Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
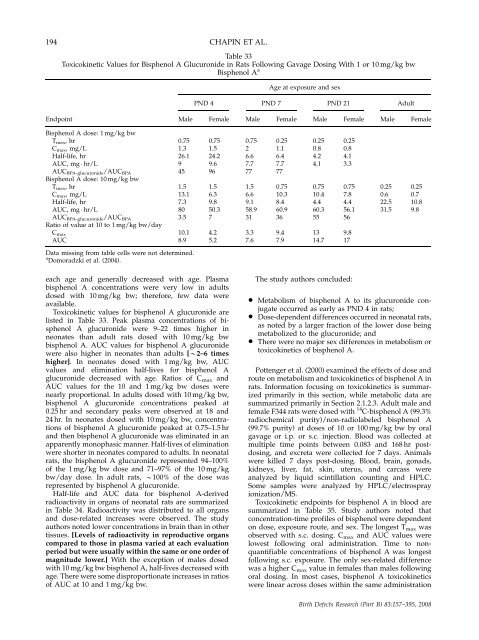
194 CHAPIN ET AL.<br />
Table 33<br />
Toxicokinetic Values for Bisphenol A Glucur<strong>on</strong>ide in Rats Following Gavage Dosing With 1 or 10 mg/kg bw<br />
Bisphenol A a<br />
Age at exposure <strong>and</strong> sex<br />
PND 4 PND 7 PND 21 Adult<br />
Endpoint Male Female Male Female Male Female Male Female<br />
Bisphenol A dose: 1 mg/kg bw<br />
Tmax, hr 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.25 0.25 0.25<br />
Cmax, mg/L 1.3 1.5 2 1.1 0.8 0.8<br />
Half-life, hr 26.1 24.2 6.6 6.4 4.2 4.1<br />
AUC, mg � hr/L 9 9.6 7.7 7.7 4.1 3.3<br />
AUCBPA-glucur<strong>on</strong>ide/AUCBPA<br />
Bisphenol A dose: 10 mg/kg bw<br />
45 96 77 77<br />
Tmax, hr 1.5 1.5 1.5 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.25 0.25<br />
Cmax, mg/L 13.1 6.3 6.6 10.3 10.4 7.8 0.6 0.7<br />
Half-life, hr 7.3 9.8 9.1 8.4 4.4 4.4 22.5 10.8<br />
AUC, mg � hr/L 80 50.3 58.9 60.9 60.3 56.1 31.5 9.8<br />
AUC BPA-glucur<strong>on</strong>ide/AUC BPA 3.5<br />
7 31 36 55 56<br />
Ratio of value at 10 to 1 mg/kg bw/day<br />
C max 10.1 4.2 3.3 9.4 13 9.8<br />
AUC 8.9 5.2 7.6 7.9 14.7 17<br />
Data missing from table cells were not determined.<br />
a Domoradzki et al. (2004).<br />
each age <strong>and</strong> generally decreased with age. Plasma<br />
bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s were very low in adults<br />
dosed with 10 mg/kg bw; <strong>the</strong>refore, few data were<br />
available.<br />
Toxicokinetic values for bisphenol A glucur<strong>on</strong>ide are<br />
listed in Table 33. Peak plasma c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s of bisphenol<br />
A glucur<strong>on</strong>ide were 9–22 times higher in<br />
ne<strong>on</strong>ates than adult rats dosed with 10 mg/kg bw<br />
bisphenol A. AUC values for bisphenol A glucur<strong>on</strong>ide<br />
were also higher in ne<strong>on</strong>ates than adults [B2–6 times<br />
higher]. In ne<strong>on</strong>ates dosed with 1 mg/kg bw, AUC<br />
values <strong>and</strong> eliminati<strong>on</strong> half-lives for bisphenol A<br />
glucur<strong>on</strong>ide decreased with age. Ratios of Cmax <strong>and</strong><br />
AUC values for <strong>the</strong> 10 <strong>and</strong> 1 mg/kg bw doses were<br />
nearly proporti<strong>on</strong>al. In adults dosed with 10 mg/kg bw,<br />
bisphenol A glucur<strong>on</strong>ide c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s peaked at<br />
0.25 hr <strong>and</strong> sec<strong>on</strong>dary peaks were observed at 18 <strong>and</strong><br />
24 hr. In ne<strong>on</strong>ates dosed with 10 mg/kg bw, c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
of bisphenol A glucur<strong>on</strong>ide peaked at 0.75–1.5 hr<br />
<strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong>n bisphenol A glucur<strong>on</strong>ide was eliminated in an<br />
apparently m<strong>on</strong>ophasic manner. Half-lives of eliminati<strong>on</strong><br />
were shorter in ne<strong>on</strong>ates compared to adults. In ne<strong>on</strong>atal<br />
rats, <strong>the</strong> bisphenol A glucur<strong>on</strong>ide represented 94–100%<br />
of <strong>the</strong> 1 mg/kg bw dose <strong>and</strong> 71–97% of <strong>the</strong> 10 mg/kg<br />
bw/day dose. In adult rats, B100% of <strong>the</strong> dose was<br />
represented by bisphenol A glucur<strong>on</strong>ide.<br />
Half-life <strong>and</strong> AUC data for bisphenol A-derived<br />
