Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
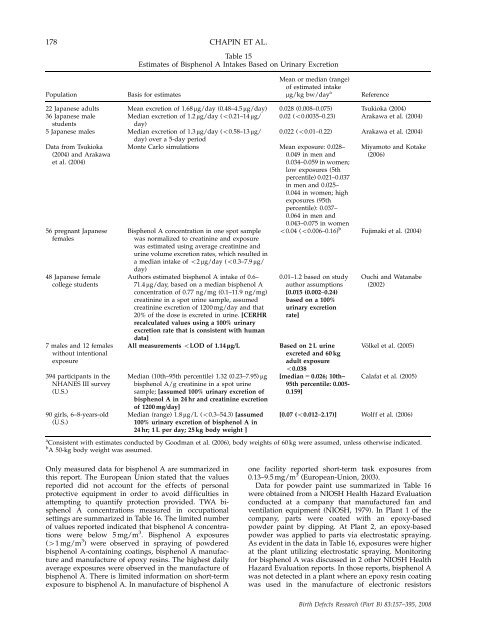
178 CHAPIN ET AL.<br />
Table 15<br />
Estimates of Bisphenol A Intakes Based <strong>on</strong> Urinary Excreti<strong>on</strong><br />
Mean or median (range)<br />
of estimated intake<br />
Populati<strong>on</strong> Basis for estimates mg/kg bw/day a<br />
Reference<br />
22 Japanese adults Mean excreti<strong>on</strong> of 1.68 mg/day (0.48–4.5 mg/day) 0.028 (0.008–0.075) Tsukioka (2004)<br />
36 Japanese male Median excreti<strong>on</strong> of 1.2 mg/day (o0.21–14 mg/ 0.02 (o0.0035–0.23) Arakawa et al. (2004)<br />
students day)<br />
5 Japanese males Median excreti<strong>on</strong> of 1.3 mg/day (o0.58–13 mg/<br />
day) over a 5-day period<br />
0.022 (o0.01–0.22) Arakawa et al. (2004)<br />
Data from Tsukioka M<strong>on</strong>te Carlo simulati<strong>on</strong>s Mean exposure: 0.028– Miyamoto <strong>and</strong> Kotake<br />
(2004) <strong>and</strong> Arakawa 0.049 in men <strong>and</strong> (2006)<br />
et al. (2004) 0.034–0.059 in women;<br />
low exposures (5th<br />
percentile) 0.021–0.037<br />
in men <strong>and</strong> 0.025–<br />
0.044 in women; high<br />
exposures (95th<br />
percentile): 0.037–<br />
0.064 in men <strong>and</strong><br />
0.043–0.075 in women<br />
56 pregnant Japanese Bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> in <strong>on</strong>e spot sample o0.04 (o0.006–0.16) b<br />
Fujimaki et al. (2004)<br />
females was normalized to creatinine <strong>and</strong> exposure<br />
was estimated using average creatinine <strong>and</strong><br />
urine volume excreti<strong>on</strong> rates, which resulted in<br />
a median intake of o2 mg/day (o0.3–7.9 mg/<br />
day)<br />
48 Japanese female Authors estimated bisphenol A intake of 0.6– 0.01–1.2 based <strong>on</strong> study Ouchi <strong>and</strong> Watanabe<br />
college students 71.4 mg/day, based <strong>on</strong> a median bisphenol A author assumpti<strong>on</strong>s (2002)<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> of 0.77 ng/mg (0.1–11.9 ng/mg) [0.015 (0.002–0.24)<br />
creatinine in a spot urine sample, assumed based <strong>on</strong> a 100%<br />
creatinine excreti<strong>on</strong> of 1200 mg/day <strong>and</strong> that urinary excreti<strong>on</strong><br />
20% of <strong>the</strong> dose is excreted in urine. [CERHR rate]<br />
recalculated values using a 100% urinary<br />
excreti<strong>on</strong> rate that is c<strong>on</strong>sistent with human<br />
data]<br />
7 males <strong>and</strong> 12 females All measurements oLOD of 1.14 lg/L Based <strong>on</strong> 2 L urine Völkel et al. (2005)<br />
without intenti<strong>on</strong>al excreted <strong>and</strong> 60 kg<br />
exposure adult exposure<br />
o0.038<br />
394 participants in <strong>the</strong> Median (10th–95th percentile) 1.32 (0.23–7.95) mg [median 5 0.026; 10th– Calafat et al. (2005)<br />
NHANES III survey bisphenol A/g creatinine in a spot urine 95th percentile: 0.005<br />
(U.S.) sample; [assumed 100% urinary excreti<strong>on</strong> of 0.159]<br />
bisphenol A in 24 hr <strong>and</strong> creatinine excreti<strong>on</strong><br />
of 1200 mg/day]<br />
90 girls, 6–8-years-old Median (range) 1.8 mg/L (o0.3–54.3) [assumed [0.07 (o0.012–2.17)] Wolff et al. (2006)<br />
(U.S.) 100% urinary excreti<strong>on</strong> of bisphenol A in<br />
24 hr; 1 L per day; 25 kg body weight ]<br />
a<br />
C<strong>on</strong>sistent with estimates c<strong>on</strong>ducted by Goodman et al. (2006), body weights of 60 kg were assumed, unless o<strong>the</strong>rwise indicated.<br />
b<br />
A 50-kg body weight was assumed.<br />
Only measured data for bisphenol A are summarized in<br />
this report. The European Uni<strong>on</strong> stated that <strong>the</strong> values<br />
reported did not account for <strong>the</strong> effects of pers<strong>on</strong>al<br />
protective equipment in order to avoid difficulties in<br />
attempting to quantify protecti<strong>on</strong> provided. TWA bisphenol<br />
A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s measured in occupati<strong>on</strong>al<br />
settings are summarized in Table 16. The limited number<br />
of values reported indicated that bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
were below 5 mg/m 3 . Bisphenol A exposures<br />
(41 mg/m 3 ) were observed in spraying of powdered<br />
bisphenol A-c<strong>on</strong>taining coatings, bisphenol A manufacture<br />
<strong>and</strong> manufacture of epoxy resins. The highest daily<br />
average exposures were observed in <strong>the</strong> manufacture of<br />
bisphenol A. There is limited informati<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> short-term<br />
exposure to bisphenol A. In manufacture of bisphenol A<br />
<strong>on</strong>e facility reported short-term task exposures from<br />
0.13–9.5 mg/m 3 (European-Uni<strong>on</strong>, 2003).<br />
Data for powder paint use summarized in Table 16<br />
were obtained from a NIOSH Health Hazard Evaluati<strong>on</strong><br />
c<strong>on</strong>ducted at a company that manufactured fan <strong>and</strong><br />
ventilati<strong>on</strong> equipment (NIOSH, 1979). In Plant 1 of <strong>the</strong><br />
company, parts were coated with an epoxy-based<br />
powder paint by dipping. At Plant 2, an epoxy-based<br />
powder was applied to parts via electrostatic spraying.<br />
As evident in <strong>the</strong> data in Table 16, exposures were higher<br />
at <strong>the</strong> plant utilizing electrostatic spraying. M<strong>on</strong>itoring<br />
for bisphenol A was discussed in 2 o<strong>the</strong>r NIOSH Health<br />
Hazard Evaluati<strong>on</strong> reports. In those reports, bisphenol A<br />
was not detected in a plant where an epoxy resin coating<br />
was used in <strong>the</strong> manufacture of electr<strong>on</strong>ic resistors<br />
Birth Defects Research (Part B) 83:157–395, 2008