- Page 2:
Makingthe LawWork forEveryoneCopyri
- Page 5 and 6:
In reply to its expression of sorro
- Page 7 and 8:
group chaired by Commission members
- Page 9 and 10:
so that their informal contracts ha
- Page 11 and 12:
Table of contentsChapter 1 Access t
- Page 13 and 14:
Reforming Rules Regarding Bearers a
- Page 15 and 16:
The Economics of Informality and th
- Page 18 and 19:
Taking Microcredit Out of the Ghett
- Page 21 and 22:
5.6 Empowerment Domain 1: Access to
- Page 23 and 24:
1. IntroductionThe Commission on Le
- Page 25 and 26:
Theoretical perspectives that infor
- Page 27 and 28:
long-term migrant or refugee popula
- Page 29 and 30:
digital camera that could be used t
- Page 31 and 32:
or social services fraud. Thus, alt
- Page 33 and 34:
3. Strategies to CreateAffordable,
- Page 35 and 36:
is secured through social pressure
- Page 37 and 38:
sufficient guidance as to the best
- Page 39 and 40:
even better, by showing the ones wi
- Page 41 and 42:
A related option is teaching the po
- Page 43 and 44:
some other trusted service provider
- Page 45 and 46:
From an economic perspective this s
- Page 47 and 48:
2007). Such mechanisms prove prefer
- Page 49 and 50:
can play an important role in mobil
- Page 51 and 52:
motives — such as the desire to m
- Page 53 and 54:
of some legal action brought by the
- Page 55 and 56:
ernments may consider to remove art
- Page 57 and 58:
sations may make better decisions a
- Page 59 and 60:
ence others in the supply chain to
- Page 61 and 62:
ing access to justice for disadvant
- Page 63 and 64:
ardisation and simplification) and
- Page 65 and 66:
ary or informal systems, may improv
- Page 67 and 68:
Box 2 Coping with Legal Pluralism i
- Page 69 and 70:
cies (including local authorities)
- Page 71 and 72:
(ADB 2001b). These and other exampl
- Page 73 and 74:
e restructured in a way that reduce
- Page 75 and 76:
impact of a proposed action on some
- Page 77 and 78:
5. Conclusions andRecommendationsIn
- Page 79 and 80:
Chapter 1 Endnotes1 Excellent recen
- Page 81 and 82:
Lopez-de-Silanes, F. 2002. The Poli
- Page 84 and 85:
ChapterTWOEmpowering thePoor Throug
- Page 86 and 87:
the West, but that has made entire
- Page 88 and 89:
and insurance — to facilitate tra
- Page 90 and 91:
Table 1 Mapping the dynamics of leg
- Page 92 and 93:
creasing finance for land reform an
- Page 94 and 95:
I. IntroductionAs these lines are b
- Page 96 and 97:
contributed to its substance. But a
- Page 98 and 99:
sis to protect transactions or to p
- Page 100 and 101:
in their countries is added reason
- Page 102 and 103:
is concentrated in the hands of the
- Page 104 and 105:
property, contribute to the exclusi
- Page 106 and 107:
There may be sound policy reasons f
- Page 108 and 109:
system as a system of rules regardi
- Page 110 and 111:
Box 3 Namibian land reformIn Namibi
- Page 112 and 113:
Box 4 Focus AfricaCustomary rights
- Page 114 and 115:
property, some indigenous peoples a
- Page 116 and 117:
• Where consensus is hard to obta
- Page 118 and 119:
and the establishment of transparen
- Page 120 and 121:
which develop into a fully serviced
- Page 122 and 123:
Box 5 Sale of land: examples oflega
- Page 124 and 125:
as collateral more of the poor woul
- Page 126 and 127:
Enhancing Access to Land and Real P
- Page 128 and 129:
Box 8 Example of Singapore:public h
- Page 130 and 131:
Box 10 Slum upgradinginitiative in
- Page 132 and 133:
2. Pay Attention to Sequencing. The
- Page 134 and 135:
Foster Coalitions of Change in Favo
- Page 136 and 137:
Chapter 2 EndnotesUniversal Declara
- Page 138 and 139:
ers, refl ecting the allocation of
- Page 140 and 141:
ing industry through the scheme. (S
- Page 142 and 143:
193 See Tomlinson 2007.194 UN-ESCAP
- Page 144 and 145:
presented at the National Workshop
- Page 146 and 147:
Property Rights.’ At: http://www.
