THESE UNIQUE El Hassane Kéhien-Piho TOU - Nutridev
THESE UNIQUE El Hassane Kéhien-Piho TOU - Nutridev
THESE UNIQUE El Hassane Kéhien-Piho TOU - Nutridev
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
54<br />
E.H. Tou et al. / International Journal of Food Microbiology 106 (2006) 52–60<br />
Consistency of gruels was measured with a Bostwick<br />
consistometer (Bookwalter et al., 1968), at 45 -C over a period<br />
of 30 s.<br />
3. Results<br />
3.1. Description of the traditional processing of pearl millet<br />
into ben-saalga<br />
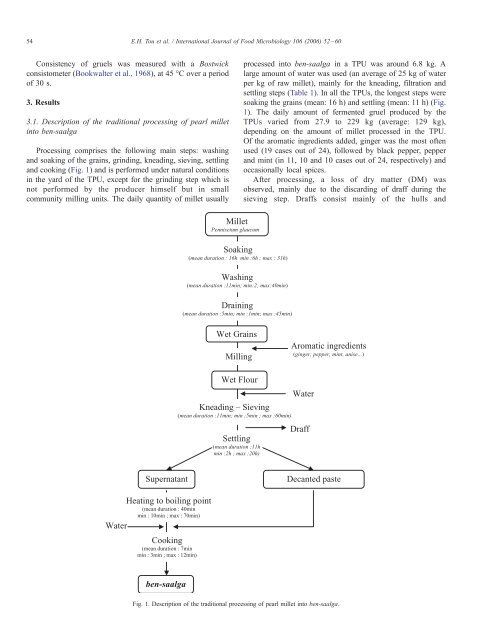
Processing comprises the following main steps: washing<br />
and soaking of the grains, grinding, kneading, sieving, settling<br />
and cooking (Fig. 1) and is performed under natural conditions<br />
in the yard of the TPU, except for the grinding step which is<br />
not performed by the producer himself but in small<br />
community milling units. The daily quantity of millet usually<br />
processed into ben-saalga in a TPU was around 6.8 kg. A<br />
large amount of water was used (an average of 25 kg of water<br />
per kg of raw millet), mainly for the kneading, filtration and<br />
settling steps (Table 1). In all the TPUs, the longest steps were<br />
soaking the grains (mean: 16 h) and settling (mean: 11 h) (Fig.<br />
1). The daily amount of fermented gruel produced by the<br />
TPUs varied from 27.9 to 229 kg (average: 129 kg),<br />
depending on the amount of millet processed in the TPU.<br />
Of the aromatic ingredients added, ginger was the most often<br />
used (19 cases out of 24), followed by black pepper, pepper<br />
and mint (in 11, 10 and 10 cases out of 24, respectively) and<br />
occasionally local spices.<br />
After processing, a loss of dry matter (DM) was<br />
observed, mainly due to the discarding of draff during the<br />
sieving step. Draffs consist mainly of the hulls and<br />
Millet<br />
Pennisetum glaucum<br />
Soaking<br />
(mean duration : 16h min :6h ; max : 31h)<br />
Washing<br />
(mean duration :11min; min:2; max:40min)<br />
Draining<br />
(mean duration :5min; min :1min; max :45min)<br />
Wet Grains<br />
Milling<br />
Aromatic ingredients<br />
(ginger, pepper, mint, anise...)<br />
Wet Flour<br />
Water<br />
Kneading – Sieving<br />
(mean duration :11min; min :5min ; max :60min)<br />
Settling<br />
(mean duration :11h<br />
min :2h ; max :20h)<br />
Draff<br />
Supernatant<br />
Decanted paste<br />
Heating to boiling point<br />
(mean duration : 40min<br />
min : 10min ; max : 70min)<br />
Water<br />
Cooking<br />
(mean duration : 7min<br />
min : 3min ; max : 12min)<br />
ben-saalga<br />
Fig. 1. Description of the traditional processing of pearl millet into ben-saalga.