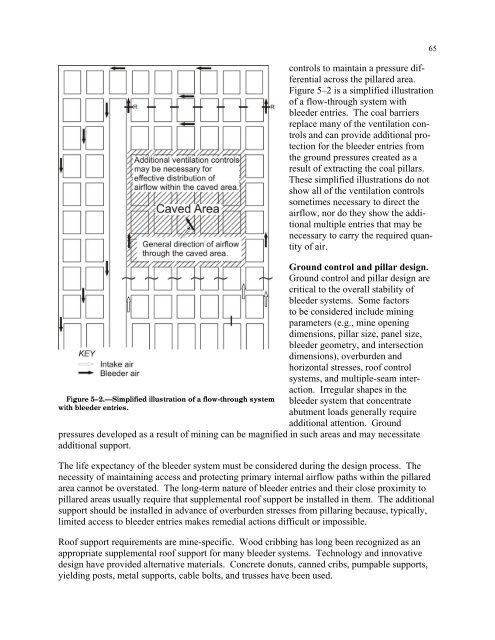
Figure 5–2.—Simplified illustration of a flow-through systemwith bleeder entries.65controls to ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> a pressure differentialacross the pillared area.Figure 5–2 is a simplified illustrationof a flow-through system withbleeder entries. The coal barriersreplace many of the ventilation controlsand can provide additional protection<strong>for</strong> the bleeder entries fromthe ground pressures created as aresult of extract<strong>in</strong>g the coal pillars.These simplified illustrations do notshow all of the ventilation controlssometimes necessary to direct theairflow, nor do they show the additionalmultiple entries that may benecessary to carry the required quantityof air.Ground control and pillar design.Ground control and pillar design arecritical to the overall stability ofbleeder systems. Some factorsto be considered <strong>in</strong>clude m<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>gparameters (e.g., m<strong>in</strong>e open<strong>in</strong>gdimensions, pillar size, panel size,bleeder geometry, and <strong>in</strong>tersectiondimensions), overburden andhorizontal stresses, roof controlsystems, and multiple-seam <strong>in</strong>teraction.Irregular shapes <strong>in</strong> thebleeder system that concentrateabutment loads generally requireadditional attention. Groundpressures developed as a result of m<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g can be magnified <strong>in</strong> such areas and may necessitateadditional support.The life expectancy of the bleeder system must be considered dur<strong>in</strong>g the design process. Thenecessity of ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g access and protect<strong>in</strong>g primary <strong>in</strong>ternal airflow paths with<strong>in</strong> the pillaredarea cannot be overstated. The long-term nature of bleeder entries and their close proximity topillared areas usually require that supplemental roof support be <strong>in</strong>stalled <strong>in</strong> them. The additionalsupport should be <strong>in</strong>stalled <strong>in</strong> advance of overburden stresses from pillar<strong>in</strong>g because, typically,limited access to bleeder entries makes remedial actions difficult or impossible.Roof support requirements are m<strong>in</strong>e-specific. Wood cribb<strong>in</strong>g has long been recognized as anappropriate supplemental roof support <strong>for</strong> many bleeder systems. Technology and <strong>in</strong>novativedesign have provided alternative materials. Concrete donuts, canned cribs, pumpable supports,yield<strong>in</strong>g posts, metal supports, cable bolts, and trusses have been used.