- Page 148 and 149:
Empowerment, issue 2, Oslo: 65-90.R
- Page 150 and 151:
ChapterTHREETowards a GlobalSocial
- Page 152:
and grounded in conditions of freed
- Page 155 and 156:
voluntary code-of-conduct initiativ
- Page 157 and 158:
outside their protective reach. The
- Page 159 and 160:
and sustainable solutions and peopl
- Page 161 and 162:
Segmentation in the Informal Labour
- Page 163 and 164:
Informalisation of Labour MarketsTh
- Page 165 and 166:
pation worldwide has given rise to
- Page 167 and 168:
through a variety of legal instrume
- Page 169 and 170:
Box 4 Social case for labourregulat
- Page 171 and 172:
Box 5 ILO Conventions and Recommend
- Page 173 and 174:
provision of full, productive, free
- Page 175 and 176:
Labour Conference in 1996, in recog
- Page 177 and 178:
different paths to enforcement, wit
- Page 179 and 180:
Table 1 Mean Measures of Regulation
- Page 181 and 182:
However, a more detailed examinatio
- Page 183 and 184:
countries this translates into unem
- Page 185 and 186:
legislative changes, it will critic
- Page 187 and 188:
6. Principles and practicesof Labou
- Page 189 and 190:
The Homeless People’s Federation
- Page 191 and 192:
Conclusions for national strategies
- Page 193 and 194:
tions and responsive mechanisms tha
- Page 195 and 196:
ticularly the prohibition of forced
- Page 197 and 198:
Annex 1:Recent and current initiati
- Page 199 and 200:
the following four-fold test: ‘(1
- Page 201 and 202:
Nations, the ILO and the World Bank
- Page 203 and 204:
able to go beyond general statement
- Page 205 and 206:
Case 8:Minimum Living Standard Secu
- Page 207 and 208:
Case 11:China’s positive response
- Page 209 and 210:
er, perhaps even prepaid, to ease t
- Page 211 and 212:
48 Including the UN funds, programm
- Page 213 and 214:
the Formal Economy and Informal Reg
- Page 215 and 216:
131—182.Sabel, C., D. O’Rourke,
- Page 217 and 218:
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY‘The opposite of
- Page 219 and 220:
vast majority earn their living in
- Page 221 and 222:
and economic activity. First, in or
- Page 223 and 224:
ment procurement, tax rebates, and
- Page 225 and 226:
developing countries, however, info
- Page 227 and 228:
of the provision of adequate infras
- Page 229 and 230:
preneurs and small sector enterpris
- Page 231 and 232:
negative manifestations of informal
- Page 233 and 234:
million persons and their dependent
- Page 235 and 236:
within which business operates offe
- Page 237 and 238:
developed countries. In 1998, women
- Page 239 and 240:
four percent employed in the public
- Page 241 and 242:
3.Business Rights:Unlocking Barrier
- Page 243 and 244:
Street VendorsCommon issues and cha
- Page 245 and 246:
Box 3 Most Difficult Places toDo Bu
- Page 247 and 248:
Case Study:Ukraine and Private Busi
- Page 249 and 250:
The Chart below captures broadly th
- Page 251 and 252:
in helping the poor create wealth.
- Page 253 and 254:
tively unknown markets that require
- Page 255 and 256:
Case Study:Linking Markets: Promoti
- Page 257 and 258:
micro-finance activities. Micro-fin
- Page 259 and 260:
Remittances — the transfer of fun
- Page 261 and 262:
Case Study:Durban: A Heterogeneous
- Page 263 and 264:
5. Institutional changesand legal t
- Page 265 and 266:
step toward this kind of structure.
