THESE UNIQUE El Hassane Kéhien-Piho TOU - Nutridev
THESE UNIQUE El Hassane Kéhien-Piho TOU - Nutridev
THESE UNIQUE El Hassane Kéhien-Piho TOU - Nutridev
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Projet d’article<br />
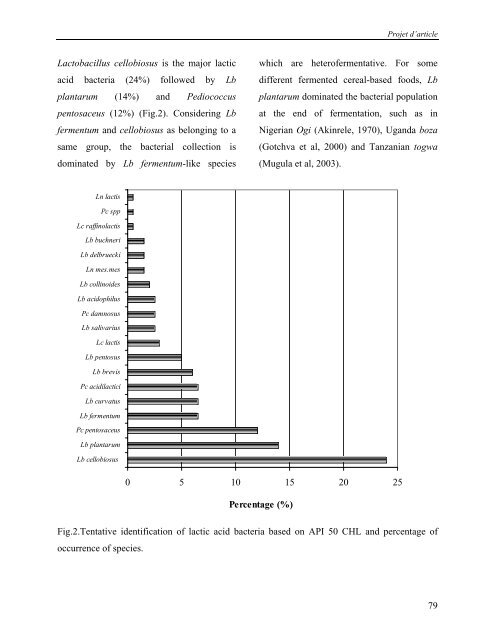
Lactobacillus cellobiosus is the major lactic<br />
acid bacteria (24%) followed by Lb<br />
plantarum (14%) and Pediococcus<br />
pentosaceus (12%) (Fig.2). Considering Lb<br />
fermentum and cellobiosus as belonging to a<br />
same group, the bacterial collection is<br />
dominated by Lb fermentum-like species<br />
which are heterofermentative. For some<br />
different fermented cereal-based foods, Lb<br />
plantarum dominated the bacterial population<br />
at the end of fermentation, such as in<br />
Nigerian Ogi (Akinrele, 1970), Uganda boza<br />
(Gotchva et al, 2000) and Tanzanian togwa<br />
(Mugula et al, 2003).<br />
Ln lactis<br />
Pc spp<br />
Lc raffinolactis<br />
Lb buchneri<br />
Lb delbruecki<br />
Ln mes.mes<br />
Lb collinoides<br />
Lb acidophilus<br />
Pc damnosus<br />
Lb salivarius<br />
Lc lactis<br />
Lb pentosus<br />
Lb brevis<br />
Pc acidilactici<br />
Lb curvatus<br />
Lb fermentum<br />
Pc pentosaceus<br />
Lb plantarum<br />
Lb cellobiosus<br />
0 5 10 15 20 25<br />
Percentage (%)<br />
Fig.2.Tentative identification of lactic acid bacteria based on API 50 CHL and percentage of<br />
occurrence of species.<br />
79