radioactivity in organs of ne<strong>on</strong>atal rats are summarized<br />
in Table 34. Radioactivity was distributed to all organs<br />
<strong>and</strong> dose-related increases were observed. The study<br />
authors noted lower c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s in brain than in o<strong>the</strong>r<br />
tissues. [Levels of radioactivity in reproductive organs<br />
compared to those in plasma varied at each evaluati<strong>on</strong><br />
period but were usually within <strong>the</strong> same or <strong>on</strong>e order of<br />
magnitude lower.] With <strong>the</strong> excepti<strong>on</strong> of males dosed<br />
with 10 mg/kg bw bisphenol A, half-lives decreased with<br />
age. There were some disproporti<strong>on</strong>ate increases in ratios<br />
of AUC at 10 <strong>and</strong> 1 mg/kg bw.<br />
The study authors c<strong>on</strong>cluded:<br />
* Metabolism of bisphenol A to its glucur<strong>on</strong>ide c<strong>on</strong>jugate<br />
occurred as early as PND 4 in rats;<br />
* Dose-dependent differences occurred in ne<strong>on</strong>atal rats,<br />
as noted by a larger fracti<strong>on</strong> of <strong>the</strong> lower dose being<br />
metabolized to <strong>the</strong> glucur<strong>on</strong>ide; <strong>and</strong><br />
* There were no major sex differences in metabolism or<br />
toxicokinetics of bisphenol A.<br />
Pottenger et al. (2000) examined <strong>the</strong> effects of dose <strong>and</strong><br />
route <strong>on</strong> metabolism <strong>and</strong> toxicokinetics of bisphenol A in<br />
rats. Informati<strong>on</strong> focusing <strong>on</strong> toxicokinetics is summarized<br />
primarily in this secti<strong>on</strong>, while metabolic data are<br />
summarized primarily in Secti<strong>on</strong> 2.1.2.3. Adult male <strong>and</strong><br />
female F344 rats were dosed with 14 C-bisphenol A (99.3%<br />
radiochemical purity)/n<strong>on</strong>-radiolabeled bisphenol A<br />
(99.7% purity) at doses of 10 or 100 mg/kg bw by oral<br />
gavage or i.p. or s.c. injecti<strong>on</strong>. Blood was collected at<br />
multiple time points between 0.083 <strong>and</strong> 168 hr postdosing,<br />
<strong>and</strong> excreta were collected for 7 days. Animals<br />
were killed 7 days post-dosing. Blood, brain, g<strong>on</strong>ads,<br />
kidneys, liver, fat, skin, uterus, <strong>and</strong> carcass were<br />
analyzed by liquid scintillati<strong>on</strong> counting <strong>and</strong> HPLC.<br />
Some samples were analyzed by HPLC/electrospray<br />
i<strong>on</strong>izati<strong>on</strong>/MS.<br />
Toxicokinetic endpoints for bisphenol A in blood are<br />
summarized in Table 35. Study authors noted that<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>-time profiles of bisphenol were dependent<br />
<strong>on</strong> dose, exposure route, <strong>and</strong> sex. The l<strong>on</strong>gest T max was<br />
observed with s.c. dosing. C max <strong>and</strong> AUC values were<br />
lowest following oral administrati<strong>on</strong>. Time to n<strong>on</strong>quantifiable<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s of bisphenol A was l<strong>on</strong>gest<br />
following s.c. exposure. The <strong>on</strong>ly sex-related difference<br />
was a higher Cmax value in females than males following<br />
oral dosing. In most cases, bisphenol A toxicokinetics<br />
were linear across doses within <strong>the</strong> same administrati<strong>on</strong><br />
Birth Defects Research (Part B) 83:157–395, 2008