- Page 267 and 268:
key topics in simple and clear lang
- Page 269 and 270:
oped as part of a long-term regulat
- Page 271 and 272:
cured creditors have priority to th
- Page 273 and 274:
• Access to improved skills and t
- Page 275 and 276:
Case Study:Identity, Voice, and Ass
- Page 277 and 278:
6. Pursuing the agenda forchangeOve
- Page 279 and 280:
Case Study:Technology and the Infor
- Page 281 and 282:
is not the aim to diminish the enor
- Page 283 and 284:
in risky environments — in urban
- Page 285 and 286:
accepted customary forms could mean
- Page 287 and 288:
Recommendations and Key MessagesObj
- Page 289 and 290:
Chapter 4 Endnotes1 A business has
- Page 291 and 292: than the rich. It further demonstra
- Page 293 and 294: ______., ‘Ghana Decent Work Pilot
- Page 296 and 297: ChapterFIVERoad Maps forImplementat
- Page 298 and 299: Following the contextual analysis
- Page 300 and 301: establish a ‘legal empowerment pr
- Page 302 and 303: targeted indicators endorsed by nat
- Page 304 and 305: 1. Introduction: Attributesof Legal
- Page 306 and 307: 2. Implementation:Challenges andOpp
- Page 308 and 309: nature need to be rewritten or abol
- Page 310 and 311: Figure 5.2 Influences on Policy Imp
- Page 312 and 313: Table 5.2 Illustrative Stakeholder
- Page 314 and 315: effective land control does not nec
- Page 316 and 317: actors and assuming they will behav
- Page 318 and 319: cymakers must tailor their empowerm
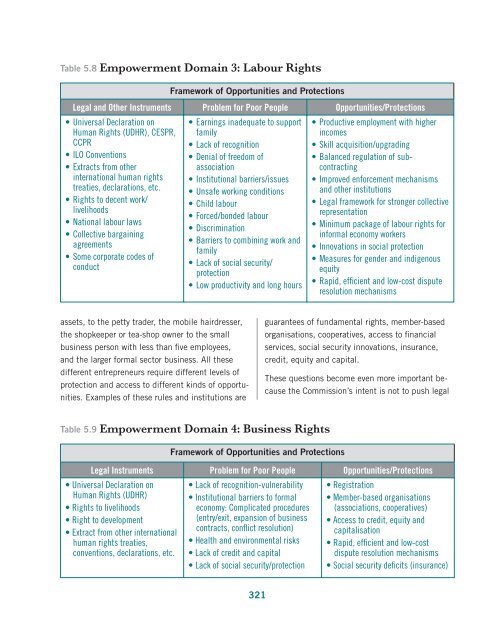
- Page 320 and 321: ut some community members report be
- Page 322 and 323: efore taking on implementation, or
- Page 324 and 325: Table 5.3. Political Administrative
- Page 326 and 327: not give up their position willingl
- Page 328 and 329: Box 5.5 Authority Systems: Land Rig
- Page 330 and 331: Afinal source of complexity is that
- Page 332 and 333: almost always have the upper hand b
- Page 334 and 335: Table 5.4 Skeleton Diagnostic Tool:
- Page 336 and 337: 3.Roadmaps toImplementationReforms
- Page 338 and 339: Table 5.5 Country Specific Implemen
- Page 340 and 341: Table 5.7 Empowerment Domain 2: Pro
- Page 344 and 345: Table 5.10 LEP Implementation Strat
- Page 346 and 347: plans, poverty reduction strategies
- Page 348 and 349: Box 5.7 Land Sector Harmonisation,
- Page 350 and 351: quality and utility in establishing
- Page 352 and 353: Table 5.12 A Framework for a Demand
- Page 354 and 355: Empowerment of the poor in the end
- Page 356 and 357: 4.Bring existing technical solution
- Page 358 and 359: Annex 1: PolicyImplementation Tools
- Page 360: MIS: A Management Information Syste
- Page 363 and 364: Training (on leadership, group work
- Page 365: of labour disputes: An internationa
- Page 368 and 369: on whether patent and copyright pro
- Page 370 and 371: oads — cover only a limited numbe
- Page 372 and 373: 28 http://www.ilo.org/dyn/gender/ge
- Page 374: Ouchi, Fumika. 2004. Twinning as a